International Journal of Aquaculture, 2015, Vol.5, No.23 1
-
12
5
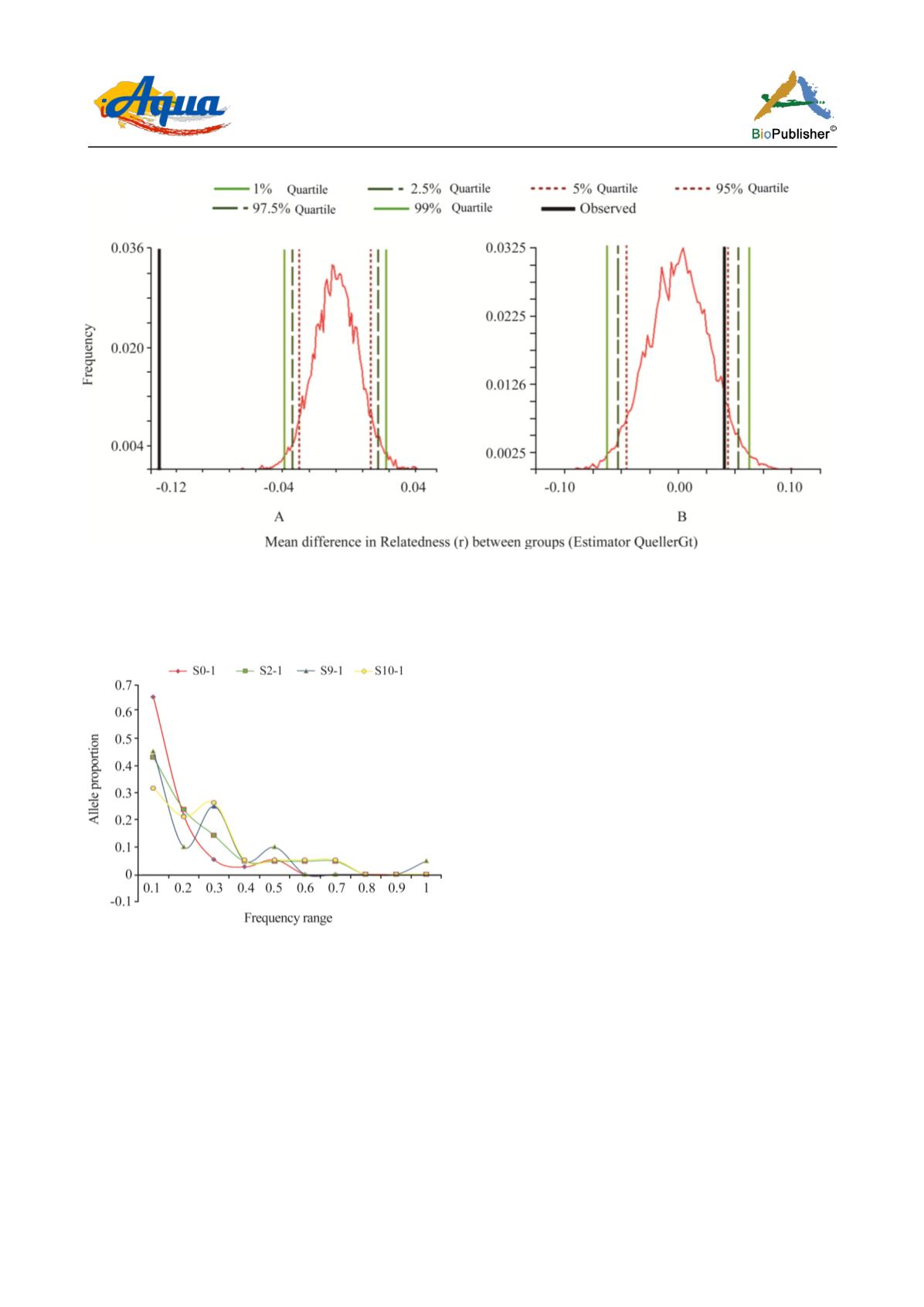
Figure 5 Two examples of 10000 bootstrap comparisons of Queller and Goodnigh relatedness coefficient distribution calculated using
the Coancestry program. A: comparison between S0-1 and S10-1. B: comparison between S2-1 and S10-1. Note that in A the
observed values (solid black line) are outside the distribution, so differences are significant. In B, the observed values are extremely
closed to the 95 % quartile
Figure 6 Allele distribution by frequency ranges for the first
introduced to Cuba (S0-1) and cultured stock of
P. vannamei
and its second (S2-1), ninth (S9-1) and tenth (S10-1) progenies
sells, it is accompanied however by a scarce genes
fluxes and a bottleneck effect has been very well
described not only in captive (Benzie, 2000) but also
in natural shrimp population (Nahavandi et al., 2011).
So, the main strategy in most shrimp producing
countries is to maintain the highest possible genetic
variation and the lowest possible consanguinity in
their brood stocks as well as a good selection of
productive traits of interest one generation after the
other. In that way, genetic markers as allozymes (Rivera-
García and Grijalva-Chon, 2006), RAPD (Freitas and
Galetti, 2005; Rajakumaran et al., 2013), mitochondrial
DNA (Robainas-Barcia and García- Machado, 2012)
and microsatellites (Cruz et al., 2004; Luvesuto et al.,
2007; Perez-Enriquez et al., 2009; Souza De Lima et
al., 2010; Vela-Avitúa et al., 2013) have been used.
Another molecular markers as AFLP has been used to
map species genome (Wilson et al., 2002; Li et al., 2003)
In Cuba, both allozymes (García-Machado et al., 2001;
Espinosa-López et al., 2003) and microsatellites
(Espinosa-López et al., 2001; Borrell et al., 2007) have
been used for characterization of natural populations (
L.
schmitti
and
F. notialis
) and so, the creation of adequate
brood stocks of the autochthonous species
P. schmitti
.
Once the most sell in the world species,
Penaeus
vannamei
, was introduced in the country for culture, it
was characterized at each time (Borrell et al., 2006;
Machado-Tamayo, 2006; Artiles et al., 2011a) as well
as some crossings (Pérez-Beloborodova et al., 2012)
using microsatellites by virtue of better properties
such as codominance and high variability and also to
compare among different stocks and recommend
crossings to production. However, tendencies in yield
and productive traits were not previously reported.


