International Journal of Marine Science 2015, Vol.5, No.55: 1-9
6
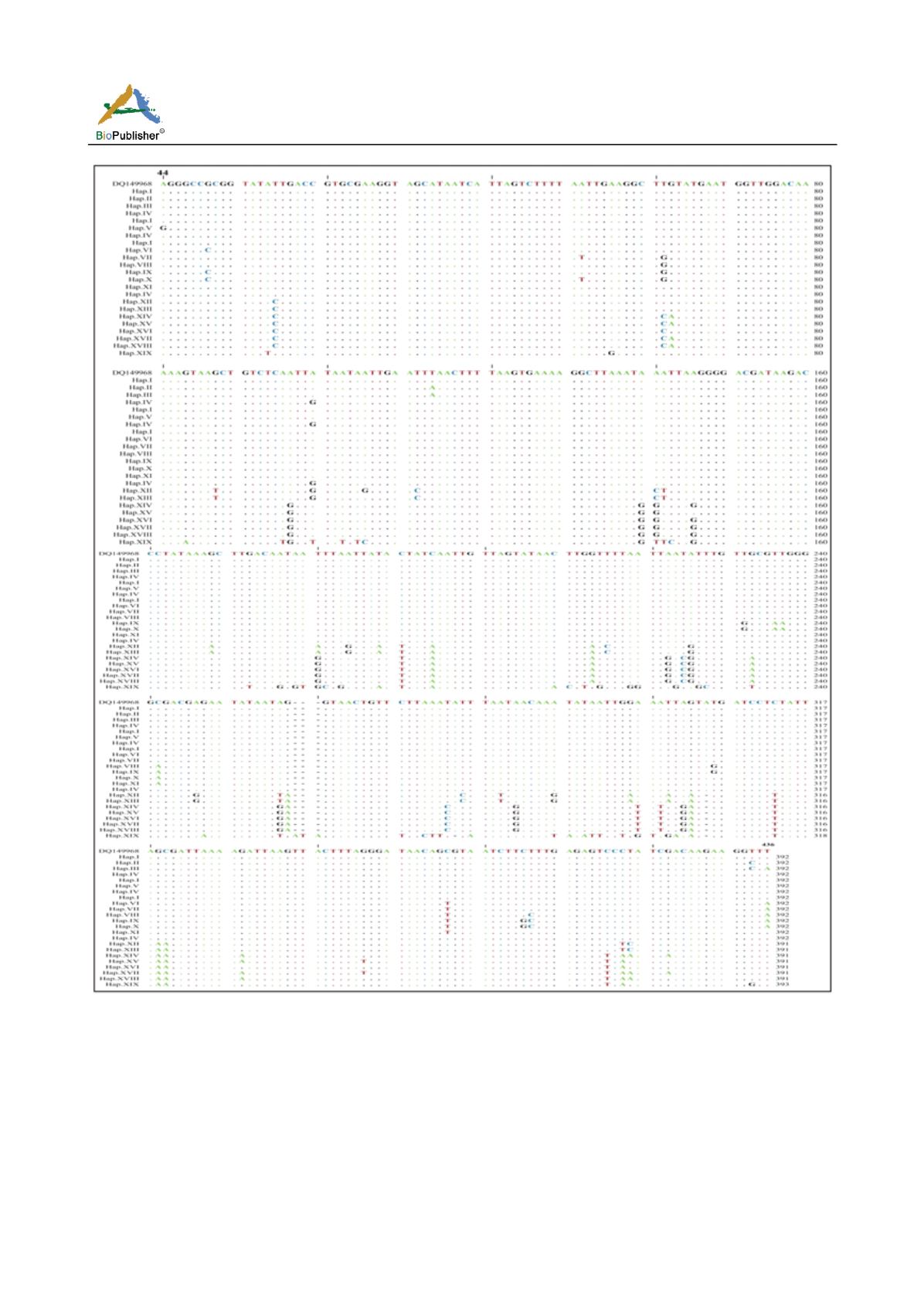
Figure 3 Sequence alignment of partial 16S rRNA gene of 4 taxa including three populations of
F. indicus
(Ha.I-Hap.XI)
, P. monodon
(Hap.XII-Hap.XIII)
P. semisulcatus
(Hap.XIV-Hap.XVIII) and
M. monoceros
(Hap.XIX) from Sudanese Red Sea coast. The
sequence numbered with reference to to the published sequence of the 16S rRNA gene region of
F. indicus
[gene bank: accession
number DQ149968) Dots denote identity to the top sequence. Dashes denote gaps.
3.6 Phylogenetic analysis
In Figure 4 the phylogenetic tree was constructed
based on the 392 bp, because not all base pairs
nucleotides were sequenced completely for some
specimens. The final aligned 16S rRNA sequences
consisted of 392 bp, tree was generated using
neighbour joining (NJ). Additional sequences (F.J002573,
AY751800, Gu573957) were retrieved from gene bank
to root the phylogeny. The topology of the 19
haplotypes clustered into four obvious clades with


