Molecular Plant Breeding 2020, Vol.11, No.24, 1-8
2
1 Results
1.1 Transcriptome sequencing and differential gene screening
Total RNA was extracted from anther samples of dual-purpose lines for library preparation. The library was
sequenced with Illumina HiSeq
TM
2500. FDR and log
2
FC were used to screen the differential genes. The
screening conditions were FDR<0.05 and |log
2
FC|>1 (Roberts et al., 2011). There were 35 336 genes in the
reference genome. Through comparison, the number of known genes detected in the male sterile line (K) and
sterile line (B) of pepper (Yinchuan Cavel) was 23 768, accounting for 67.26% of the comparison genes. A total of
3 319 genes were detected with significant difference, including 800 genes significantly up and 2 519 genes
significantly down.
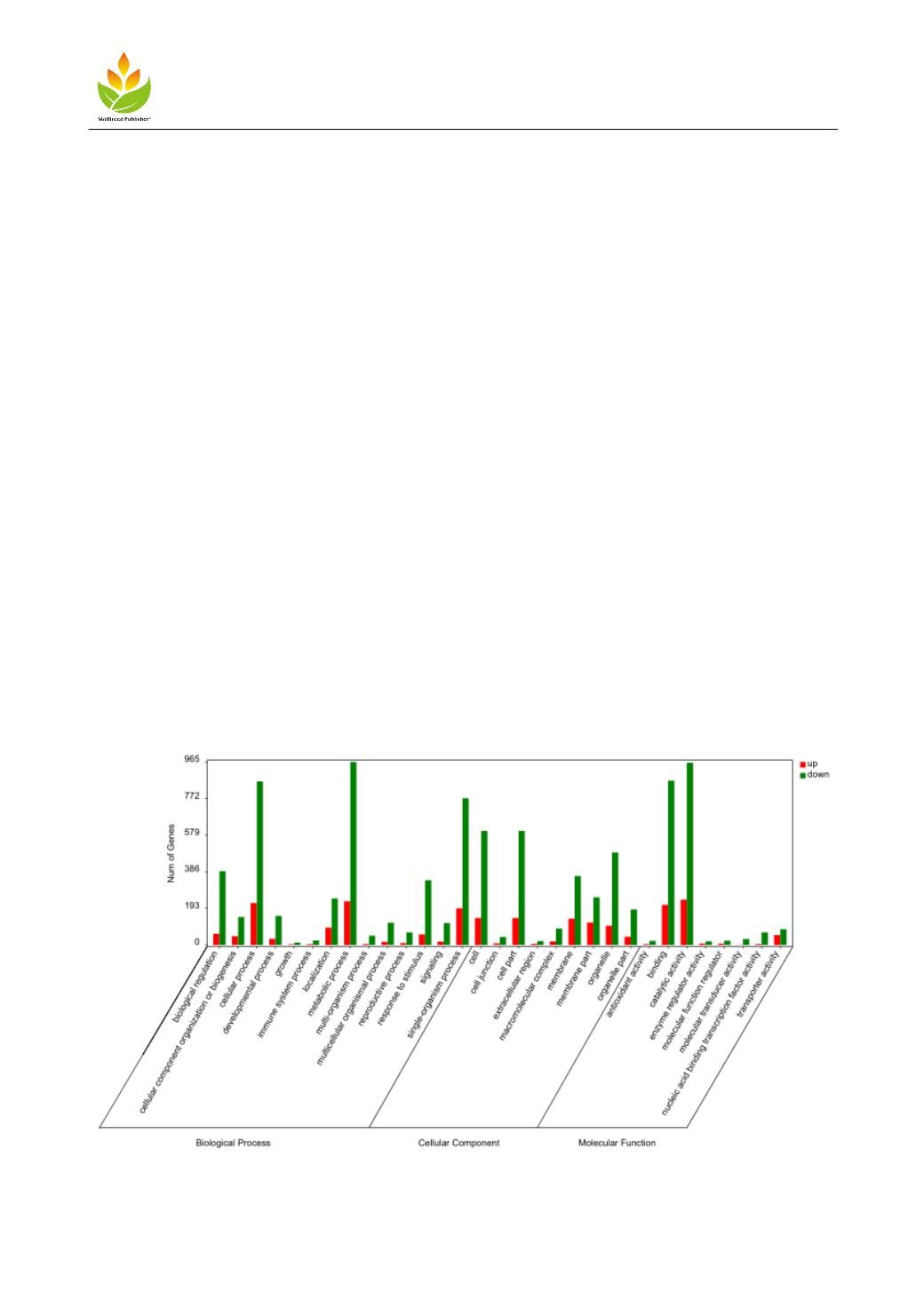
1.2 Different Gene (GO) Annotation
Go functional classification annotation and significant enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes in
Pepper (Yin Chuan Cavel) Male Sterility Lind (Qin et al., 2020), K-VS-B (Figure 1): 230 genes down regulated
and 965 genes up-regulated in metabolic process; 221 genes down-regulated and 863 genes up-regulated in cell
process; 239 genes down-regulated and 691 genes up-regulated in catalytic activity; 211 genes down-regulated
and 876 genes up-regulated in combining process. The differential genes were mainly concentrated in the process
of metabolism, catalysis and metabolic regulation, which indicated that the differential gene expression of Pepper
(Yin Chuan Cavel) Male Sterility Lind was significant in its metabolic activity, and the enrichment of differential
genes involved in metabolic regulation was relatively rich.
1.3 Metabonomics determination and analysis
Anther samples were divided into fertile group and sterile group. 536 metabolites were detected in the anthers of
fertile and sterile lines of pepper (Yinchuan Cavel) by UPLC-MS/MS detection platform. There were 102
differential metabolites, including 34 down regulated and 68 up regulated. As shown in Figure 2, the differential
metabolites were divided into 19 groups, there are 17 amino acid derivatives, 16 Nucleotides and derivatives, 13
glyceryl ester, 10 sphingolipids, 8 Flavonoid and 8 Phenolic acids, 6 others (mainly related to sugar metabolism).
RCA analysis of K-vs-B differential metabolites mix. Mix The quality control results are shown in Figure 3. The
detected differential metabolites are R2>0.93, close to 1, indicating that the results have high repeatability.
Figure 1 Differential gene GO terms of K-VS-B


