Genomics and Applied Biology 2018, Vol.9, No.10, 62-71
64
human breast cancer cells. If this expression level increases in the tumor, it means that the tumor will deteriorate
to the advanced stage of cancer and cannot be treated, so it can be used as an important tumor marker for
diagnostic detection (Gupta et al., 2010). LncRNA also regulates the genes that encode proteins that are
self-related. If the regulation of these lncRNA is wrong, it may also lead to the occurrence of diseases. Relevant
studies have shown that p15, a gene that inhibits cancer, can be transcribed to generate an antisense lncRNA,
which is able to induce DNA methylation, leading to leukocytosis (Yu et al., 2008). In addition, there are other
related diseases, such as liver cancer related lncRNA:ZFAS1. If the expression of this lncRNA increases in mice,
the metastasis of liver cancer cells will be promoted (Li et al., 2015).
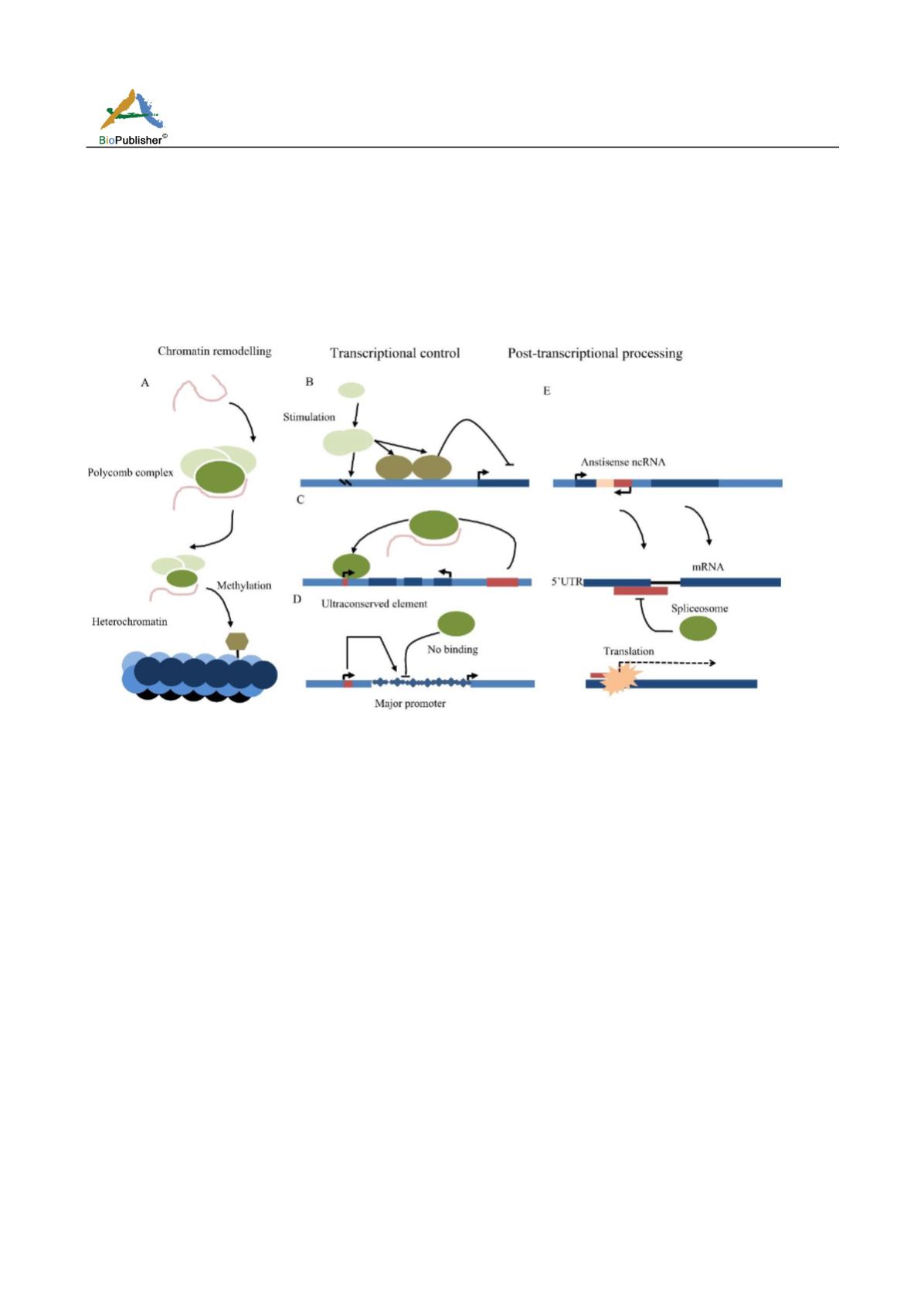
Figure 2 Expression regulation on genes by lncRNA at 3 levels
Another disease is also closely related to lncRNA. Alzheimer’s disease is also known as senile dementia. Some
recent studies have found that lncRNA is also an important factor in the formation of Alzheimer’s disease. The
main cause of Alzheimer’s disease is the amyloid produced by a secretase, which will induce Alzheimer’s disease
if it accumulates in the body (Burns, 2009). The antisense chain of the secretase encoding gene BACE1 can be
transcribed to generate lncRNA:BACE1AS (Tan et al., 2013). This lncRNA prevents mRNA produced by the
coding genes of secretase from being degraded, leading to the continuous increase of amyloid protein, while the
accumulation of amyloid in turn leads to the expression of secretase encoding genes. This kind of positive
feedback mechanism makes Alzheimer’s disease or senile dementia worse. According to this mechanism,
silencing or inactivating lncRNA might be a way to treat or alleviate Alzheimer’s disease.
3 Research Progress of LncRNA in Plant
Compared with lncRNA in animals, researches of lncRNA in plant are far from enough. Relatively few species
are studied on lncRNA at present. Studies on lncRNA in mammals are relatively abundant, compared with those
in plants. Among them, human and mouse lncRNA have been studied relatively deeply in mammals (Sun et al.,
2012; Shi et al., 2013), while the types of plants studied are more limited. These lncRNA in plants have
surprisingly strong tissue expression specificity. A specific example is the identification of rice lncRNA at the
genome-wide level through the use of high-throughput sequencing technology (Zhang et al., 2014). Analysis of
the identified rice lncRNA revealed that these lncRNA had high tissue specific expression.
It was found in the studies on rice lncRNA that some of these lncRNA were highly expressed during sexual
reproduction of rice, suggesting that the function of these lncRNA was related to sexual reproduction in rice.
Further studies showed that one lncRNA (XLOC_057324) in rice could affect the development of rice spikes. The


