Basic HTML Version


Plant Gene and Trait 2012, Vol.3, No.6, 28
-
33
http://pgt.sophiapublisher.com
29
yellowing and dehydration of tobacco leaves in the
curing process; the yellowing characteristics of the
tobacco (yellowing index) usually used as a measure
of the indicators for the easy curing potential. In
general, easy curing potential is defined as the easy
curing tobacco leaves being easy to yellow and
dehydration, and synchronization of yellowing and
dehydration; whereas it is defined as not easy to cure.
At present, there is little researches in tobacco QTL
mapping. Xiao et al (2008) used DH population to
conduct the QTLs for the traits of the total sugar,
nicotine, and potassium in flue-cured tobacco, detected
seven QTLs; Chen et al (2009) using AFLP and SRAP
molecular markers analyzed the black shank incidence
and disease index of burley tobacco for QTL analysis,
seven QTLs related to disease resistance to black
shank were detected in four linkage groups; Cai et al
(2009) also used AFLP and SRAP molecular marker
technology to analyze the chemical composition traits
and agronomic traits of burley tobacco and detect the
2 QTLs related to the nicotine and total nitrogen and
one QTL for total sugar, while one QTL for each trait
of plant height, stem girth, internode length, and the
length of the middle leaves; Li et al (2011) carried out
the six important traits QTL mapping for tobacco
nicotine, total chlorine, total potassium, leaf length,
angle between stem and leaf, and powdery mildew,
which detected two QTLs for nicotine, two QTLs for
total chlorine, one for total potassium, four QTLs for
leaf length, one QTL for angle of stem and leaf and
one for powdery mildew. It has not yet to be
reported regarding easy curing potential.
The main purpose of this study is to map the QTL
related to the trait of easy curing potential by using
F
2
population derived from the cross of Yunyan85 ×
Dabaijin599 based on SSR molecular marker
genetic linkage map of the flue-cured tobacco, in
order to speed up the breeding process for breeding
fluecured tobacco cultivars with excellent easy
curing potential trait.
1 Result and Analysis
1.1 The construction of genetic map
Ninety-one pairs of polymorphic SSR markers were
screened from 1 900 pairs of the tested SSR primers,
which accounts for 4.79% polymorphism rate. 20 of
91 pairs of SSR markers exhibited segregation
distortion that was nor consistent with the Mendelian
laws. The genetic linkage map of the flue-cured
tobacco was constructed that consisted of 17 linkage
groups with 75 SSR markers, there were 16 pairs of
molecular markers didn’t join to the map. The total
genetic distance of the map is 672.2 cM, and the
genetic distances of linkage groups from the shortest
to the longest are 0.6 cM to 186.5 cM; the average
distance between the marks is 11.60 cM, the shortest
is 0.6 cM, the longest is 43.9 cM. The number of
markers on linkage groups from at least two to the
maximum 16; distorted markers are mainly scattered
in the linkage groups No.1, No.9 and No.16, while
there is no distorted markers in the linkage group
No.7.
1.2 The co-relationship of the trait of easy curing
potential (yellowing index) and genetic analysis
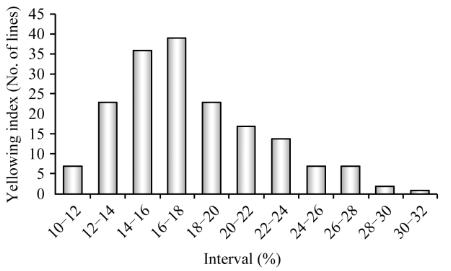
By using T-test, the final results showed that there
was highly significant differences of yellowing
index between the P1 and the P2 (P<0.01). F
2
populations presented obviously differences in
yellowing index ranged from 10.48 to 30.48, 17.93
in average and 4.190 for the standard deviation,
showing genetic characteristics of quantitative trait
with continuous distribution. The distribution of F
2
population with
-
0.099 39 for kurtosis and 0.654 8
for skewness, of which has less than 1.0 of the
absolute value, is a typical distribution of quanti-
tative traits suitable for QTL Mapping. Data are
shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.
Figure 1 Frequency distribution of yellowing index in F
2
population

