Basic HTML Version
徐小万等
, 2011,
利用
cDNA-AFLP
技术分析不同耐性辣椒叶片表达差异
,
分子植物育种
Vol.9 No.66 (doi: 10.5376/mpb.cn.2011.09.0066)
1488
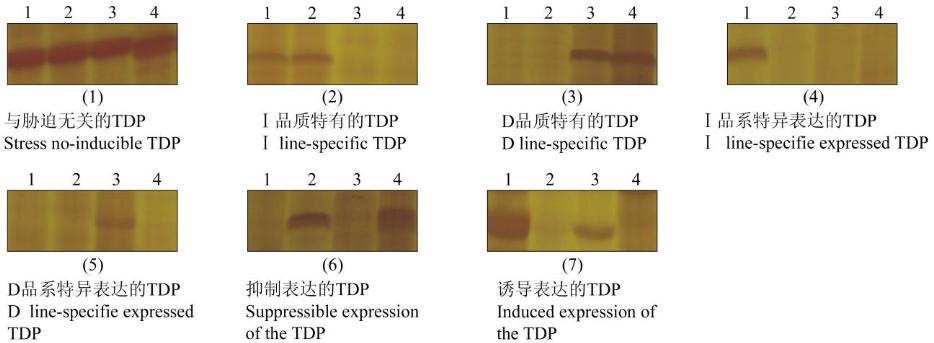
图
3 cDNA-AFLP
分析获得的差异表达片段
注
: 1, 2, 3, 4
分别为Ⅰ品种
(
系
)
高温高湿处理
4 d
与正常条件
, D
品种
(
系
)
高温高湿处理
4 d
与正常条件
Figure 3 Different expression fragments gotten from cDNA-AFLP analysis
Note: Lane 1, 2, 3, 4 are the expression fragments of
Ⅰ
, D line, at 40
℃
/30
℃
(d/n), 90% RH and 28
℃
/18
℃
(d/n), 75% RH for 4 d
表
1 cDNA-AFLP
片段差异表达分析
Table 1 Analysis of differentially expressed fragments from cDNA-AFLP
引物组合
SNI
SIN
SS
SIR
SIS
总计
Primer combination
Total
A7T5
36
5
2
1
0
44
A12T4
48
1
3
0
0
52
A12T6
48
3
3
2
1
57
A9T10
50
2
2
1
1
56
A8T5
46
2
3
0
2
53
A15T10
49
0
3
0
1
53
Total
277
13
16
4
5
315
Rate (%)
87.94
4.13
5.08
1.27
1.59
100
注
: SNI:
与高温高湿胁迫无关的基因
; SIN:
高温高湿胁迫诱导基因
; SS:
高温高湿胁迫抑制基因
; SIR:
在耐高温高湿材料中
特异表达的基因
; SIS:
在热湿敏感材料中特异表达的基因
SNI: stress non-inducible frafgments at high temperature and high air humidity; SIN: stress inducible fragments at high temperature
and high air humidity; SS: stress suppressible gene at high temperature and high air humidity; SIR: expressed gene induced at high
temperature and high air humidity in resistant line; SIS: expressed gene induced at high temperature and high air humidity in
susceptible line
SIR)
的扩增产物占
1.27%
;在热湿敏感品种
(
系
)
中
受高温高湿胁迫诱导
(expressed gene induced at
high temperature and high air humidity in susceptible
line, SIS)
特异表达基因的扩增产物占
1.59%
。这些
扩增产物与各自遗传背景密切相关,代表了耐高
温高湿或对热湿敏感的辣椒叶片中高温高湿诱导
表达的基因,可能与耐高温高湿或对热湿敏感的
机制有关。
2
讨论
在非生物逆境胁迫下植物基因表达模式发生
改变,诱导表达一部分基因、同时抑制表达另一部
分基因,以抵御非生物胁迫
(Altenbach and Kothari,
2004)
。本研究所得差异片段也反映了这一变化。
Bachem
等
(1996)
年发展了
cDNA-AFLP
技术,将
AFLP
用于
mRNA
的表达差异分析,保留了
AFLP
技
术的可靠性与高效性、又具有可重复性
(Money et al.,
1996)
,可用于植物生长发育过程中基因的分离与表

