GMO Biosafety Research 2014, Vol.6, No.1, 1-9
2
if the individual has different specification. This
technology has been utilized for the fixing of the
nature of plants, including their resistance to biotic
and abiotic stress, their tolerance to certain conditions
such as drought, salinity, herbicides, aluminum or iron
(Josine et al. 2011).
Biosafety regulations on Genetically engineered
products
Genetic engineering technology has been developed in
Indonesia since the 1990s and as a result of modern
technology, it is necessary to manage the product
settings to prevent some causes like bad influences on
human, animal and the environment, especially
biodiversity. The regulatory and management of
Indonesia biological safety have been established by
Governmental Regulation (GR) No. 21 of 2005 about
GEPs Biosafety and Presidential Regulation (PR) No.
39 of 2010 about Commission of Biosafety of GEPs,
which provide recommendations to the ministries and
involved agencies related in the prerelease of GEPs.
Both of these regulations confirm the status of GEPs
that will be commercialized in Indonesia have to pass
the biosafety assessment in accordance with the
precautionary principle on Cartagena Protocol. The
uniqueness of biosafety assessment in Indonesia is
that there are some additional considerations like;
religion or belief values, ethics values and esthetics
values, which are included in the terms of doing risk
assessment. Besides, the main goal of this protocol is
to ensure the adequate protection level on transferring,
handling and using safe delivery or cross-border
transfer.
Before the setting of GR No. 21 of 2005, the
government uses The Decree of Four Joint Minister
which was signed in 1999. Under this decree, Bt
cotton eventually obtain the permission from the
Minister of Agriculture to be released in a limited field
(South Sulawesi) in 2001, in succession until 2003,
even though after that planting of Bt cotton was
stopped planting because of some problems that occur
due to unprepared conditions of government and
communities for GEPs application. Then, in 2011,
Food Safety Certificate was issued from some GEPs
like corn and soybean- with some properties from
different events. In the same year, permission of feed
product distribution (Ronozyme AX (CT)) and
permission of the releasing the sugarcane in order to
tolerant the drought, as the result, of the development
of the national private companies are also issued by
the relevant institution
.
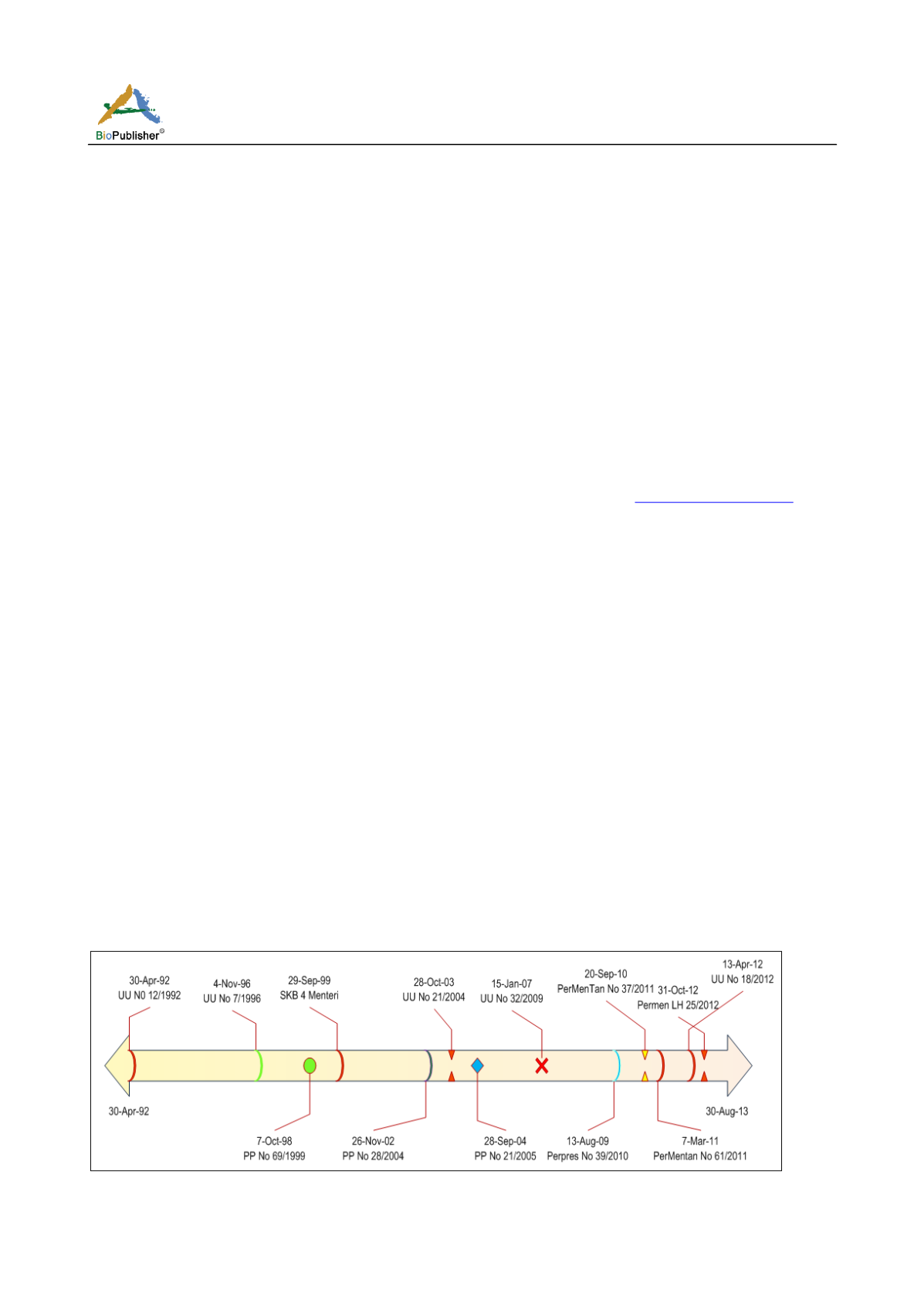
The time line of the enactment of laws and regulations
related to the usage of GEPs regulations in Indonesia
from 1992 to 2012 (Figure 1) has produced some
other regulations and laws that should be able to be
implemented for GEPs management in Indonesia. But
due to some technical and bureaucracy constraints of
the government, the implementations of GEPs
management become not optimal as can be seen on so
many aspects defined in the regulations but have not
been able to be implemented yet.
It can be noted that the legal instrument set for the
implementation of the GEPs management in Indonesia
has been complete, because it has been included on
foods (Law (UU) No. 7/1996; Government Regulation
(GR) No. 69/1999 about Labeling of GEPs food;
Government Regulation No 28 / 2004 about Quality,
Nutrition of Food), Plant cultivation (Law No.
12/1992; Decision Letter No 4 1999 Minister about
Figure 1 The time line of regulations regarding to biosafety


