Basic HTML Version






Plant Gene and Trait 2012, Vol.3, No.1, 1
-
5
http://pgt.sophiapublisher.com
3
1.2 Blast analysis of full length cDNA and putative
amino acid sequence
Nucleotide-nucleotide blast analysis showed the full
length cDNA sequence of
Goactin1
gene had a very
high homologue to
Actin
gene of
Populus trichocarpa,
Vigna radiata, Betula luminifera, Oryza sativa, Zea
mays, Arabidopsis thaliana, Nicotiana tabacum,
Gossypium hirsutum, Pisum sativum, Ricinus communis,
Pyrus communis, Aegiceras corniculatum, Prunus
salicina, Phaseolus vulgaris, Phalaenopsis sp, Picea
abies, Larix gmelinii, Mimosa pudica, Diospyros kaki,
Plantago major, Linum usitatissimum
and
Solanum
tuberosum
. And the homologue of
Populus trichocarpa
(XM_002311131, GENE: 7467546),
Vigna radiate
(AF143208.1) and
Betula luminifera
(FJ410442.1)
was the highest, which reached 84 percent. Moreover,
by comparing the deduced amino acid sequences
(BlastP) with the protein data bank, the result showed
that Goactin1 also had very high homologue to actin
protein of many other species in the data bank. The
maximum number of amino acid homologue was 99
percent from
Ricinus communis
(XP_002530711.1,
EEF31665.1),
Solanum tuberosum
(CAA39280.1),
Gossypium hirsutum
(AAC31886.1),
Populus tricho-
carpa
(XP_002308365.1, XP_002322664.1, ABK92789.1,
XP_002311167.1, EEE88534.1, XP_002316289.1,
ABK92513.1, EEF02460.1),
Caragana Korshinskii
(ACK87035.1) and
Nicotiana tabacum
(ACH69153.1,
CAA45149.1).
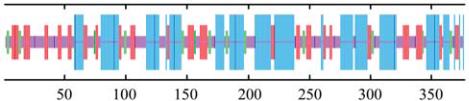
1.3 Characteristic analysis of Goactin1 protein
ProtParam analysis showed Goactin1 theoretical
molecular weight and isoelectric point were 41.7 kD
and 5.31 respectively, and there was 50 negative
charge amino acids (Asp +Glu) and 38 positive charge
amino acids (Arg +Lys). The protein was composed of
Alpha helix (39.26%), Random coil (33.69%), Extend
strand (20.42%)and Beta turn (6.63%) in secondary
structure analyses by SPOMA program (Combet et al.,
2000) (Figure 2). Through conservative domain analysis
by cdart program (NCBI), A conservative domain:
Actin superfamily, was discovered (Figure 3), which
included 6 ATP binding sites, 11 profilin binding sites,
and 9 gelsolin binding sites (Marchler-Bauer et al.,
2009; Marchler-Bauer and Bryant, 2004).
Figure 2 Secondary structure of putative Goactin1 protein
Note: Blue line: Alpha helix; Deep red line: Extended strand;
Green line: Beta turn; Pale Red: Random coil
Figure 3 Conservative domain of Goactin1 amino acid
sequence
1.4 Tertiary structure of Goactin1 protein
Based on 3D structure of 2BTF A chain, a tertiary
structure model of Goactin1 was established by
ESyPred 3D program (Figure 4), and there was 88.3%
homologue between them (Lambert et al., 2002).
Figure 4 Tertiary structure of putative Goactin1 protein based
on A chain of 2BTF
1.5 Molecular phylogenetic tree analyses of
Goactin1
Based on multisequencing comparison between Goactin
1 and actin amino acid sequence of other species by
ClustalX (1.81) program, circular molecular phylogenetic
tree was established use MEGA 4.0 program (Neighbor
Joining method). Analytical result was showed at figure
5. With
Solanum tuberosum
(gi|231503|, gi|231496|),
Gossypium hirsutum
(gi|54035683|),
Nicotiana tabacum
(gi|197322805|, gi|461465|),
Brachypodium sylvaticum
(gi|226858185|),
Arabidopsis thaliana
(gi|15231447|,
gi|15238387|, gi|28393806|),
Goactin1
were gathered

