Basic HTML Version

Journal of Mosquito Research, 2013, Vol.3, No.4, 21
-
32
ISSN 1927-646X
http://jmr.sophiapublisher.com
28
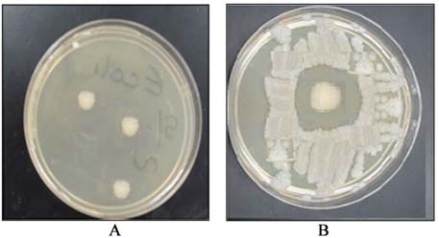
A control Petri dish was prepared by placing a filter
paper saturated with elution buffer instead of the
recombinant Tsf protein as shown in Figure 9A, where
the buffer did not affect growth of bacterial cells. This
indicated that the recombinant mosquito transferrin
(Tsf) protein is a potent inhibitor for the growth of the
Mach1™- T1
®
E. coli
strain.
Figure 9 Test for the antibacterial activity of purified
recombinant mosquito Tsf
Note: A (control plate), B (test plate)
3.6 Characterization of
Cx. quinquefasciatus
transferrin (CqTrf) partial cDNA and its position
in a molecular phylogeny
A PCR amplification approach using degenerate
primers derived from conserved domains of insect
transferrins permitted cloning of the isolated 858 bp
partial cDNA sequence for CqTrf that encodes a
deduced 248-aa peptide (Figure 7) with a molecular
mass of approximately 63 KDa and an estimated pI
value of 6.90. The complete nucleotide sequence of
Cx. quinquefasciatus
transferrin messenger RNA
which is 1 979 bp nucleotide long are deposited in
GenBank, EMBL, DDBJ, PDB sequences database
under accession number XM_001865823.1.Blastx
comparisons and ClustalW alignment with other insect
transferrins further confirmed its identity as CqTrf
which is also supported by the protein molecular mass
and isoelectric point calculations.
Figure 10 Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence of
Cx. quinquefasciatus
Transferrin molecule with some of the sequences
resulted from homology search

