基本HTML版本




Intl. J. of Mol. Evol. and Biodivers. 2012, Vol. 2, No.1, 1-7
http://ijmeb.sophiapublisher.com
6
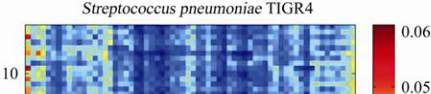
Figure 3 The color matrix of
Streptococcus pneumonia
TIGR4
Note: The horizontal axis and the longitudinal axis represent
the kinds of combination of trinucleotide respectively
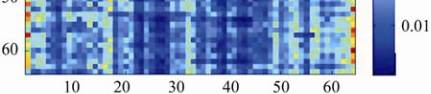
Figure 4 The joint histogram of trinucleotide transition
probability matrix of organisms
Note: (a) Represents the joint histogram for both of
Streptococcus pneumonia
TIGR4 itself; (b) represent the joint
histogram for
Streptococcus pneumonia
TIGR4 and
Streptococcus pneumonia
D39
The formula used for joint histogram divergence is
(2)
Where
i
and
j
represent the row number and column
number of matrix HIST respectively;
HIST[i,j]
represents the value of the
i
-th row, the
j-
th column
element in matrix
HIST
.
3.4 Estimation of the novel evolution analysis method
The Euclidean distance is usually used to calculate the
diversity between sequences based on oligonucleotide
frequencies. And the joint histogram divergences of
trimucleotide transition probability matrixes were
compared with the Euclidean distances to evaluate the
discrimination of the novel evolution analysis method.
The Euclidean distance based on oligonucleotide
transition probability matrixes of two genomes was
calculated as
(3)
N
1ji,
2
ji,
ji,
y x
D
Here
N
represents the row number and column
number of oligonucleotide transition probability
matrix;
x
i ,j
and
y
i ,j
represent the element value of the
i
-th row and the
j
-th column in two transition
probability matrixes respectively.
Additionally, the traditional method for phylogenic
inference based on single gene or several genes has
limited discrimination, and it cannot distinguish the
intraspecies organisms efficiently (Bohlin et al., 2008).
So the joint histogram divergence was used to
reconstruct the phylogeny tree of organisms that is
hard to be identified by single gene. Here, for 11
organisms, their sequence alignment of 16S rRNA
gene was completed by CLUSTAL X, and the single
gene-based tree was constructed by neighbor-joint
method. Meanwhile, the joint histogram divergence
matrixes of these genomes were created and the
phylogeny tree was constructed by PHYLIP. Finally,
we compared the topologies of 16S rRNA gene-based
tree with those of genomes’ joint histogram distance
matrix-based tree to examine their ability to
reconstruct the phylogenetic relationship among these
11 microbial organisms. The result would be critical
for test the validity of our new method in differentiating
microbial species in closely related organisms.
) ,(
) ,(
2
,
,
j i
ji
j i
HIST
j i
HIST
i j
HD
Authors’ Contributions
CTY collected and analyzed the data, drafted and modified the
manuscript; QSH wrote and analyzed part of data. FZ also
analyzed part of data; YF directed the whole project, drafted
and modified the manuscript. All authors have read and
approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Science Foundation of
China grants 10972081 and 11072080.
References
Amoutzias G.D., Robertson D.L., Oliver S.G. and Bornberg-Bauer E., 2004,
Convergent evolution of gene networks by single-gene duplications in

