Molecular Plant Breeding 2016, Vol.7, No.33, 1
-
15
5
M39-1-2-21-2, M39-1-2-21-2, 9482-01-03, JMB8401, Ca41, and Pi9-G7-2K-1 while Halilbey showed
susceptibility to these strains. Osmancik-97 showed resistance to seven strains (33.3%) while its progenies showed
average resistance to 19 strains (90.5%) and ranged from 17 to 21 (81% to 100%). Progenies from Osmancik-97
showed resistance to M36-1-3-10-10, Ca23-49, M39-1-2-21-2, BN111, 9482-01-03, IK81-3, and B90002 for which
Osmancik-97 was susceptible (Table 1). ABL1 to ABL11 were also evaluated for field blast resistance in Turkey.
The RPs, Osmancik-97 and Halilbey, were susceptible while all the selected ABLs were resistant (Table 2). These
results clearly showed the production of improved breeding lines from susceptible RPs by introgressing the
Pi40
gene for blast resistance.
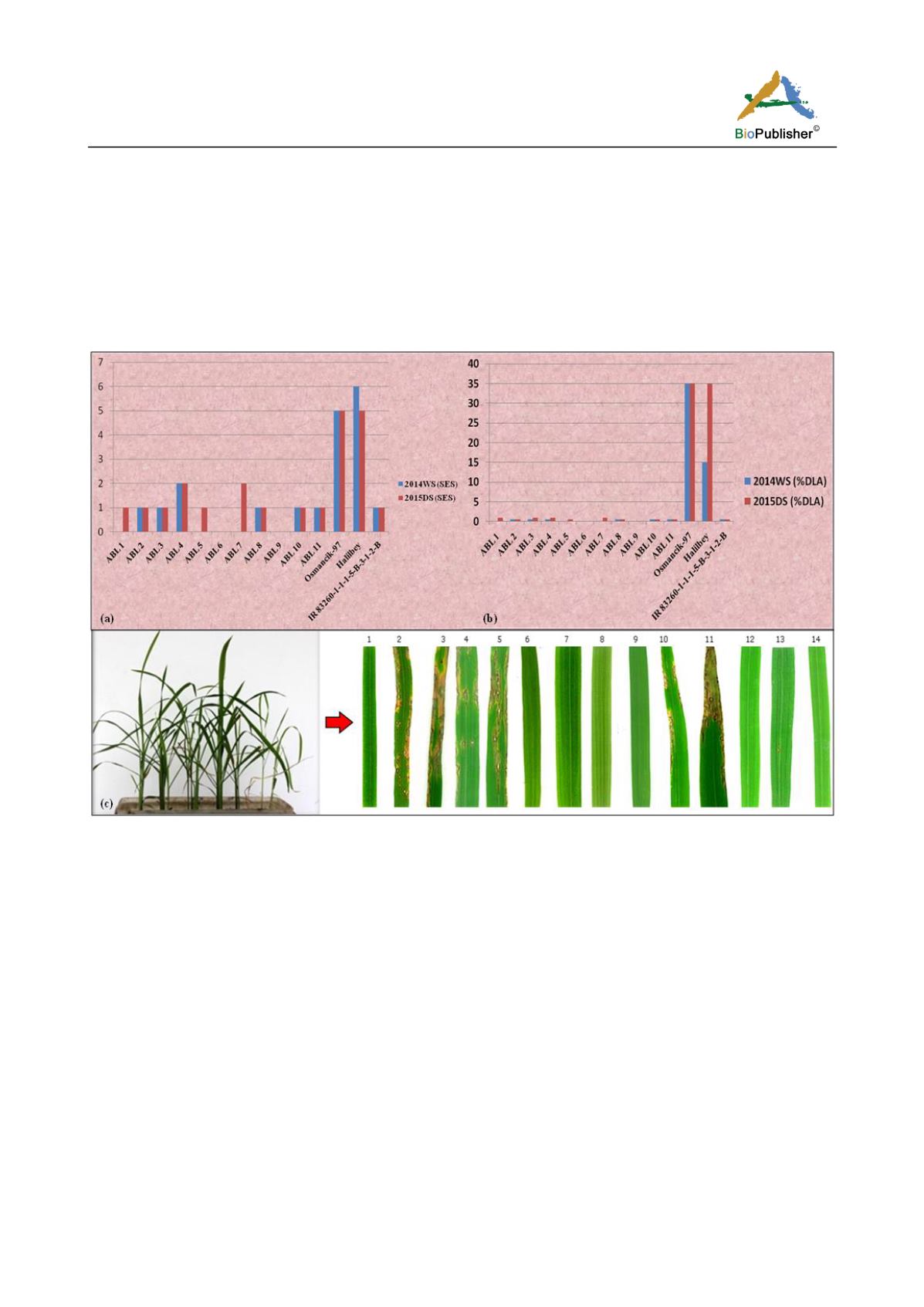
Figure 2 Screening for blast resistance under field and glasshouse conditions. (a) Disease scores of advance backcross lines (ABLs)
and parents using Standard Evaluation System of IRRI and (b) Percent diseased leaf area of ABLs and parents. (c) Blast disease
reaction in glasshouse of ABLs and parents using strain M101-1-2-9-1. Legend: 1=
Pi40
; 2=LTH, 3=CO39, 4=Osmancik-97,
5=Halilbey; 6=IR83260-1-1-1-5-B-3-1-2-B, 7-14=ABLs.
2 Discussion
Host-plant resistance is the most important breeding strategy to breed cultivars with durable resistance to blast
disease of rice (Khush and Jena, 2009). Some cultivars with major resistance genes (
Pi2
and
Pi9
) are cultivated
for a long period of time without loss of resistance to blast (Bonman et al., 1992; Bonman and Mackill, 1988;
Jeung et al., 2007). Additionally, a novel resistance gene,
Pi40
has been tested for its durability of blast resistance
and the gene has shown promise for durable resistance that is being used in several rice breeding programs (Suh et
al., 2009).
Although a number of resistance genes have been identified and used in the breeding program, most of those
genes breakdown within a short period (Fukuta et al., 2009). Wild species of rice are reservoir of many valuable
genes including blast resistance which could be exploited for improving elite cultivars (Jeung et al., 2007). One of
the several identified genes,
Pi40
is derived from the wild species,
O. australiensis
(Acc. 100882) of EE genome
and reported to have resistance to a diverse group of
M. grisea
isolates (Suh et al., 2009).


