Basic HTML Version


International Journal of Marine Science 2014, Vol.4, No.52, 1-9
http://ijms.biopublisher.ca
5
mg. L
-1
), respectively after 96 h (Figures 2a-2e).
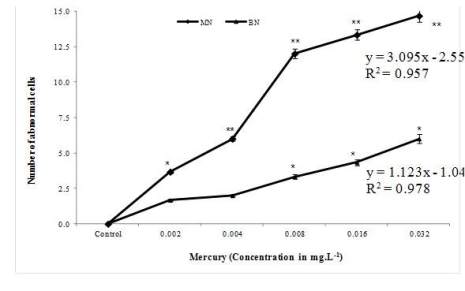
Variability analysis of MN showed higher mean
frequency of 14.7 MN/1000 cells in mercury (0.034
mg. L
-1
), followed by cadmium (14.864 mg. L
-1
),
copper (0.16 mg. L
-1
), zinc (16.444 mg. L
-1
) and lead
(0.96 mg. L
-1
). Significant increase (P < 0.05) in MN
frequency was observed in the mussels treated with
metals when compared to control groups. The highest
induction of MN was caused by mercury (0.034 mg.
L
-1
) (Figure 2d).
Figure 2a MN and BN induction in
M. philippinarum
exposed
to copper (MN: Micronuclei; BN: Binucleus) *
P
< 0.05 and **
P
< 0.01 statistically significant when compared to control
(analyzed by one way ANOVA
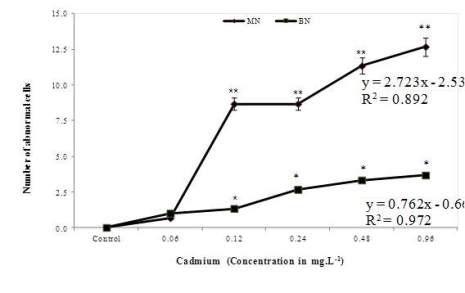
Figure 2b MN and BN induction in marine bivalve
M.
philippinarum
exposed to cadmium (MN: Micronuclei; BN:
Binucleus) *
P
< 0.05 and **
P
< 0.01 statistically significant
when compared to control (analyzed by one way ANOVA)
2.3 Induction of Binucleus (BN)
In
control groups i.e., seawater medium, the mean BN
frequency was the range between 0 and 0.3. The mean
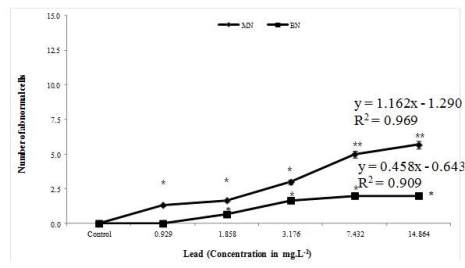
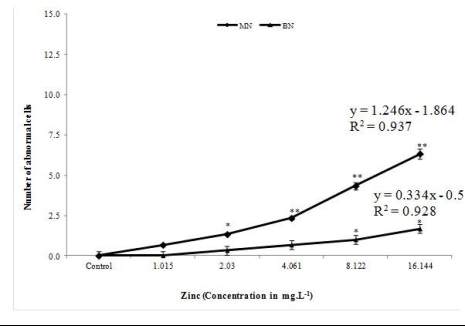
frequency of BN of metal exposed animal was 4.3, 2.0,
3.7, 1.7 and 6.0 in the highest concentration of copper
(0.16 mg. L
-1
), cadmium (14.864 mg. L
-1
), lead (0.96
mg. L
-1
), zinc (16.444 mg. L
-1
) and mercury (0.034 mg.
Figure 2c MN and BN induction in marine bivalve
M.
philippinarum
exposed to lead (MN: Micronuclei; BN:
Binucleus) *
P
< 0.05 and **
P
< 0.01 statistically significant
when compared to control (analyzed by one way ANOVA)
Figure 2d MN and BN induction in marine bivalve
M.
philippinarum
exposed to mercury (MN: Micronuclei; BN:
Binucleus) *
P
< 0.05 and **
P
< 0.01 statistically significant
when compared to control (analyzed by one way ANOVA)
Figure 2e MN and BN induction in marine bivalve
M.
philippinarum
exposed to zinc (MN: Micronuclei; BN:
Binucleus). *
P
< 0.05 and **
P
< 0.01 statistically significant
when compared to control (analyzed by one way ANOVA)
L
-1
), respectively after 96 h (Figures 2a-2e). Variability
analysis of BN showed the higher frequency of 6.0

