Basic HTML Version

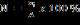


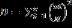
International Journal of Marine Science 2014, Vol.4, No.65, 1-7
http://ijms.biopublisher.ca
3
current velocity, pH, salinity and depth. Nitrate
and phosphate contents were measured using
Spectrophotometer UV-Visible 1240 Shimadzu in the
laboratory.
1.4 Sampling of distribution of soft corals
Observations of soft coral distribution were done
using line intercept transect (LIT) method and transect
quadrant refers to (English et al., 1994). Transect lines
were installed parallel to each other and to the
coastline with a length of 50 m for each. Placement of
quadrant transects (1x1 m) using purposive sampling.
Corals within each of the transect quadrants were
recorded and photographed for documentation. In this
research LIT were used measure diversity and coral
cover. The collected data involved the percentage of
live coral cover and the percentage of dead coral cover.
Hard coral species were identified according to (Allen
and Steene, 1996), (Veron, 2000) and (Suharsono,
2010).
Soft coral were sampled using a knife and wrapped
with plastic bags. All samples were inserted into the
cooler box and immediately taken to the laboratory.
They were identified according to (Allen and Steene,
1996); (Fabricius and Alderslade, 2001); and
(Manuputty, 2010).
1.5 Data analysis
The percentage of coral cover (
Life form
)
Percentage of coral cover (N) was calculated by
summing (ni) coral species, and divided by (A) the
transect area, and multiplied by 100% (Suharsono,
1995) with the formula:
………………………………
(1)
Coral covered were categorized into 0 to 24.9% in
poor cover, 25 to 49.9% is moderate cover, 50 to
74.9% is good, and 75-100% is excellent (Gomez and
Yap, 1988).
Diversity of soft coral
Shannon's diversity index (H') was calculated by
multiplying
pi
(proportion of the
i
-th) and log
pi
, with
the formula:
……………………………..
(2)
Diversity index criteria is as follow: H'<1: low
diversity, very strong environmental pressure, 1 <H' ≤
3: moderate diversity, environmental pressures
moderate, H '> 3: high diversity, a balance ecosystem
(Brower and Zar, 1984).
Equality (Evenness)
Shannon's Equality index (E) was calculated by
dividing
H’
by
H
max
(here
H
max
= ln
S
). Equality
assumes a value between 0 and 1. Value 1 being
complete evenness (represents excellent coral cover)
according to the formula:
……………………………
(3)
Dominance Index
Simpson's Dominance Index (D) was calculated by
dividing species number (ni) by total species (N),
according to the formula;
…………………………………..
(4)
Dominance index values between 0-1. If D is close to
1, it means that there are species dominate, if D close
to 0 means no species dominate (Odum, 1971).
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
PCA is used to examine the relationships of
biophysic-chemical parameters of the water
(temperature, depth, turbidity, flow velocity, sediment
fraction, salinity, pH, nitrate and phosphate) with the
percentage of coral cover. This analysis showed that
there were influences of each parameter on the
distribution of soft corals, and the similarity indices at
each transect.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Result
2.1.1 Physic-chemical characteristics of waters
The results of physical-chemical parameters
measurement of waters in each station showed
relatively little variations. Of the six stations that were
measured, at a depth of soft 9 meter corals diversity
was very high. Temperature around was 29 °C,
turbidity was 8,46 NTU, current speed was 0.5 ms
-1
,
substrate type was generally sandstone, salinity about
31 ‰, pH of the water about 8.07, nitrate was 0.169
mgL
-1
, and phosphate was about 0.19 mgL
-1
(Table 1).

