International Journal of Horticulture, 2017, Vol.7, No. 26, 239-245
243
Table 4 Situation of postharvest loss and price of carrot at different levels in Kalimati-Monohara corridor -May, 2016
Situation
Farm gate
Collection point
Wholesale
Retail
Postharvest loss (%)
10
2
5
18
Price (NRs/kg)
45
47
52
75
Note: NRs = Nepalese currency
Major Physiological Disorders
Cracking of carrot root is a major problem at carrot growing areas in Nepal. It may cause by a fluctuating water
supply. When there is heavy rainfall after a period of drought, the inner flash of the carrot expands faster than the
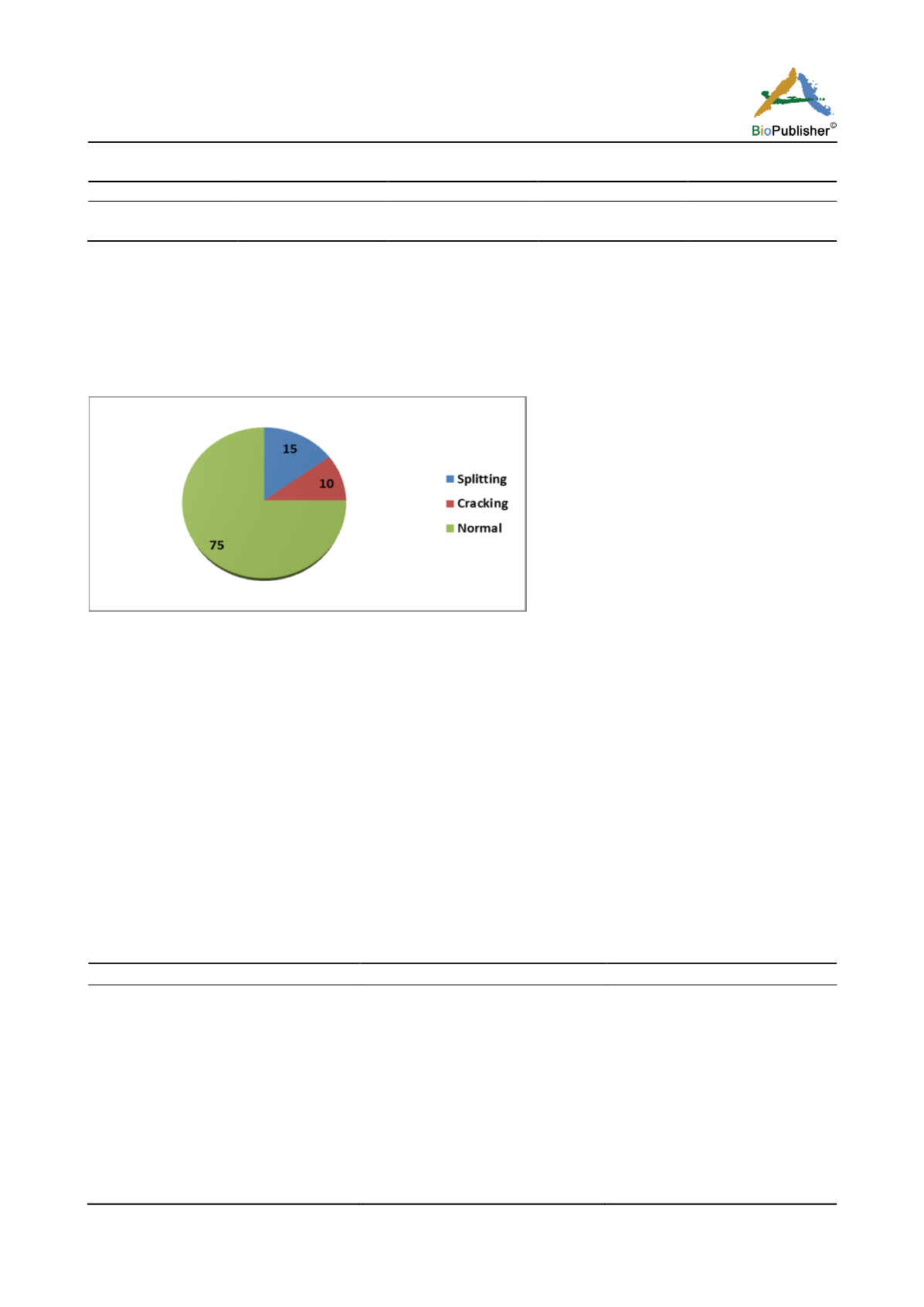
toughened skin, causing the skin to crack. It was found that at farm gate level 75% carrots were in normal
condition. However, 10% carrots were cracked and 15% were having splitting problem (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Condition of marketable carrot after harvest at farm gate level in Manohara Khola, Bodephant and Mulpani
5 Effect of Calcium Chloride on Storage Life of Carrot at Room Temperature
Shelf-life & TSS
The calcium treatments significantly influenced the shelf life of carrot roots. The maximum shelf life (11 days)
was noticed in 2.5 % calcium chloride treated roots compared to the control (6 days). These results were in
conformity with that of wills and Tirmazi (1982). The experiment conducted by Isaac and Maalekuu (2013), had
also the similar type of results. This result is also agreement with the earlier report of Sharma et al. (1996), which
indicated that calcium chloride has the capacity to strengthen cell walls of fruits which help to prevent invasion of
fungal spores.
However, total soluble solid (TSS) was not affected by calcium treatment (Table 5). As the storage period
prolonged, the TSS of carrot roots increased due to the water loss and that lead to higher concentration of sugars
in carrot. Agar and Kaska (1995) also reported similar results. The experiment conducted by Bhattarai and
Gautam (2006) had also the similar type of results.
Table 5 Effect of calcium chloride on shelf-life & TSS of carrot root at room temperature in HRD, Khumaltar (2016/17)
Treatment
TSS (
0
Brix)
Shelf life (Days)
0.5% CaCl
2
7.47
6.67
1 % CaCl
2
5.80
7.33
1.5 % CaCl
2
6.23
7.33
2 % CaCl
2
7.13
8
2.5 % CaCl
2
6.60
10.67
3 % CaCl
2
7.30
9
3.5 % CaCl
2
6.93
7
Control (tap water)
6.07
6
F-test
NS
*
LSD (0.05)
2.054
1.413
CV %
17.7
7.75


