International Journal of Clinical Case Reports 2016, Vol.6, No.21, 1-5
2
presence of circulating stem cells. This report presents a case of single tooth gingival recession defects treated
with combined CAF and PRF technique.
Case Report
A 35 year old female patient reported to the Department with the chief complaint of sensitivity to cold water in the
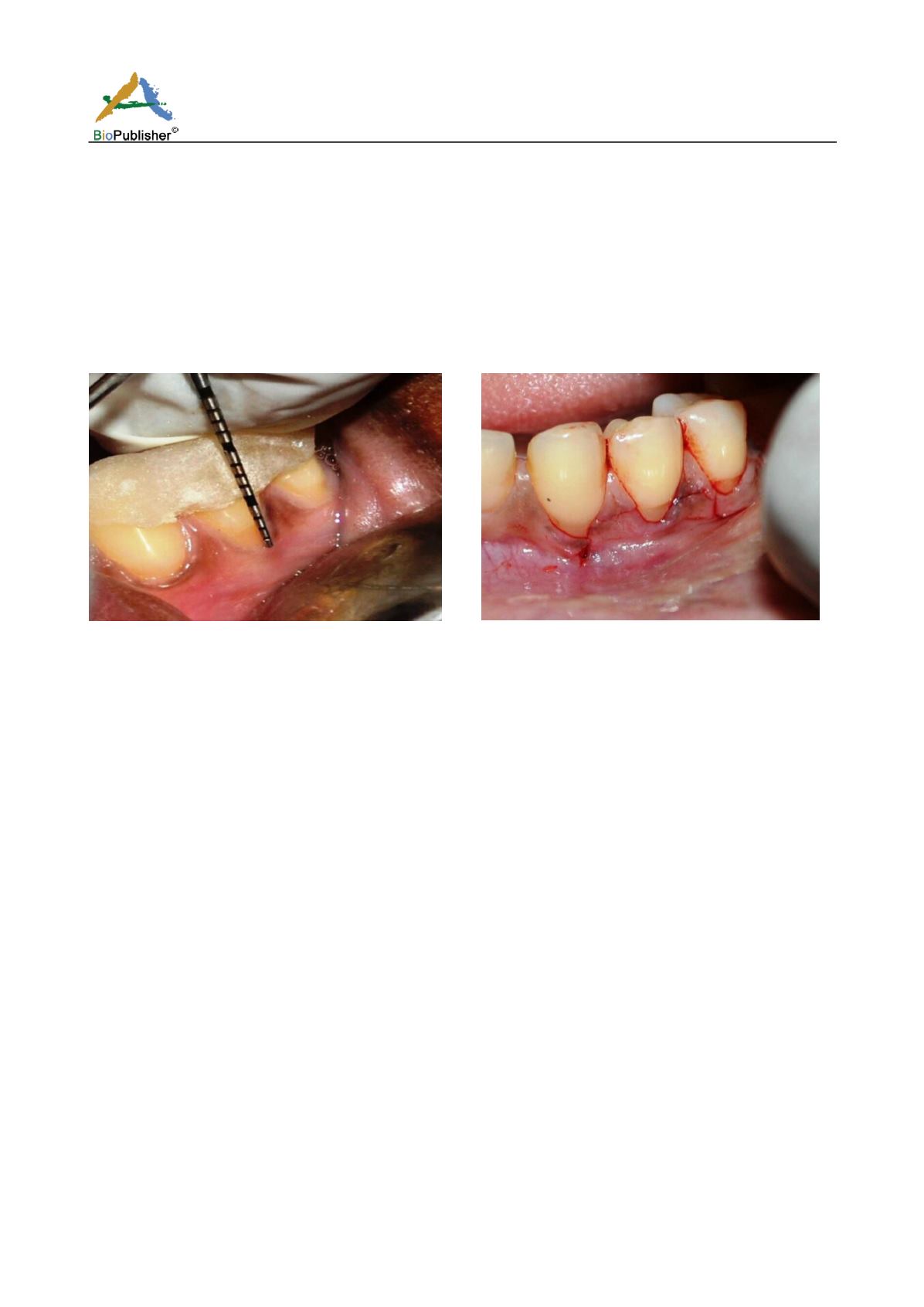
lower left back tooth region. No relevant medical and dental history was reported. On clinical examination, left
mandibular first premolar was identified with gingival recession defects at multiple places (Fig.1). The recession
defects, Millers’ Class I type, were measured by calculating the distance between the cemento-enamel junction
and the gingival margin and recorded to be upto3mm. A hard tissue abrasion defect was not present on the tooth.
Fig.1 Left mandibular first premolar with gingival recession
defects at multiple places
Fig.2 Surgical site delineated with two oblique releasing
incisions at the mesial and distal aspects and sulcular
incisions around the affected tooth
Pre-surgical procedure: The preparation of the patient included scaling and root planning of the entire dentition with oral
hygiene instructions. The surgical procedure was explained to the patient and a written, informed consent was obtained.
Surgical procedure: The operative site was anaesthetized using 2% xylocaine with adrenaline. A coronally advanced flap
technique was performed at the surgical site. This site was delineated by two oblique releasing incisions at the mesial and
distal aspects and sulcular incisions around the affected tooth (Fig.2). A full thickness flap was elevated to expose at least
3mm of the marginal bone apical to the dehiscence area (Fig.3). Ahorizontal releasing incision was made in the periosteum
at the base of the flap to facilitate tension free coronal advancement of the surgically created flap. The exposed root
surfaces were scaled and root planed.
Preparation of PRF membrane: After the recipient site preparation was completed, the required quantity of blood was
drawn in a 10ml test tube without an anti-coagulant and centrifuged immediately using a tabletop centrifuge for 10mins.at
3,000rpm. The resultant product consisted of the following three layers (Fig.4):
Top most layers consisting of acellular platelet-poor plasma (PPP);
PRF clot in the middle; and
red blood cells (RBCs) at the bottom.
After centrifugation, the PRF clot was removed from the tube using sterile tweezers, separated from the RBCs base using
scissors, and placed in a sterile metal cup. At the recipient site, the PRF clot was placed over the denuded root surfaces and
the flap was pulled over it. The area was compressed using digital pressure in order to obtain a PRF membrane and the flap
was coronally advanced and sutured (Fig.5). Aperiodontal dressing was placed over the surgical area (Fig.6).


