基本HTML版本

International Journal of Clinical Case Reports 2014, Vol. 4, No. 6, 1-4
http://ijccr.biopublisher.ca
2
During visit, the patient also reported an annoying
right hearing loss, which lasted from about 1 month:
otoscopy was normal, but at a more accurate
evaluation, a nystagmus was shown. Using Frenzel’ s
glasses, we saw a spontaneous horizontal and second
degree nystagmus beating to the right, which did not
change with positioning maneuvers (sitting position;
supine; left side; right side; Rose’s position, with
hyperextended head) and which was not inhibited by
fixation. Halmagyi Test (Head Impulsive Test, HIT)
was difficult to interpret; Head Shaking Test (HST)
did not change the spontaneous nystagmus. Romberg
Test was indifferent, showing a good functional
compensation of the patient. Facial nerves were
working perfectly.
Investigating her history, patient reported a slight
dizziness from about one month, without real
vertiginous episodes. Vertigo is understood as a
sensation of rotation of the person in the surrounding
environment, or movement of the environment itself;
it is present from 18% to 58% of patients with VS (2):
this symptom is not as frequent as expected, as the VS
grows slowly, and nervous system has time to adjust
to the new situation, compensating for as long as
possible. The patient denied tinnitus, that is
conversely described in 53% to 70% of patients with
VS (2). She was in good health, with exception of a
mild hypercholesterolemia, treated with diet alone.
She denied similar episodes in the past, recent head
trauma or a history of migraine. She is not a smoker,
as it was ascertained, remembering protective effect of
cigarette smoking about the risk of VS, reported in
literature (3,4,5).
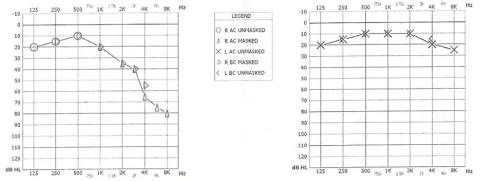
Audiometric examination (Figure 1) showed a slight
sensorineural hearing loss on the mid frequencies and
a severe hearing loss on the acute frequencies at the
right ear, with left normoacusia (compatible with
patient’s age); left pure tone average (PTA),
considering 500 Hz, 1000 Hz, 2000 Hz and 4000 Hz,
was 32,5 dB; tympanograms were bilaterally normal
and stapedial reflexes were absent. Wrongly, speech
discrimination (SD) was not performed.
Figure 1 Tonal audiometry
On suspicion of a central nervous system affection, a
HRCT scan with enhancement was performed. A
33x23 mm mass, located at right cerebellopontine
angle, with internal cystic-necrotic component was
found; a suspected contralateral similar lesion of 17
mm was also described (Figure 2).
Consequently, a Magnetic Resonance Imaging with
gadolinium was indicated: this exam showed an expansive
lesion of right cerebellopontine angle, with intra-
extrameatal development (28 mm in largest
extrameatal diameter), and a large cystic intralesional
component, compatible with an eighth cranial nerve
neuroma; the tumor determined a moderate com-
pression on right middle cerebellar peduncle, with
minimal surrounding edema; all was normal on the
left side (Figure 3-4-5).

