Genomics and Applied Biology 2018, Vol.9, No.9, 56-61
57
Nonspecific immunity is an extremely important immune response in teleost fish. In this study, we located and
stained NCCRP-1 receptor in
Oreochromis niloticus
by immunohistochemical method to determine the
distribution of NCC in various tissues, and would lay a foundation for the study of non-specific immunity related
to tilapia in subsequent experiments.
1 Results and Analysis
1.1 Distribution of NCCRP-1 in tissues
In this study, the distribution of NCCRP-1 in the tissues was determined by antibody incubation staining and four
tissues including brain, head kidney, liver and spleen were selected. The nuclei of most tissue cells were stained
blue by hematoxylin, and the positive result of DAB staining was brownish yellow. The results indicated that
NCCRP-1 was distributed in all four selected tissues. It was the least distributed in the brain, showing dispersion
or aggregation. In other three tissues, the distribution of NCCRP-1 was more than that in brain, and was also
distributed in dispersion, occasionally aggregated, or concentrated on the surface of the mucosa (Figure 1).
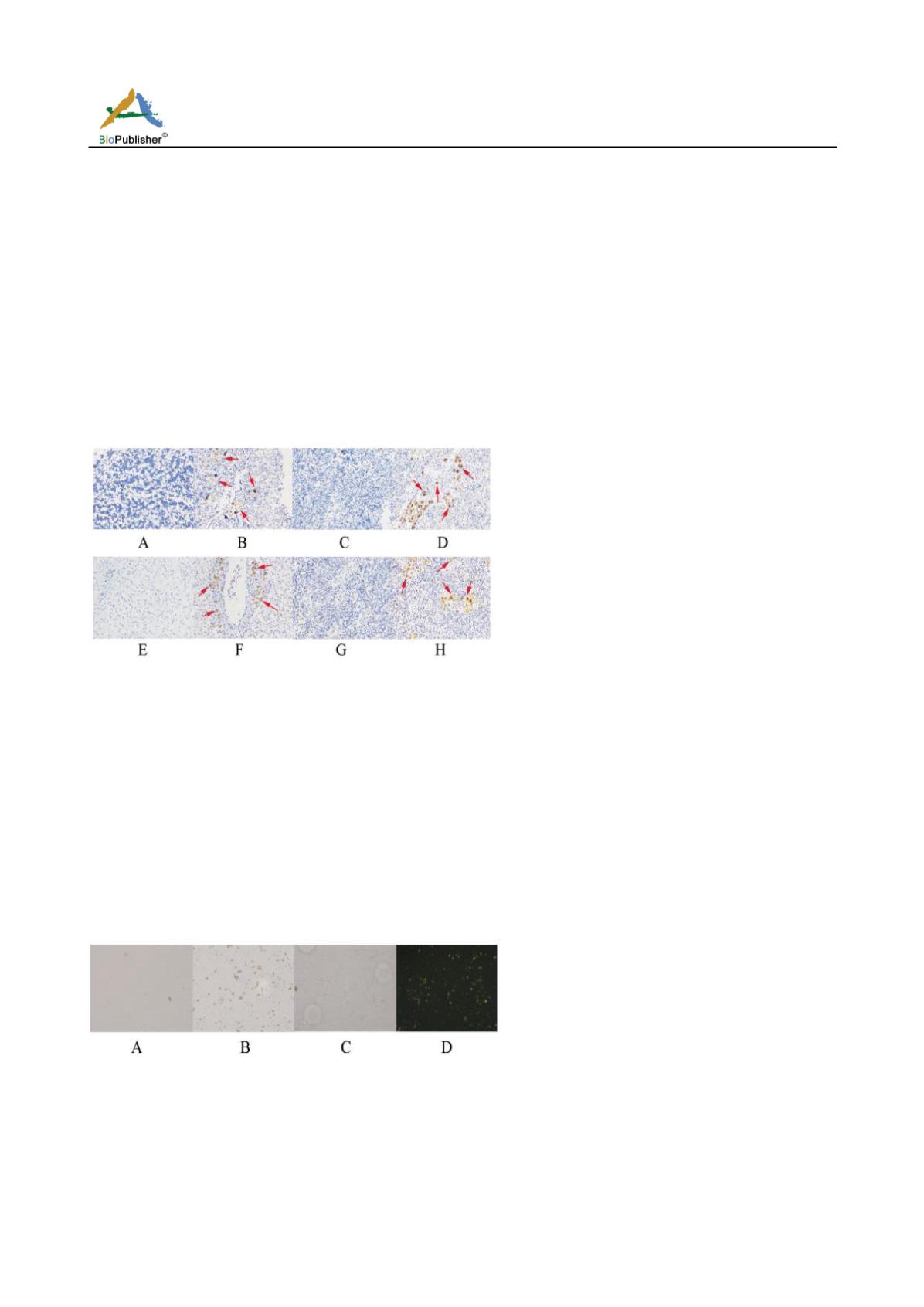
Figure 1 Four tissues sections of Nile tilapia
Note: A: Brain control; B: Brain; C: Head Kidney control; D: Head Kidney; E: Liver control; F: Liver; G: Spleen control; H: Spleen;
Red arrow: NCC; Magnification: 200×
1.2 Isolation, purification and identification of NCC from head kidney
Cell suspension containing NCC from
Oreochromis niloticus
head-kidney was obtained by two layers of
discontinuous gradient Percoll separation method. Trypan blue staining and counting showed that the cell survival
rate was 85%. Through antibody incubation and HRP staining, NCC was found to be brownish yellow under light
microscope. In addition, NCC was found to be yellow-green fluorescence under fluorescence inversion
microscope by combining with FITC fluorescent antibody. Moreover, when high purity NCC was incubated and
stained with antibodies, we found that compared with normal tissue cells, NCC individuals were smaller, and cell
shapes were diverse. Nuclei occupied most of the space of the whole cell with less cytoplasm, and some cells
could be observed a split in the nucleus (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Staining of NCC in head kidney of Nile Tilapia
Note: A: HRP control; B: HRP staining; C: FITC control; D: FITC staining; Magnification: 400×
2 Discussion
NCC is an important lymphocyte in teleost fishes, and plays an important role in nonspecific immunity
(Jaso-Friedmann et al., 2001). Therefore, studying the amount and distribution of NCC in fish will help us better
understand the specific functions of various tissues and organs and the mechanism of NCC action. After
exogenous stimulation of teleost fish, the extracellular structure of NCCRP-1 is responsible for binding antigens,
while the intracellular structure is responsible for activating and regulating the killing function of NCC


