Cotton Genomics and Genetics 2016, Vol.7, No.2, 1-23
8
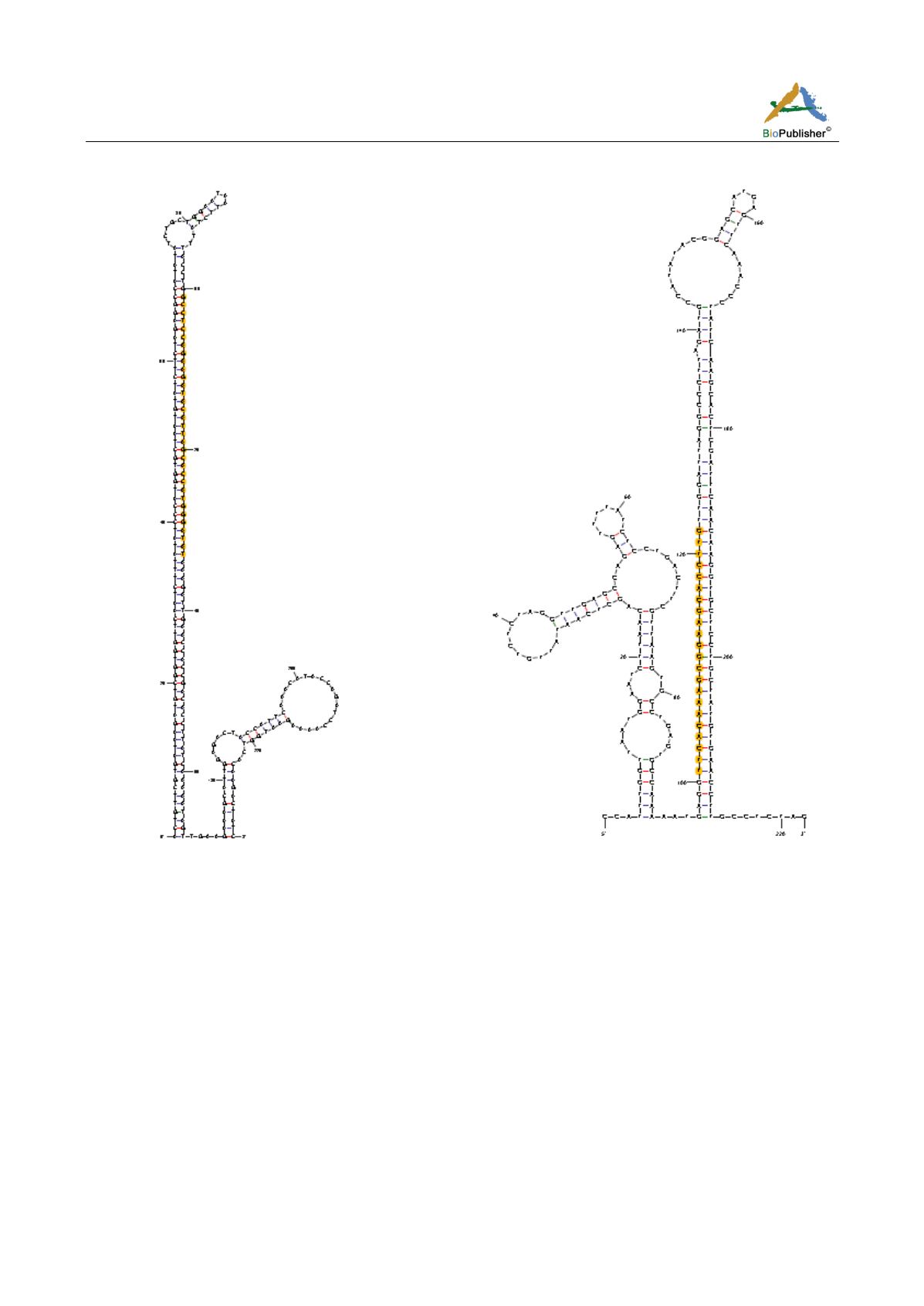
Figure 3 Secondary hairpin structures predicted for putative novel miRNAs. The highlighted nucleotides are the sequence of putative
novel miRNA found in this study and the remaining are the sequences of
G. raimondii.
1.4 Targets of miRNAs identified in this study
It is known that miRNAs mediate plant abiotic stress responses through regulating their target genes and thus
serving as key players in the gene regulation networks. The targets of miRNAs were predicted by the web tool
psRNATarget (Dai and Zhao, 2011) using the
Gossypium
(cotton) DFCI Gene Index (CGI) Release 11
(
) as the sequence library for the targets search. The predicted targets
of some of the drought-responsive miRNAs, identified in this study, were found to be involved in diverse cellular
processes including development, transcription, protein degradation, detoxification, nutrient status, and cross-
adaptation to various abiotic stresses (data not shown). Besides, miRNAs reported here have also shown
(elsewhere) to target several genes that are associated with abiotic stress resistance.
2 Discussion and Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of miRNAs and their targets in cotton genome presents a necessary milestone in
our understanding of gene regulation under water stress, which is an important abiotic stress that limits the cotton
lint production and fiber quality, worldwide. This is especially true in some cases where knowledge of the miRNA
Ghi-miR(contig-4796)
Ghi-miR(contig-13785)


