Basic HTML Version

Rice Genomics and Genetics 2012, Vol.3, No.1, 1
-
7
http://rgg.sophiapublisher.com
4
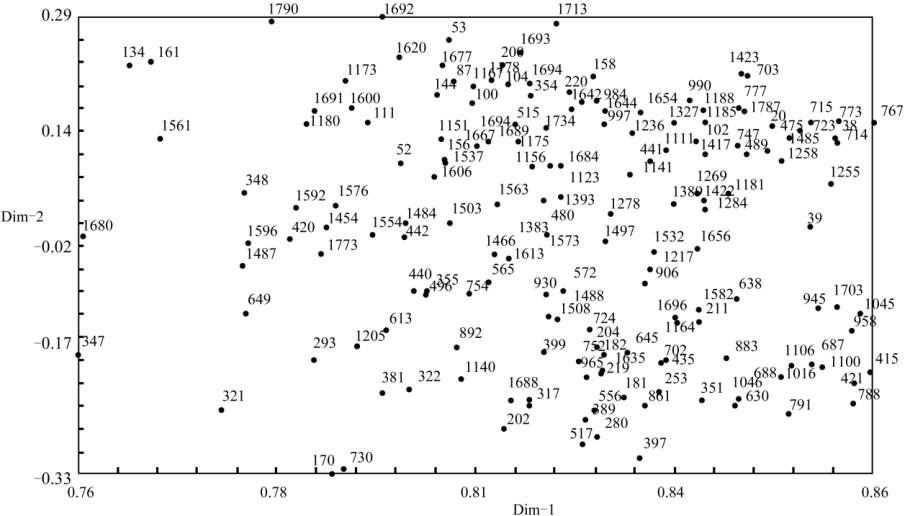
Figure 3 Scatter plots of the first and second principal coordinates of the USDA rice mini -core 171 accessions generated from the
principal coordinates analysis on polymorphisms by 19 OsSPL primers
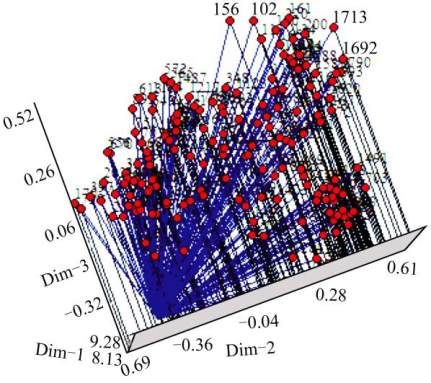
Figure 4 Three dimensional plots of the first and second principal
coordinates of the USDA rice mini-core 171 accessions generated
from the principal coordinates analysis on polymorphisms by
OsSPL
primers
plant or brown 1 000
-
grain weight between each
subgroup and the total sample, which indicated that the
traits of tillers per plant and the brown 1 000
-
grain
weight of each accession of the subgroups were random.
As shown in Table 2, the standard deviation of each
trait of each subgroup was essentially similar to the
standard deviation of each trait of the total sample except
that for the days to heading and spikelets per panicle of
subgroup
Ⅴ
, which indicated that the classification
was reliable. Thus, according to the Hardy-Weinberg
equilibrium, the OsSPL genes were associated with the
traits of spikelets per panicle, plant height and days to
heading.
2 Discussion
2.1 Polymorphism of the
OsSPL
gene family
As a plant-specific transcription factor family, the
SPL
gene family regulates many important biological
functions (Birkenbihl et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2008;
Wang et al., 2009; Dai et al., 2010; Miura et al., 2010;
Jiao et al., 2010). Rice is a model plant in genomics
research, and the full genome sequence has been
drafted. At present, rice functional genomics shifts to
focus on gene function research and gene diversity
analysis. The USDA Rice Core Collection consists of 1
794 accessions, which represent 18 412 rice germplasm
samples from 116 countries, essentially covering the
global rice-growing regions. 88% reliability that the
information in the USDA Rice Core Collection is

