Basic HTML Version



Medicinal Plant Research 2014, Vol.4, No.4, 30
-
34
http://mpr.sophiapublisher.com
31
1Results
1.1 DPPH radical scavenging activity
DPPH radical scavenging activity assay is one of the
most favourable methods for determination of
antioxidant capacity of fruit samples due to its
simplicity and reproducibility.
The DPPH scavenging activity of samples and
ascorbic acid, as a control, was calculated according to
their ability that cause reduction in initial absorbance
of DPPH solution. The percentages of DPPH
reduction against concentrations of samples and
ascorbic acid were provided by graphs in Graph Pad
Prism (R
2
=0.9681 and 0.9948, respectively). IC
50
values of ascorbic acid and
P. peruviana
were
calculated as 1.06±0.008 µg/ml and 430±3 µg/ml,
respectively (Table 1).
Table 1 IC
50
values of
P. peruviana
extract and ascorbic acid
for antioxidant capacity
Sample
IC
50
(µg/mL)
P. peruviana
430±3
Ascorbic acid
1.06±0.008
1.2. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxic effect of
P. Peruviana
extracts were
evaluated with MTT assay. According to the results,
extract has cytotoxic activity on Saos-2, HT-29 and
Hep3B cells. IC
50
values and viability % change for
these cell lines for 48 h are given in Figure 1 and
Figure 2. For 24 h, cell proliferation has been seen
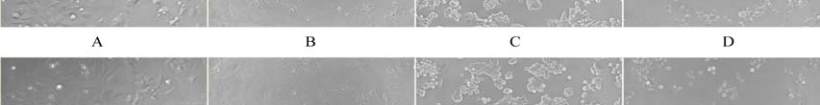
instead of growth inhibition. Cell death and
morphological changes of Saos2, HT-29 and Hep3B
cell lines via microphotography are also shown in
Figure 3. There is no growth inhibition observed on all
cell lines for 24 h and on LNCap, MCF-7 and Vero for
neither 24 h nor 48 h (results are not given for MCF-7
and LNCap cell lines).
Figure 1 IC
50
values for Saos-2, HT-29, Hep 3B and SH-SY5Y
cell lines for 48 h
Figure 2 Cell viability after 48 h treatment with different
concentrations of
P. peruviana
extracts
Figure 3 Morphological differences of control cultures and extract treated cultures

