Basic HTML Version


Rice Genomics and Genetics 2012, Vol.3, No.8, 50
-
54
http://rgg.sophiapublisher.com
52
139 heterozygotes: 86 normal, χ
2
=0.828) without
segregation distortion. It was further evidence that the
low glutelin trait was controlled by a dominant gene.
And the protein and molecular markers amplification
phenotype were consistent highly.
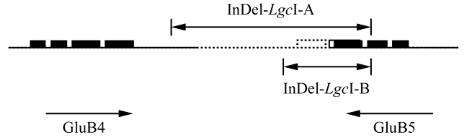
Figure 2 Locations of the primer sequences and the deleted
fragment in
Lgc1
Note: The black box: the exon in
GluB-4
and
GluB-5
; The
dotted line: a 3.5 kb deletion between
GluB-4
and
GluB-5
; The
Single and double arrowheads denote the direction of gene
transcription and the region of PCR primers designed,
respectively
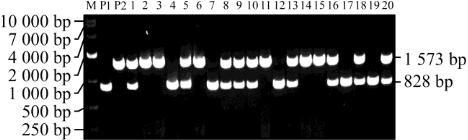
Figure 3 PCR products amplified from partial individual plants
of F
2
(W3660/Nanjing46) with two InDel markers
Note: M: DNA Marker; P1: W3660; P2: Nanjing46; 1~20:
Individual plants of F
2
1.3 Detection of two InDel markers in normal
glutelin content rice varieties
In order to further validate the detection accuracy of
two InDel markers for rice varieties from different
areas, we used 12 rice varieties in this study, including
the W3660 with gene
Lgc1
, by using PCR validation.
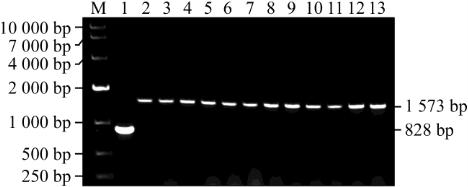
The results of electrophoresis of PCR showed that 12
normal rice varieties with 1 573 bp and W3660 with
828 bp were amplified (Figure 4). These results were
fully affirmed that the two InDel markers can be used
to distinguish whether containing
Lgc1
gene or not in
rice varieties.
2 Discussion
Due to renal failure in protein metabolism, patients
with diabetes or kidney disease cannot eat rice with
Figure 4 PCR products amplified from conventional rice with
two InDel markers
Note: M: DNA Marker; 1: W 3660; 2: Nanjing 44; 3: Kanto
194; 4: Nanjing 11; 5: Wuyunjing 7; 6: Nipponbare; 7: Ning
5055; 8: Wuyujing 3; 9: Ningjing 3; 10: Aichi 106; 11: Huajing
3; 12: Yandao 9; 13: Wuyujing 18
an absorbable-protein content of more than 4%.
Obviously, rice, as an important food crop, is not only
staple food but also a health diet for people. It was
first time that Japanese breeders developed low
glutelin functional rice variety LGC-1. Then it was
widely cultivated for test since 1994 and used in
clinical trials for kidney disease patients. Results
showed that the patient’s condition improved
significantly. For this reason, LGC-1 was considered
to be very effective in patients with nephropathy
(especially rice as the staple food) diet supplements
(Mochizuki and Hara, 2000).
Cultivation of functional rice varieties with low
glutelin is useful. On the one hand, it is a good
opportunity for the breeders to expand the breeding
direction. On the other hand, it also brings a
tremendous benefit and gospel to kidney patients. As
the demand for low glutelin rice is growing, breeding
of new low glutelin rice varieties to acclimate
different ecological areas has become a new hot spot.
In recent years, although some low glutelin materials
were reported (Iida et al., 1997), the
Lgc1
gene is
still very popular for breeders and consumers.
Consequently, how to identify
Lgc1
gene more
accurately, quickly and simply has become an urgent
problem for low glutelin breeding in rice. With the
development of biotechnology, molecular marker-assisted
selection has become an important supplementary
means for breeding. Its polymorphism directly reveals
the differences in genomic DNA. Currently, many
gene markers linked were reported, but they showed

