Basic HTML Version


Int. J. of Marine Science 2012, Vol.2, No.6, 43
-
50
http://ijms.sophiapublisher.com
49
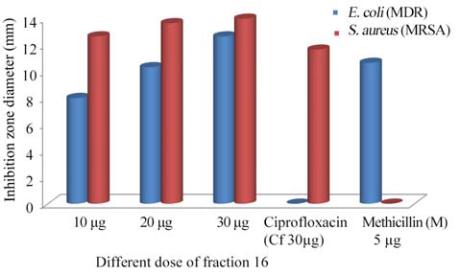
Figure 4 Antibacterial activity of purified compounds from
marine sponge
Aurora globostellata
3.7 Sponge extracts elution
Based on the antimicrobial assays, the extract that
registered the maximum antimicrobial activity was
selected for further study. EtoAc extract was very
effective in antimicrobial properties so the ethyl
acetate extract were chosen for further separation. The
crude EtOAc extract (13.2 g) was applied over a flash
chromatography column of silica gel 60 (150 g) and
eluted with a solvent gradient system of EtOAc and
MeOH, Fractions (50 mL) being collected as follow:
The various fractions were collected from followed
solvent system: 1) Hexane 100%; 2) Hexane 99%:
ethyl acetate 1%; 3) Hexane 98%: ethyl acetate 2%; 4)
Hexane 96%: ethyl acetate 4%. Up to 22
nd
fraction
were eluted. The fractions thus obtained were once
again evaporated and concentrated. They were again
assayed for antibacterial, antifungal activity and
spectral studies.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. A.J.A. Ranjit Singh, Principal, Sri Paramakalyani
College, Alwarkurichi, Tirunelveli, Tamilandu, India for providing the
laboratory facilities to carry out the microbiological work. We acknowledge
the
financial
support
received
from
PURSE
scheme,
Ref.No:MoES/11-MRDF/1/25/P/09-PC Ministry of Earth and Science,
Government of India, New Delhi.
References
Amade P., Charroin C., Baby C., and Vacelet J., 1987, Antimicrobial
activities of marine sponges from the Mediterranean Sea, Marine
Biology, 94: 271-275
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00392940
Attaway D.H., and Zaborsky O.R., eds., 1993, Marine Biotechnology Vol.I.
Pharmaceutical and bioactive natural products, Plenum Press, New
York, pp.1-44
Baker B.J., Scheuer P.J., and Shoorley J.N., 1988, Papuamine an antifungal
pentacyclic alkaloid from a marine sponges, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 110:
965-966
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja00211a046
Blunt J.W., Brent R.C., Murray H.G., Munaro P.T., and Michele R.P., 2010,
Marine Natural Product - A Review, Natural Product Reports, 27:
165-237
http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b906091j
PMid:20111802
Buchanan M.S., Edser K.G., Whitmore J., and Quinn R.J., 2001,
Cheilanthane sesterterpenes, protein kinase inhibitors, from a marine
sponge of the genus Ircinia, J. Nat. Prod., 64: 300-303
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np0004597
PMid:11277743
Burkholder P.R., Pfister R.M., and Leitz F.P., 1969, Production of a pyrrole
antibiotic by a marine bacterium, Appl. Microbiol., 14: 649-653
Caiferi F., Fattorusso E., and Scafati M.O.F., 1998, Novel bromopyrrole
alkaloids from the sponge
Agelas dispar
,
Journal of Natural Products,
61:122-125
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np970323h
PMid:9461661
Charan R.D., Garson M.J., Brereton I.M., Willis A.C., and Hooper J.N.A.,
1996, Haliclonacylamins A and B: cytotoxic alkaloids from the tropical
marine sponges
Haliclona
sp., Tetrahedron, 52: 9111-9120
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0040-4020(96)00436-X
Clark R.J., Garson M.J., and Hooper J.N.A., 2001, Antifungal alkyl amino
alcohols from the tropical marine sponge
Haliclona sp.
, J. Nat. Prod.,
64: 1568–1571
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np010246x
PMid:11754615
Crews P., and Harrison B., 2000, New triterpene ketides (Merotriterpenes),
halicotriol A and B from an Indo-Pacific Haliclona sponge, Tetrahedron,
56: 9039-9046
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(00)00758-4
Fahy E., Molinski T., Harper M.K., Sullivan B.W., Faulkner D.J., Parkanyi
L., and Clardy J., 1988, Haliclonadiamine: an antimicrobial alkaloid
from the sponge
Haliclona
sp., Tetrahedron Lett., 29: 3427-3428
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0040-4039(88)85180-3
Ford J., and Capon R.J., 2000, Discorhabdin R: a new antibacterial
pyrraloiminoquinone from two latrunculid marine sponges,
Latrunculia
sp. and
Negombasto
sp., Jour. of Nat. Prod., 63:1527-1528
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np000220q
PMid:11087598
Harborne J.B., ed., 1998, Phytochemical Methods: A guide to modern
techniques of plant analysis, 2
nd
ed. London, Chapman and Hall, pp.
54-84.
Ivanova E.P., Mikhailov V.V., Kuznetsova T.A., Kalinoskaya G.B., Elyakov
E.A., and Garagulya A.D., 1994, Heterotrophic bacteria associated with
the sponge
Dendrilla
sp. and their physiological activity, Russian
Jou
r
nal Marine Biology, 19: 139-144
Ivanova E.P., Mikhailov V.V., Kuznetsova T.A., Kalinovskaya N.I., Elyakov
G.B., Kiprianova E.A., and Garagulya A.D., 1993, Heterotrophic
bacteria associated with the sponge
Dendrilla
sp. and their physiological
activity, Morya Marine Biology, 3: 3-10
Kokubo S., Yogi K., Udin M.J., Inuzuka T., Suenaga K., Veda K., and
Uemura D., 2001, Kohamaic acids A and B, novel cytotoxic
sesterterpenic acids, from the marine sponge
Ircinia
sp., Chem. Lett.,
176-177
http://dx.doi.org/10.1246/cl.2001.176
Leone P., De A., Carrol A.R., Towerzey L., King G., McArdle B.M., Kern G.,
Fisher S., Hooper J.N.A., and Quinnm R.J., 2008, Exiguaquinol: A
Novel Pentacyclic Hydroquinone from
Neopetrosia exigua
that Inhibits
Helicobacter pylori
MurI, Org. Lett., 10: 2585
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ol800898z
PMid:18489104
Ovenden S.P.B., and Capon R.J., 1999, Newpapuin A and Sigmosceptrillins
D and E. New Norterpene cyclic peroxides from a southern Australian
marine sponge,
Sigmodceptrella
sp., Journal of Natural Products, 62:
214-218
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np980223r
PMid:10075744
Parameswarn P.S., Kamat S.Y., Chandramohan D., Nair S., and Das B.,
1992, Antibacterial compounds from the sponge Haliclona species, In:

