International Journal of Clinical Case Report 2016, Vol.6, No.19, 1-3
2
Neurofibromas lesions
Figure 2 Cutaneous lesions: neurofibromas
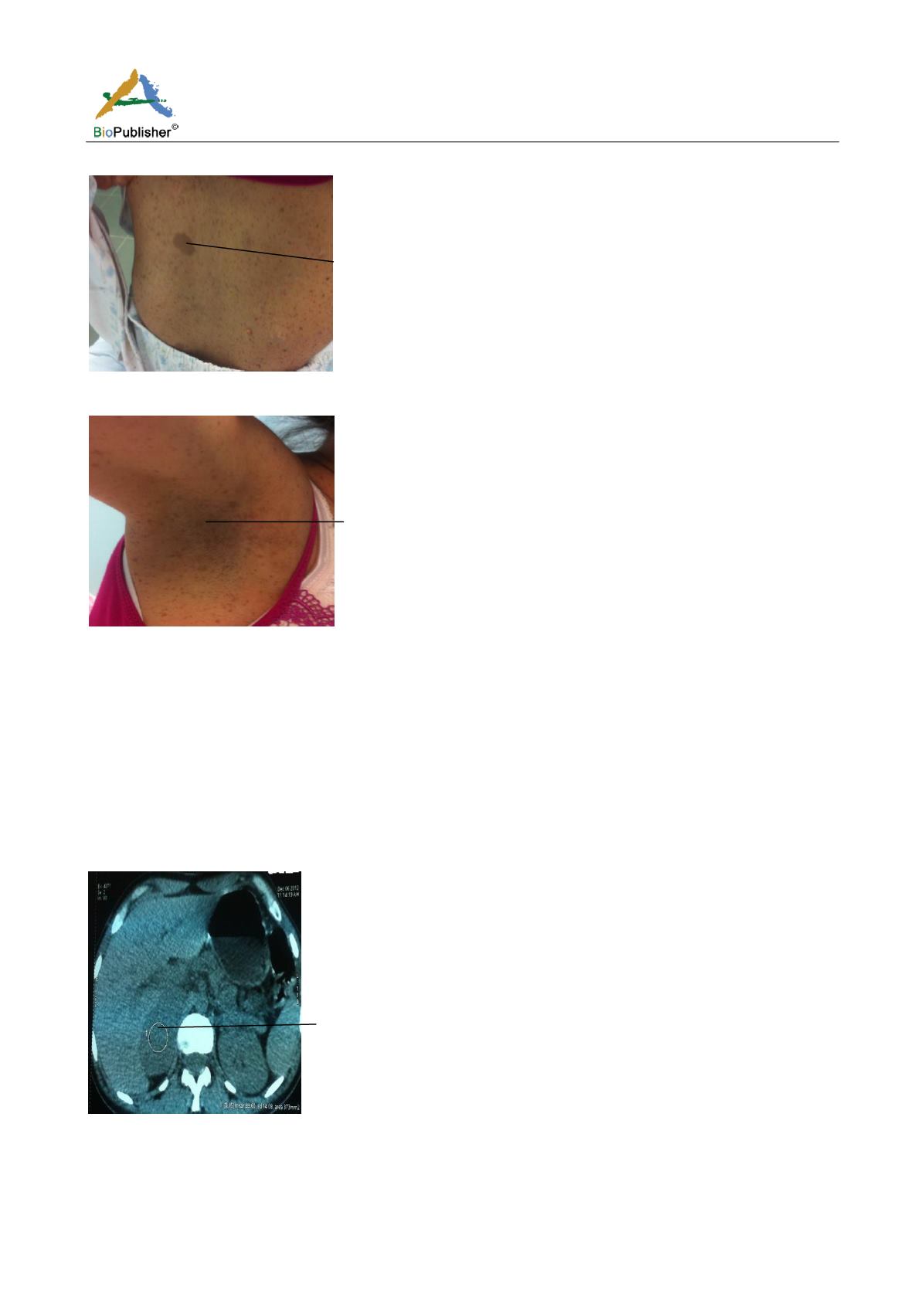
Lentiginous
Figure 3 Cutaneous lesions: lentiginous
Laboratory tests showed: fasting glucose: 0.93 g/L, sodium: 139.1 mmol/L, potassium: 3.80mmol/L, cortisol after
1 mg overnight dexamethasone suppression test: 1.27 μg/dl (negative), elevated urinary derivatives methoxylated:
normetanephrine=16.98 mmol/24 hours (>4N) and metanephrine=22.26 mmol/24 hours (>4N), TSH=1.83 μUI/ml,
PTH=53.2 pg/ml, calcitonin=11 pg/ml. A radiological assessment with an abdominopelvic computed tomography
(CT) scan showed a right adrenal tissue mass measuring 47×48×38 mm (enhanced CT also showed 83% at rate of
absolute percentage wash out, and 64% at rate of relative percentage wash out, early density 167 UH, delayed
density 60 UH, spontaneous density 39 UH) (Figure 4). The MIBG scintigraphy confirmed the neuroendocrine
nature of the mass and the absence of other sites. A right adrenalectomy with subcostal incision was performed
and the histological examination revealed a benign pheochromocytoma.
Right adrenal mass
Figure 4 Abdominopelvic computed tomography
3 Discussion
Our patient had a pheochromocytoma associated with von Recklinghausen disease which was revealed by an
adrenal incidentaloma. Pheochromocytomas are neuroendocrine tumors developed at the expense of cells derived


