Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics 2018, Vol.6, No.5, 33-39
36
is very low in mammals. In this review, the primary focus is on methylation analysis on the CpG context in
mammalian whole genomes.
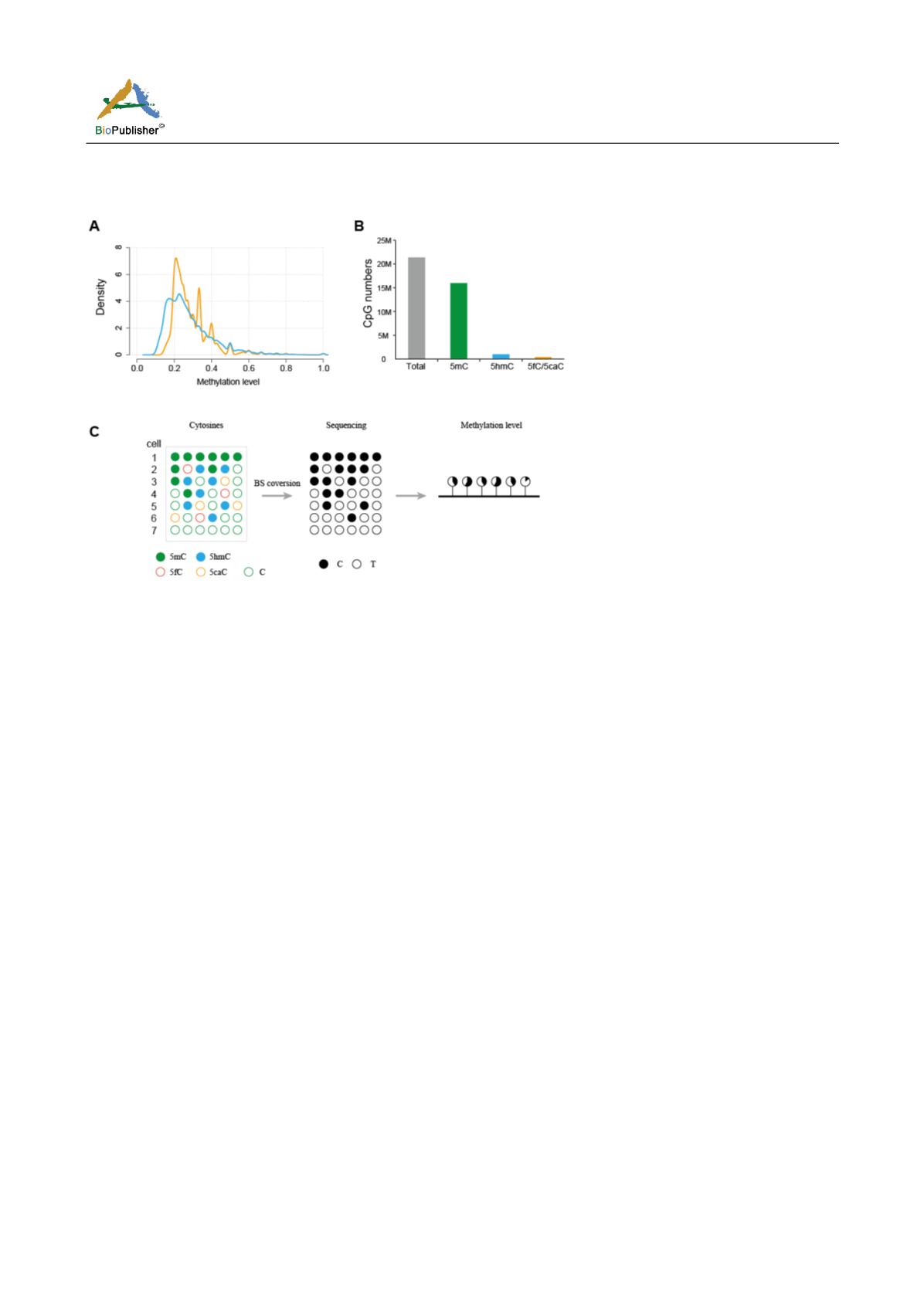
Figure 2 The complexity in the methylation level metric
3 From Methylation Site to Region: Methylation Pattern Region
Although DNA methylation in vertebrates occurs mainly at the CpG site, dinucleotides are too short to be a
biologically interesting region. At the same time, the number of CpG sites in the mammalian genome is too large
(the human genome contains about 28 million CG sites and the mouse genome contains about 2,100 CG sites), so
it is not appropriate to use a single CpG site as the basic unit of methylation analysist. The methylation status at
the CpG site is not randomly distributed in the genome, and adjacent CpG sites in linear positions usually have
similar methylation status. Therefore, researchers usually combine adjacent CpG sites into one methylation
pattern area.
On the genome, the most prominent DNA methylation feature is the CpG island, a region with high GC content
and high CpG density relative to the background genome. The vast majority of CpG islands are located in the
promoter region of the gene and are usually unmethylated. Hypermethylation of the CpG island of the promoter
inhibits the expression of adjacent genes. However, most tissue-specific DNA methylation does not occur on CpG
islands, but on the CpG island shore (Irizarry et al., 2009) adjacented to the CpG island.
Sequence-based CpG islands and CpG islands do not accurately and comprehensively reflect complex
methylation patterns across the genome. Since the birth of whole-genome bisulfite sequencing technology,
researchers have discovered and identified a series of methylated regions with distinct genomic and epigenetic
features based on genome-wide single-base methylation profiles (Table 1). Early studies divided the genome into
windows to identify methylation pattern regions, but such methods did not accurately identify the boundaries of
the region, and were extremely low depending on the size of the window. Such methods should be avoided as
much as possible.
For the identification of methylation pattern regions in the methylation group, the three-state hidden Markov
model is a suitable method. Using the methylation state (low, medium, high) of the CpG site as the implicit state
of the model and the detected methylation level as the observed state to infer the true state of the CpG site. The
three methylation states correspond to ultra-low methylation, hypermethylation, and intermediate methylation,
respectively, and intermediate methylation is caused by various factors such as cell heterogeneity, demethylation
modification, and allelic differences. It is worth noting that the β distribution is more suitable than the Gaussian
distribution when estimating the emission probability of the hidden Markov model.


