基本HTML版本

Bioscience Methods 2014, Vol.6, No.1, 1-13
http://bm.biopublisher.ca
5
clustered into two main subclusters and further into four
main clades. Two new osmotins,
StOSM
-297 and
StOSM
-306, were assigned to the same independent
branch of the phylogenetic tree. The seven osmotins on
chromosome 08 clustered into four subclades.
According to the phylogenetic relationship, one of the
two main subclusters, composed of
StOSM-
251
, -
306
-297 (clade 1), was relatively independent of the other.
After separating from
StOSM
-182 (clade 5), seven of
the eight
StOSM
genes in the other subcluster evolved
into three clades: clade 2, containing
StOSM-
5A
, -
3B
and
-
3F; clade 3,
StOSM-
1G
and
-
8E; and clade 4,
StOSM-
3C
and
-
2D.
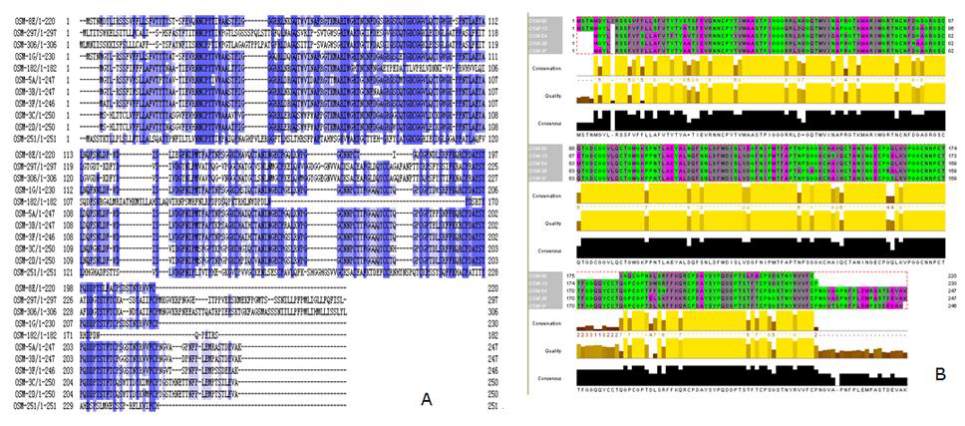
The alignment of the amino acid sequences of the
eleven osmotins revealed four conserved regions: the
NNCPYT, RIW and TGDCGG motifs, located in the
N-terminal region, and the AYSY motif, located in the
C-terminal region (Figure 6A). A Jalview of the
alignment of
StOSM-
5A
, -
3B,
-
3F,
-
1G
and
-
8E based
on their phylogenetic relationship showed that a
tandem duplication event occurred in these five genes
(Figure 6B).
Figure 6 Amino acid sequence alignments of the putative potato osmotins
Interestingly, the putative amino acid sequences of all
osmotins range from 182 aa for
StOSM
-182 to 306 aa
for
StOSM
-306.
StOSM
-182 and -306 show a greater
divergence towards the C-terminal region (Figure 6A).
The sequences of four motifs were searched in the
UniProt Knowledgebase (UniProtKB) by blastx.
However, the result of zero hits from the search
showed that the function of these conserved regions is
unknown yet.
StOSM
-182, with 182 amino acid residuals, is the
shortest osmotin protein and does not contain the
AYSY motif in its C-terminus (Figure 6A). In
addition to the common four motifs,
StOSM
-182 and
-306 share two additional motifs, FCPMKGVKRPN
and ILLPFPMLI. Neither an expression sequence tag
nor gDNA/cDNA clone of these two genes was
registered in the database. Meanwhile, there was no
hit for annotated or predicted function of these motifs
when these motif sequences BLAST was done in all
available protein database. This means that function of
these motifs is unknown yet.
1.1.4 Introns and UTRs of
StOSMs
The structure of all the
StOSM
genes was highly
conserved. Only three
StOSM
genes, including
StOSM
-182 and -306, have two introns (Figure 7).
Within the second intron of
StOSM
-182 is the first
exon of a putative gene, which encodes
ethylene-responsive proteinase inhibitor 1 (EPI). The
second and third
EPI
exons are located in the 3’ end of
the third exon of
StOSM
-182. In addition, there is one
more copy of
EPI
locating within the promoter region
of
StOSM
-3B (Figure 4).
The 3’ ends of the first introns of
StOSM
-182 and -306
share the same 7 nt. The 3’ and 5’ ends of the second

