基本HTML版本

Bioscience Methods 2014, Vol.6, No.1, 1-13
http://bm.biopublisher.ca
2
With respect to the severity of the water shortage,
each plant species is more or less tolerant to a certain
drought level. A reliable and comparable level of plant
tolerance to drought is known as the drought-lethal
critical point (DLP). The availability of water in soil at
a level lower than the DLP leads to plant death due to
cell dehydration.
In this study, with a full-length
StOSM
cDNA isolated
initially from a drought-treated subtractive library,
eleven
StOSM
genes were identified using BLAST
analysis of the Potato Genome Sequence database
(PGSD). Leaf mRNA accumulation of
StOSMs
were
assayed using RT-PCR and qRT-PCR and compared
with FPKM (Fragments Per Kilobase of exon model
per Million mapped reads) value of
StOSM
genes in
the PGSD. The result indicated that expression of
eight
StOSMs
in leafs at DLP was upregulated, three
down-regulated. The result revealed that osmotins, as
drought responsive molecules involved in withstanding
water deficits in potato.
1. Results
1.1 Composition and structure of
StOSM
family
1.1.1 Cloning and osmotic stress response function of
potato
StOSM
-3B
Through screening a subtractive cDNA library
constructed from the young leaves of potato genotype
ZHB at 20% ±2% water content in media (WCM)
(unpublished work), an expressed sequence tag (EST)
was identified. Sequence of the EST shared 99% identity
with
StOSM
-3B belonging to AY737310 from
Solanum
phureja
in the Genbank database (Castillo et al. 2005).
Using
StOSM
-3B ORF specific primers (O-F and
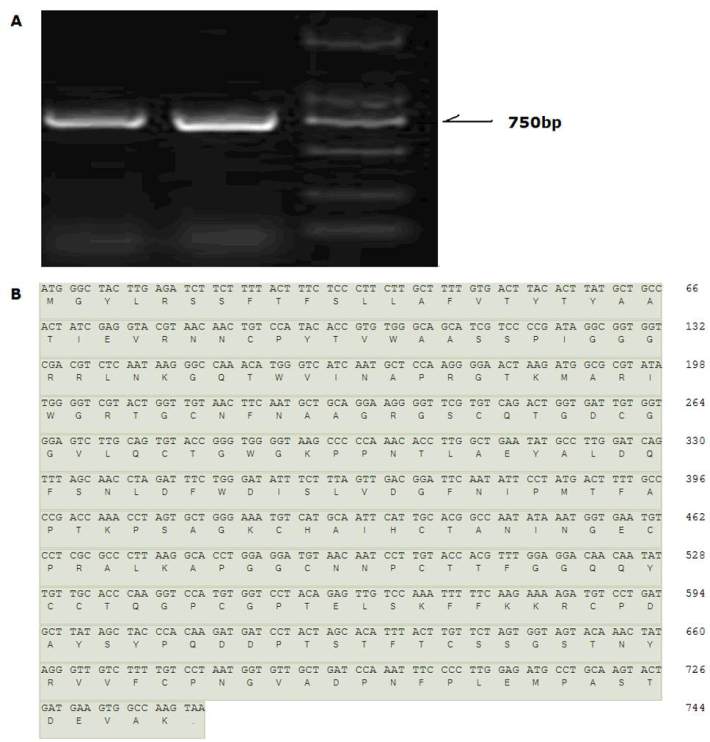
O-R), a cDNA ORF with a length of 744 bp was
cloned (Figure 1), which encoded osmotin with
248 amino acids. A sequence alignment showed 97%
Figure 1 Cloning of the
StOSM
-3B ORF from the leaves of potato ZHB under 20% WCM. A: Product of PCR with
StOSM
-3B
specific primer; B: cDNA sequence and putative amino acid sequence of
StOSM
-3B ORF isolated in this study

