Basic HTML Version

Molecular Microbiology Research (Online) 2013, Vol.3 No.2 9-20
ISSN 1027-5595
http://mmr.sophiapublisher.com
10
fields. Some of the utility of amino acid are mentioned
here as genetic, forensic and biomedical. It also serves
as an effective test in detecting the carcinogenicity of
compounds (Melcher et al., 1997).
Bacterial test system fall into 3 main classes namely
those that detect backward mutation, those that detect
forward mutation and those that rely on DNA repair
deficiency. By far, the most widely exploited method
is the indication of backward or reverse mutation in
Salmonella typhimurium
or less frequently
E. coli
(WHO, 1995).
R-factor plasmid (some strain) and multicopy plasmid
(some strain) which contains error prone DNA repair
system. The type strains also require histidine for
growth due to mutation in the gene which control
production of histidine (Ames et al., 1975).
2 Results
Man can not live without food. Foods are unavoidable
one. Thus quality of the food is of major concern to
public health authorities. Despite foods nutritious
aspect, it plays a major role in affecting the health of
people. This might be due to the adulteration and the
nature of these adulterants. This study was carried out
to assure the quality of oils and food substances. In
this context, 55 samples (oils and foods) were
analysed for their carcinogenic property using
auxotrophic mutant and treated strains of
Salmonella
typhimurium
.
Mutated strains were created by the physical and
chemical mutagenic agent UV and NTG respectively.
These results after the mutagenic treatment of wild are
recorded in the Table 1 along with the calculated value
of induced mutants.
The treated and auxotrophic strains of
S.
typhimurium
were used to test the carcinogenic
chemicals in samples by reverse mutation assay.
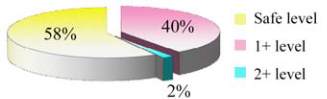
The results are recorded in Tables 2~5. It indicated
the degree of carcinogenicity. Among the 55
samples, only one sample was found to be 2+ level
while 22 sample were found to be 1+. The
remaining 32 samples were found at the Safe level
(raw oils, halwa and kesseri) (Figure 1). From the
above results, it was clear that 41.8% of samples
were positive for carcinogenicity test.
Figure 1 Degree of carcinogenicity among the 50 food samples
The positive control (Induced mutants plus
spontaneous mutants) and negative control
(Spontaneous mutants) were tested by Spot test
method (Ames, 1975). From these, the positive results
were calculated. The negative and positive control
which clearly showed that the pin pointed colonies
and large colonies are represented in Plate 2 and Plate
3. Plate 3 clearly indicates the presence of
revertants as large colonies. Large colonies were
only calculated from the results since auxotrophic
colonies turn into prototrophic.
Table 1 Calculated value of UV and NTG treatments in wild type
Salmonella typhimurium
MTCC 98
S. No.
Treated
by
Frequency
of TSM (cfu/mL)
% of TSM
Frequency
of TIM (cfu/mL)
%
of
TIM
In mutants alone (in
%)
1
UV
8.54
85.4
6.66
66.6
16.8
2
NTG
4.035 × 10
-3
40.35
2 × 10
-3
20
20.35
Table 2 Chemical carcinogenicity test by UV treated strain Ames spot test method using
Salmonella typhimurium
his MTCC 98
S. No.
Sample
No. of
colonies
Induced
mutants
Degree of
mutagenicity ( - ) and (1+)
1
Negative control (Sterile water)
220
-
-
2
Positive (Sodium acid)
280
60
1+

