Basic HTML Version



Molecular Microbiology Research (Online) 2013, Vol.3 No.2 9-20
ISSN 1027-5595
http://mmr.sophiapublisher.com
15
Table 7 Amino acid markers among
Salmonella typhimurium
strain
Treated strain (MTCC 98)
S. No.
Amino acid used
UV
NTG
MTCC 1251 Auxotrophic
mutant Strain
Wild type
1
Phenyl Alanine
+
+
-
+
2
Threonine
+
+
-
+
3
Glutamic Acid
+
+
-
+
4
Tryptophan
+
+
-
+
5
Lysine
+
+
-
+
6
Serine
+
+
-
+
7
Histidine
+
+
+
+
8
Methimine
+
+
-
+
9
Valine
+
+
-
+
10
Leucine
+
+
-
+
11
Isoleucine
+
+
-
+
12
Argine
+
+
+
+
13
Without Amino acid
-
-
-
+
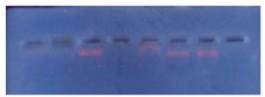
The plasmids from wild, treated and reverse mutated
strains isolated were electrophoresed in agarose gel.
After electrophoresed, gel was taken and exposed to
transilluminator under UV. Four bands were seen
where the plasmids were found in the gel (Figure 2
and Figure 3).
Figure 2 Four bands plasmids in agarose gel electrophoresis
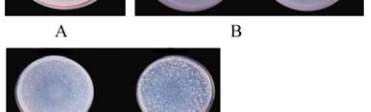
Figure 3 A : a representation of a LB agar plate; B: plates
presenting a negative control and a positive control of treated
strain of Saimonella typhimuriym by spot technique; C: plates
showing variouslevels of carcinogenicity using
Salmonella
typhimuriym
auxotrophic mutants by reverse mutations
technique
3 Materials and Methods
3.1 Sampling area
Food samples were collected from several shops in
and around Alwarkurichi, Tirunelveli District.
3.2 Sample selection
Samples tested for the presence of carcinogenic
chemicals included. Oils varied types of raw oil
(coconut oil, palm oil, sun flower oil, gingely oil and
groundnut oil); Fried oil; Reheated oil. Coloured
Foods: Jangiri; Halwa; Kesseri; Milk Sweets. Sweets
like halwa, jangiri, milk sweets and kasseri were also
collected under sterile conditions from different shops
and brought within 4~6 hours to the lab.
3.3 Treatment of strains
The
Salmonella typhimurium
MTCC 98 strain was
mutated by UV and NTG as under mentioned.
3.4 UV mutant production
The overnight culture of
S. typhimurium
was
centrifuged at 10 000 rpm for 10 minutes. The
supernatant was discarded and the pellet was
re-suspended in 1 mL sterile saline. The bacterial
suspension was decimally diluted using sterile 9 mL
saline blanks using sterile 9 mL saline banks upto 10
-8
dilution. From the dilutions 10
-2
, 10
-3
and 10
-4
, 100 μL
was spread plated on LB agar for enumerating total
viable counts. Similarly, plates were prepared for
selected dilutions to quantify the spontaneous mutants
using streptomycin incorporated LB agar plates
(dilutions from 10
-2
, 10
-3
and 10
-4
). Four sets of LB str

