Basic HTML Version



International Journal of Marine Science 2014, Vol.4, No.51, 1-3
http://ijms.biopublisher.ca
1
A Letter Open Access
Sprostoniella teria sp. Nov. (Monogenea: Capsalidae Baird, 1853: Trochopodinae)
parasite of
Platax teira
, from Iraqi marine water, Arab Gulf
Majid Abdul Aziz Bannai , Essa T. Muhammad
Aquaculture and marine fisheries, marine science center, University of Basra, Iraq
Corresponding author email
International Journal of Marine Science, 2014, Vol.4, No.51 doi: 10.5376/ijms.2014.04.0051
Received: 06 Aug., 2014
Accepted: 22 Aug., 2014
Published: 27 Aug., 2014
Copyright
©
2014 Bannai and Muhammad, This is an open access article published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits
unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Preferred citation for this article:
Bannai and Muhammad, 2014, Sprostoniella teria sp. Nov. (Monogenea: Capsalidae Baird, 1853: Trochopodinae) parasite of
Platax teira
, from Iraqi marine
water, Arab Gulf., International Journal of Marine Science, Vol.4, No.51 1
-
3 (doi: 10.5376/ijms.2014.04.0051)
Abstract
One parasite was detected as
Sprostoniella
teria
from gill filaments of
Platax teira
were collected from Arabian Gulf .
Results give an indication that the parasites are consider as new species in Iraqi marine and
Platax teira
fishes as anew host in worlds
and new geographical distribution.
Keywords
Monogenea,
Sprostoniella
teria,
Capsalidae Trochopodinae
Platax teira
, Arabian Gulf, Iraq.
Introduction
The Monogenea is a class of Platyhelminthes parasitic
mostly on external surfaces and gills of freshwater and
marine fishes. The Capsalidae are monogeneans
parasitizing ‘skin’, fins and gills of marine fishes,
approximately 200 Capsalidae species are placed in
nine subfamilies and 44–46 genera, some of which are
well known (
Benedenia
,
Capsala
,
Entobdella
,
Neobenedenia
).
Presently, there are about 200 described capsalid
species in nine subfamilies and 44–46 genera. The
host range comprises elasmobranchs (sharks and
batoids Whittington and Chisholm 2003) and teleosts,
including primitive sturgeons (Yamaguti 1963,
Whittington et al. 2004). Because of their direct life
cycle, some monogeneans can affect fish in captivity
(Chisholm et al. 2004) and there are increasing reports
that some capsalids adversely affect fish in
aquaculture and are even responsible for epizootic
events (Whittington et al. 2004).
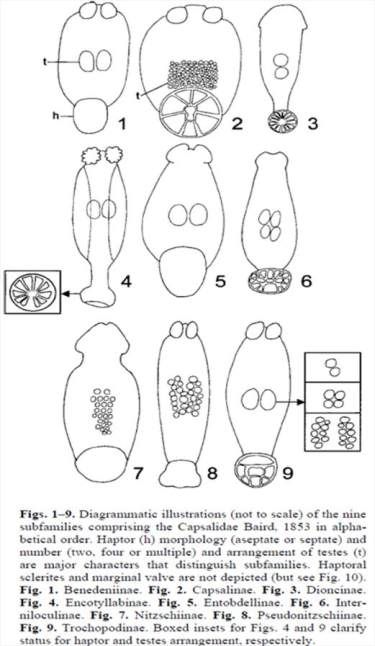
The Capsalidae Baird, 1853 (Monogenea,
Monopisthocotylea) constitutes a large taxon of seven
subfamilies, including the Encotyllabinae Monticelli,
1892, Capsalinae Baird, 1853, Benedeniinae Johnston,
1931, Nitzschiinae Johnston, 1931, Trochopodinae
Price, 1936, Entobdellinae Bychowsky, 1957 and
Interniloculinae Suriano & Beverley-Burton, 1979,
see Diagram 1 Egorova
,
1999
;
Pérez-Ponce de León &
Mendoza-Garfias, 2000.
Diagram 1 Diagrammatic of the nine subfamilies Capsalidae
According to Kritsky & Fennessy (1999) the family of
Capsalidae includes more than 40 genera of about 200
species and Capsalids parasites a wide host spectrum
of marine fishes, including elasmobranchs of the

