Basic HTML Version


International Journal of Marine Science 2013, Vol.3, No.4, 23-32
http://ijms.sophiapublisher.com
27
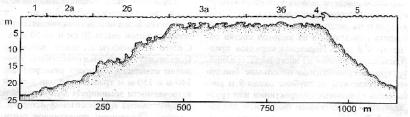
Figure 4 Scheme of the cross-section profile of Re Island reef
Note: 1: fore reef platform; 2a: the base of inner reef slope; 2b: the zone of buttress system; 3a and 3b: inner and outer reef flat; 4: reef
crest; 5: outer reef slope
degree of similarity, 78.9% of the species were in
common. The slightly lesser similarity of the reef
slope communities explained by the greater richness
of macrophytes at the reef of Re Island.
The outer reef slope. This characterized by the
presence of two morphologically differing parts, the
lower and upper (Figure 5, nomenclature by Picard,
1967; Battistini et al., 1975). In the lower part (of the
reef slope platform, at depths from 30 to 10 m) there
were numerous alcyonarian and ahermatypic corals
Balanophyllia
,
Dendrophyllia
, and
Tubastrea
and
hermatypic scleractinian were presented by stony and
encrusting forms,
Pachyseris
,
Leptoseris
,
Pectinia
,
Echinophyllia
,
Euphyllia
, and
Mycedium
. The
percentage of substrate covering by corals in that part
of slope was rather low, 0.1%~5%. The upper part of
the reef slope (buttress system, at a depth from 10 to
3 m) characterized by the presence of a system of
channels, niches and spurs. Coral species diversity and
substrate covering by corals (up to 40%) was higher
there. Patches of monospecies settlements of the
alcyonarian
Sinularia
or
Lobophytum
, of the
scleractinian
Acropora
and
Porites
, and of
Millepora
and
Heliopora
occurred. In the lower areas of the
upper part of the reef slope massive and encrusting
forms of colonies of
Goniopora
,
Goniastrea
,
Favia
,
Favites
,
Platygyra
,
Echinophyllia
,
Turbinaria
, and
Montipora
prevailed. They replaced higher up by
branching forms of colonies, primarily
Acropora
, and
species that are able to inhabit an environment of
intense hydrodynamics, viz.,
Acropora digitifera
,
A.
humilis
,
Pocillopora verrucosa
,
Goniastrea retiformis
,
Millepora platyphylla
, and
Heliopora coerulea
often
occurred.
Figure 5 The outer reef slope at Re island (depth 4 m)
Reef flat. Normally this was a vast zone with a
continuous substrate cover of corals interrupted by
sandy channels. This zone characterized by the
development of dominant species of
Acropora
and
Montipora
and of branching forms of
Porites
(
A.
humilis
,
A. monticulosa
,
M. aequituberculata
,
M.
porites
,
P. cylindrica
, etc.). The significant role in the
formation of the reef flat community belonged to the
alga
Chnoospora, Turbinaria
,
Asparagopsis
,
Hyphnea
,
Amphizoa
,
and
Peissonelia
.
The projective cover of
substrate by corals was 75%~100% as a rule.
The inner reef slope. Similarly to the outer slope it
may be divided in two morphologically differing parts.

