International Journal of Marine Science, 2017, Vol.7, No.13, 114-124
115
of the Red Sea region have been determined in some previous studies (e.g., Hamed and El-Moselhy, 2000;
Madkour and Dar, 2007; Mansour et al., 2013; El-Metwally, 2015; Dar et al., 2016). But the ecological risk of
population expansion and anthropogenic activities of the coastal cities have not been evaluated.
The main objectives of this study are: 1) to provide preliminary data on the environmental conditions and to
evaluate the risks of coastal cities expansion. 2) to perform a sediments quality assessment using
geo-accumulation index (Igeo), enrichment factor (EF) and metal pollution index (PMI). 3) to identify major
factors and characterize contamination in the coastal sediments using principal component analysis (PCA). In the
study, we will determine heavy metal concentrations in densely populated, sparsely populated and undisturbed
natural areas of Ras-Gharib, Hurghada, Safaga and Quseir Cities.
1 Materials and Methods
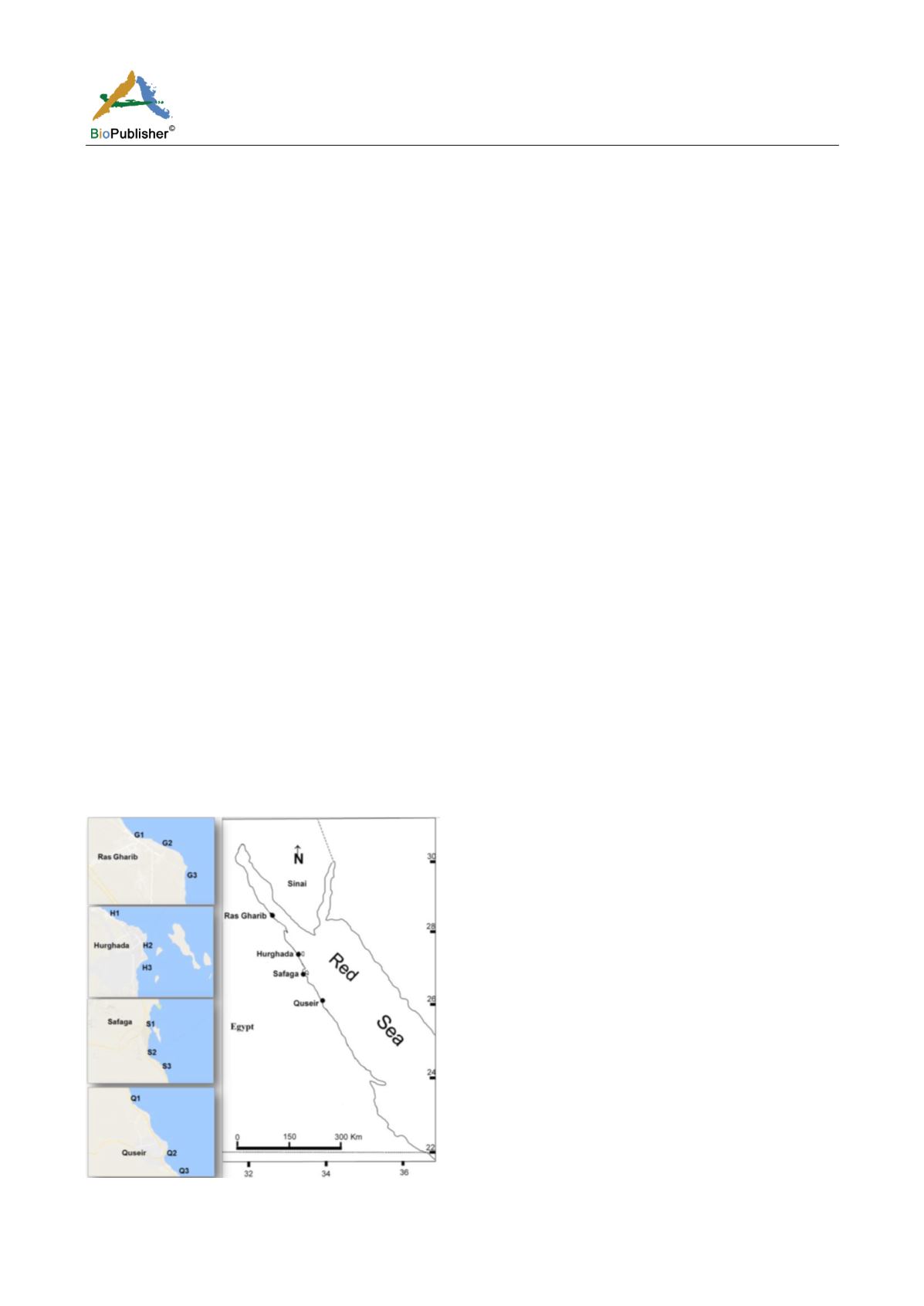
1.1 Area of study and sampling locations
A total of 12 sampling locations were selected along the Egyptian coastal area of the northern Red Sea “three
locations in each city of Ras Gharib, Hurghada, Safaga and Quseir” (Figure 1). Ras Gharib is a small city on the
Gulf of Suez. Its coastal area is affected by petroleum production and poorly treated sewage effluents. The 1
st
studied location (G1) is affected by the direct discharge of sewage, the 2
nd
location (G2) corresponded to a tidal
flat in the center of the city. The 3
rd
location (G3) situated in front of an oil company and affected by limited
public activities. Hurghada is the second largest city on the Egyptian Red Sea coast after Suez. The coastal area of
Hurghada is under the stress from the large population, tourism industry including hotels, marinas, shipyards, and
sedimentation from landfilling locations. The location (H1) is surrounded by a small population area and
influenced by the sedimentation from landfilling operations in the north of the city. (H2) is located in the center of
the tourist area; the site is between the shipyard area, marina and fishing boats, in addition, it was previously
received domestic wastewater from the center of the city. The location (H3) is restricted to touristic activity
including several ships and hotels. The anthropogenic activities in Safaga City are related to transportation and
shipping activities in addition to tourism. The location (S1) is covering the main marina of touristic boats and
small ships, (S2) adjacent to site used for shipping of phosphate, (S3) is undisturbed mangrove swamp area.
Quseir is an old city, previously was relying on fishing and shipping of ores especially phosphate ore, and recently
limited tourism industry is introduced. The studied location (Q1) is affected by a small touristic village. The
location (Q2) is at the old port that was previously used for shipping of phosphate. (Q3) is a reference undisturbed
site at the southern part of the city.
Figure 1 Sampling locations at different cities, Red Sea, Egypt


