International Journal of Horticulture, 2018, Vol.8, No.1, 1-7
5
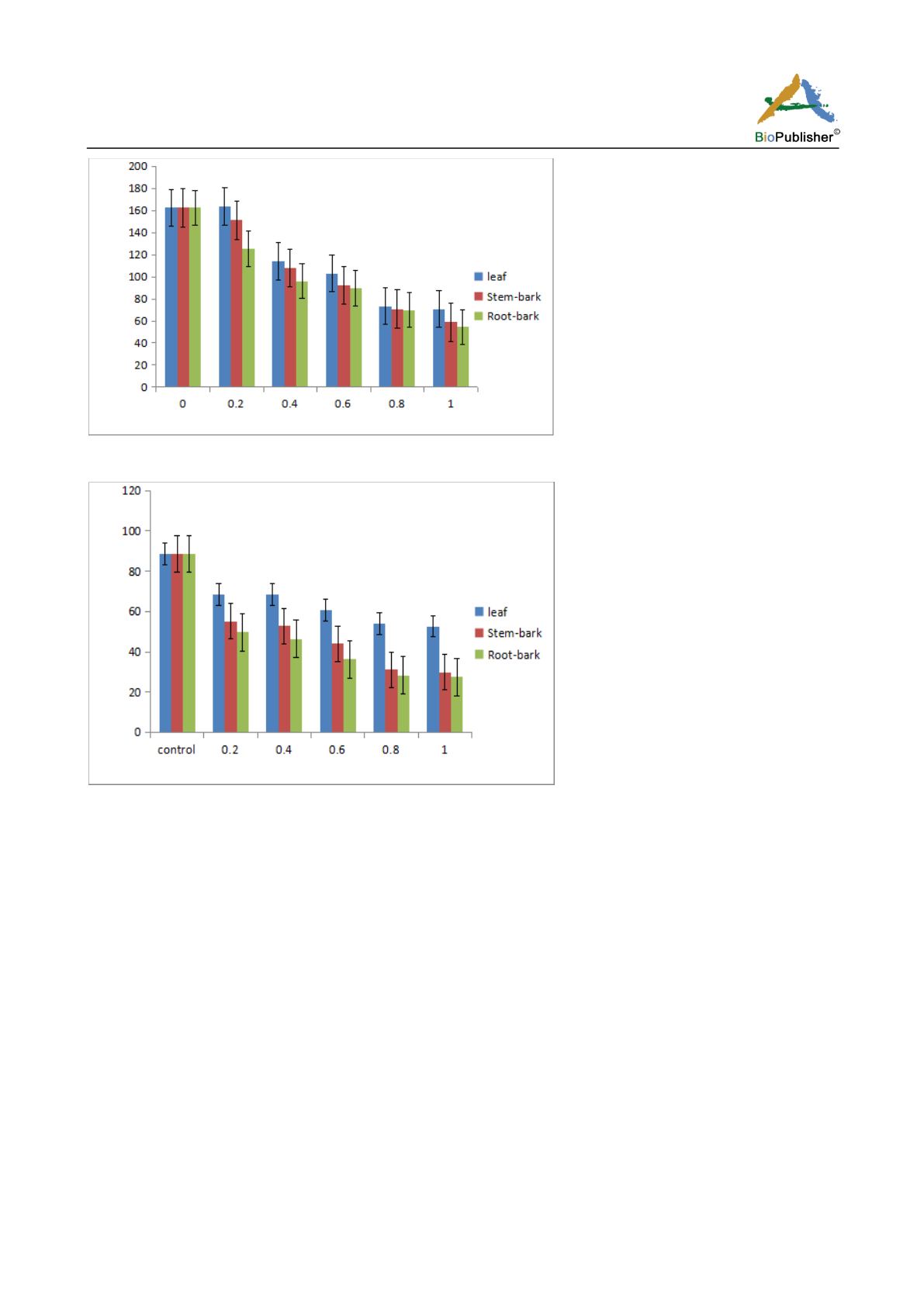
Figure 1 Oviposition of
C. maculatus
on cowpea seeds exposed to different dosages of different parts of
S.
longepedunculata
Figure 2 Percentage adult emergence of
C. maculatus
on cowpea seeds exposed to different dosages of different parts of
S.
logepedunculata
3 Discussion
The use of plant powders in the control of stored products insects is an ancient practice (Ileke and Olotuah, 2012;
Ojo and Ogunleye, 2013). In this study, the insecticidal activities of the leaf, stem bark and root bark of
S.
longepedunculata
as contact insecticides against
C. macualtus
infesting cowpea seeds were evaluated. The results
obtained from the experiment showed that the powder of
S. longepedunculata
particularly the root bark was very
potent against
C. maculatus
causing 71.25% mortality at the rate of 1.0 g / 20 g within 96 h of exposure. Plant
powders have been used to suppress the population of storage pests (Ogunleye
et al
., 2004; Ojo and Ogunleye,
2013). In this study, the observed high mortality recorded on cowpea seeds treated with the root bark may be due
to the strong choky odours it produced which could asphyxiate insects by blocking the spiracles (Amusan and
Okorie, 2002). Most insects breathe by means of trachea which usually open at the surface of the body through
spiracles, the plant powders that were mixed with the seeds might have blocked these spiracles thereby leading to
suffocation and death of the insect (Obembe and Kayode, 2013). Insecticidal property of any plant material
would depend on the active constituents of the plant material (Asawalam
et al
., 2007). Efual
et al
. (2016)
reported that the root powder of
S. logepedunculata
contains 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid methyl ester (methyl
salicylate, 1) which is responsible for its biocide effect against the stored grain insects. The result from this
investigation is similar to the observation of Efual
et al
. (2016) who reported the insecticidal, anti-ovipositant,
ovicidal and repellent properties of
S. longepedunculata
against
S. zeamais
and
C. maculatus.


