International Journal of Clinical Case Reports 2017, Vol.7, No.14, 58-61
59
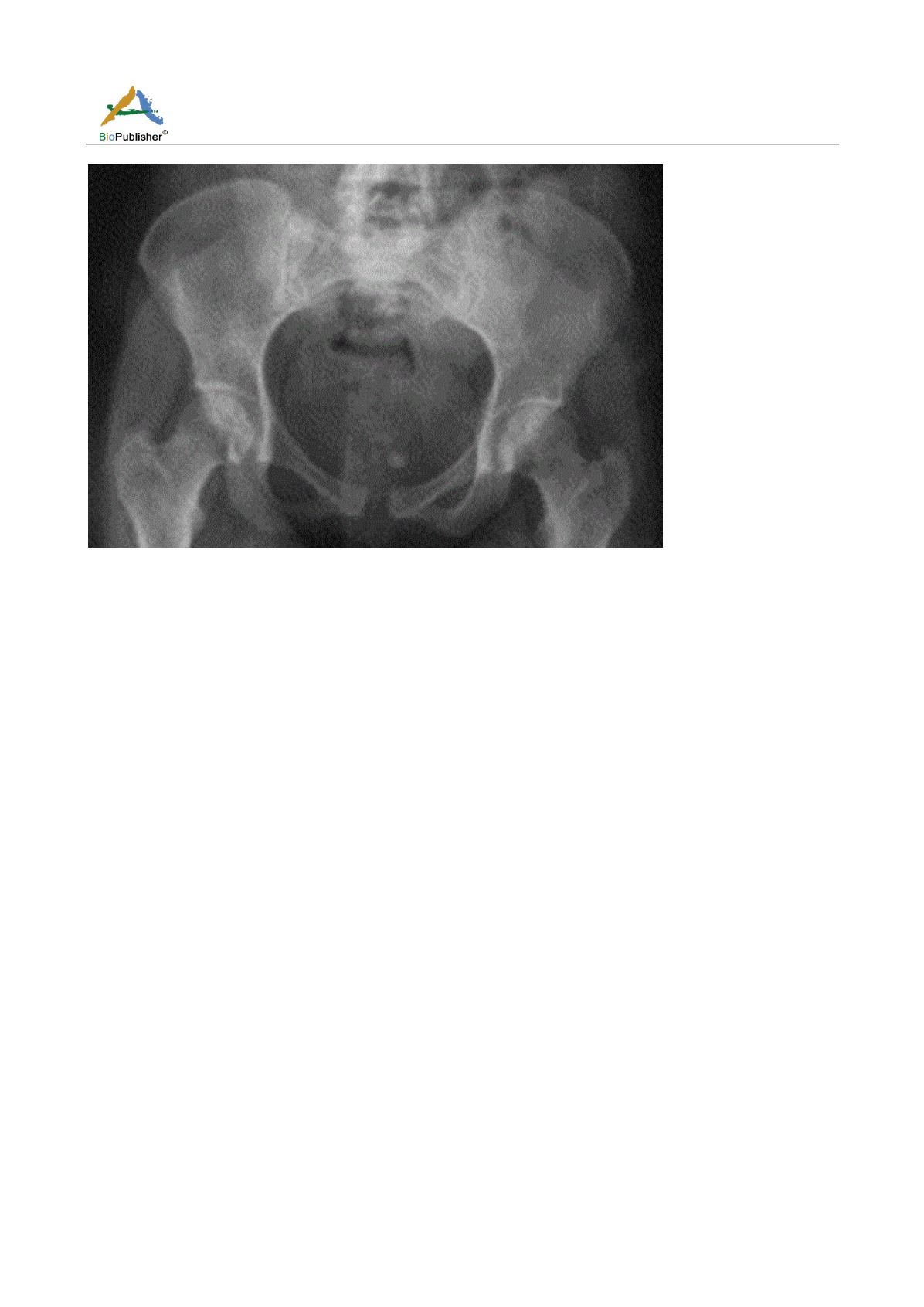
Figure 1
Radiology of the pelvis of the face objectifying an enlargement of the inter-symphyseal space
2 Discussions
Pregnancy is accompanied by changes in pelvic geometry, micro mobility of the sacroiliac joints and the pubic
symphysis, and a general laxity of the connective tissues of hormonal origin, estrogens and relaxin act on the
ligaments, muscles and enthuses of the pelvic region, for the purpose of facilitating childbirth. In addition,
biomechanical stresses increase during pregnancy; as a result the enlargement of the pubic symphysis is
physiological during pregnancy and childbirth (Timsit, 2004). However, pubic disjunction syndrome is an
underestimated and often poorly managed condition. The incidence of this syndrome in per partum is evaluated
between 1/300 and 1/30,000 in the literature (Williams et al., 1966) and can cause pubic pain and / or iliac wings
accentuated by movements and palpation, in pre-, per- or post-partum 22% of the parturientes may have pain in
the pubic symphysis, these pains are atrocious in 5-8% of the parturientes. 7% of parturients have this
symptomatology in postpartum (Albert et al., 2001).
The etiologies of this disorder remain unclear although several authors have reported the frequent association of
symphyseal disjunction and certain risk factors including fetal macrosomia, extraction maneuvers, rapid expulsion,
shoulder dystocia, twinness, joint pathologies and trauma of the pubic joint (Culligan et al., 2002). Our patient had
many risk factors, namely multiparty, macrosomia and the practice of instrumental extraction.
The diagnosis is based on the symptomatology reported by the patient and the clinical examination, in the case of
pubic disjunction, the pain may be of varying intensity, responsible in the most severe cases for total functional
impotence but the minor forms remain the more frequent (Timsit, 2004). Urinary complications in case of severe
disjunction (bladder wound, hematoma, incontinence or urinary tract infection) are possible (Scicluna et al.,
2004).
The typical symptomatology appears to include pain in the pubic symphysis with inguinal irradiation associated
with pain in the sacroiliac joint (Scicluna et al., 2004). The clinical examination notes an exquisite pain in the
palpation of the pubic symphysis, even seeing an edema of the symphysis and the palpation of an
inter-symphysary space (Luger et al., 1995).
The clinical picture in our observation was fairly typical.


