International Journal of Aquaculture, 2017, Vol.7, No.14, 94-100
98
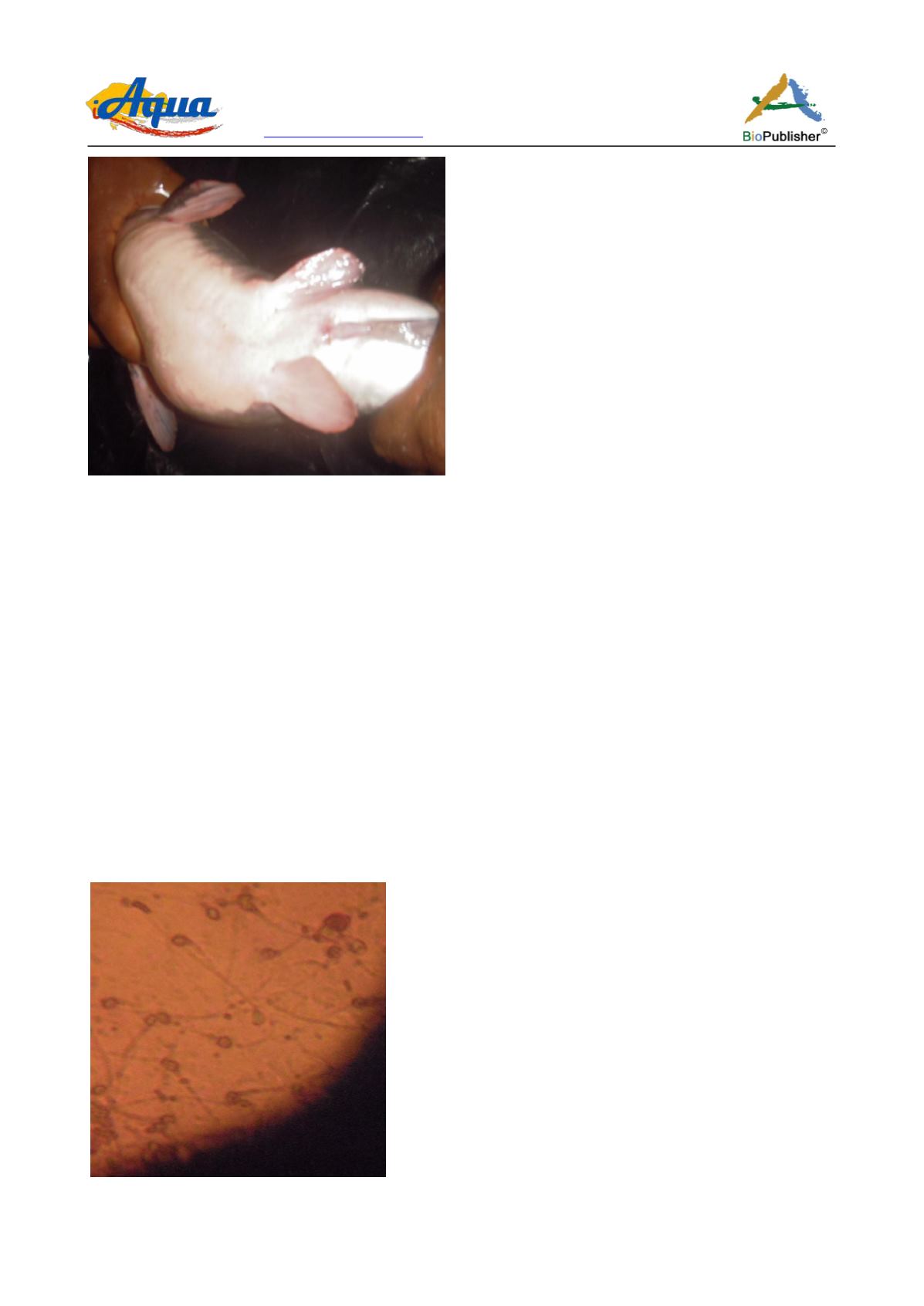
Figure 2 Photograph of genital papilla of a male brood stock of
Clarias gariepinus
4.3 Milt collection
The male brood stocks was selected and sacrificed by spinal transaction, after which the belly was dissected and
the testes were removed. Blood clots and other tissues were rinsed away using tri-sodium citrate solution. The
testes were cleaned and dried by placing on a Whartman
®
filter paper, which absorbed the excess fluid. Physical
parameters which included weight, length and width were observed for both testes. Semen was collected by gentle
perforation of the testes with a sterile needle into a 5 ml sterile container. The content of one testis (the right) was
extracted for mixture with the extender while the other was left intact.
4.4 Pre-storage parameters were determined
(1) By mixing one drop of fresh milt with one drop of distilled water on a clean slide and observed under the
microscope for motility and mass activity. (this was done for the two groups)
(2) By using an insulin syringe to collect 0.1 ml of fresh milt, this was made up to 1 ml mark with trisodium
citrate solution, giving a 1 in 10 dilution. A drop of this mixture was placed on a clean glass slide with a drop of
neutral stain (eosin–nigrosin) to make a semen smear for observing percentage live. Observation was done with a
light microscope using × 100 objective lens Figure 3 and Figure 4.
(3) Colour and volume of semen extracted were also observed.
Figure 3 Photomicrograph of (negrosin and eosin) stained milt smear (×100) of
Clarias gariepinus
with high number of
morphologically normal live cells


