International Journal of Aquaculture, 2018, Vol.8, No.17, 127-136
131
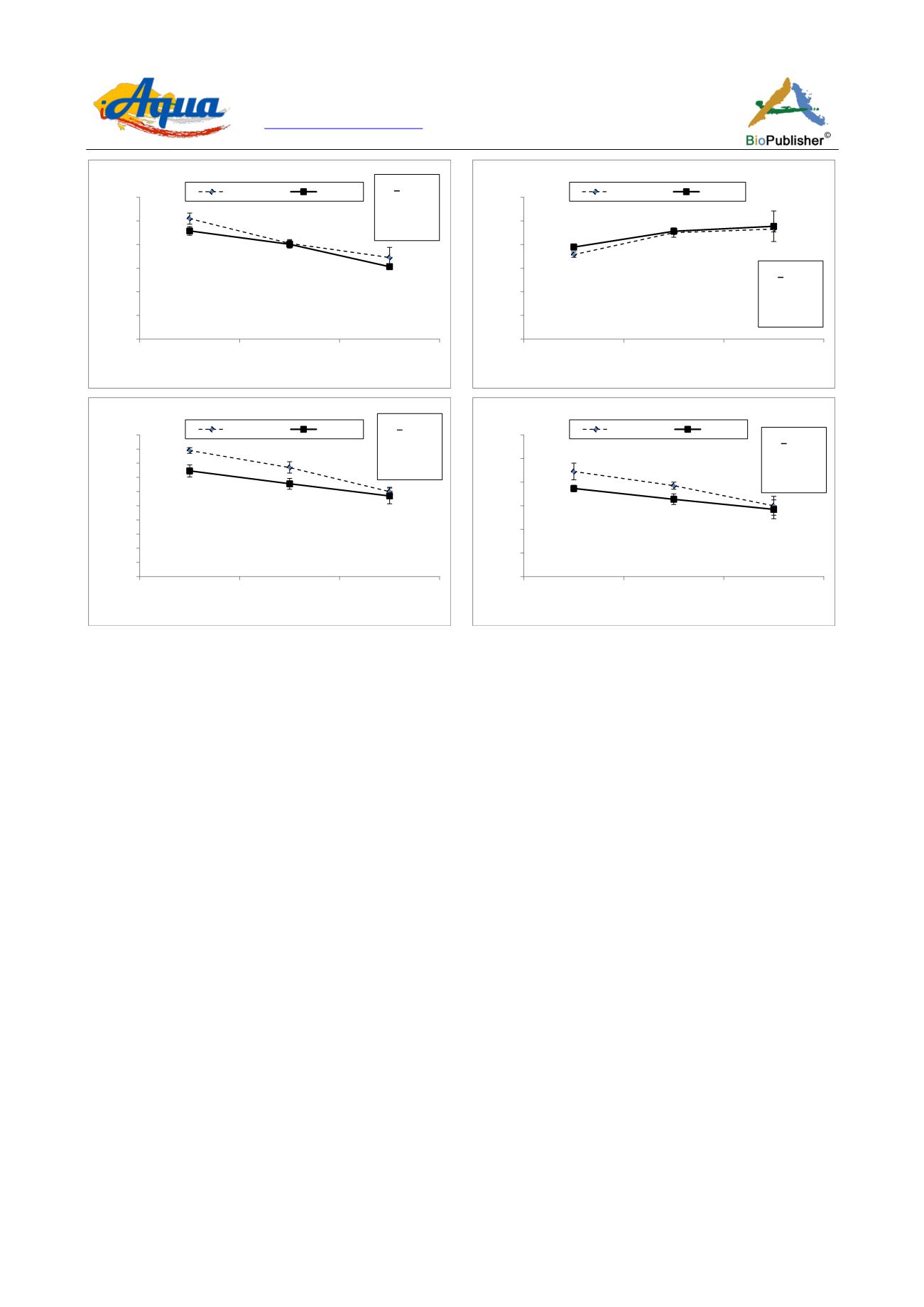
Figure 3 Sedation(S) and recovery (R) mean times recorded for
M. cephalus
and
S. aurata
adults and juveniles using different
concentrations of 2-Phenoxyethanol, Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation as (n=45) and
p
≤0.001. P values with *
superscript expressing significant differences using Mann Whitney test
2.2 Dose-response in both species to anesthetics in respect to different stages
The response of adult
M. cephalus
fish to different concentrations of clove oil reveals that sedation time was
significantly different at all concentrations displaying inverse relation to the concentration (
p
≤0.001) (Figure 4).
The maximum sedation time was recorded at (15 mL
-1
) concentration and the minimum sedation time was
recorded at (25 mL
-1
). The recovery duration on using the same concentrations reveals that the minimum recovery
duration was recorded after 1.8 ±0.232 min. Using (15 mL
-1
) concentration and was significantly different from
durations recorded on using the other two concentrations (Table 2). On the other hand using clove oil at (20, 25
mL
-1
) concentrations reveals that no significant difference was recorded concerning the recovery duration,
however, they display high significant difference form the first concentration (Table 2).
The duration recorded till complete sedation for adults
S. aurata
using the same concentrations of clove oil reveals
that none of the three concentrations affects the sedation time as no significant differences were recorded (
p
≤0.001)
(Table 2). Although sedation time did not show any significant difference using different concentrations of clove
oil, recovery time represented high significant difference on using (15 mL
-1
) concentration than using (20, 25 mL
-1
)
concentrations (
p
≤0.001).
The conduction of the three selected doses of MS-222 to induce complete sedation in adults
M. cephalus
not only
resulted in insignificant sedation durations, but also the recovery durations (
p
≤0.001). In contrast, the response of
adults
S. aurata
to MS-222 (100 mL
-1
) concentration resulted in significantly different sedation and recovery
durations using (125, 150 mL
-1
) concentrations. However, the latter concentrations showed no significant
difference in sedation and recovery durations for
S. aurata
adults (Table 3).
Juveniles
M. cephalus
and
S. aurata
response to the entire selected concentrations (50, 75 and 100 mL
-1
) to induce
complete sedation were insignificantly different (
p
≤0.001). Whereas, juveniles
S. aurata
showed significantly
different durations reaching recovery in response to the entire concentrations (
p
≤0.001). The response of
M.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
conc300
conc350
conc400
Mean
SD (min)
S duration
Adult
M. cephalus
S.aurata
P < 0.001
0.0002*
0.4612
0.0112*
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
conc300
conc350
conc400
Mean
SD (min)
R duration
Adult
M. cephalus
S.aurata
P < 0.001
0.0002*
0.4092
0.3154
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
conc300
conc350
conc400
Mean
SD (min)
S duration
Juveniles
M. cephalus
S.aurata
P < 0.001
0.0001*
0.0001*
0.060
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
conc300
conc350
conc400
Mean
SD (min)
R duration
Juveniles
M. cephalus
S.aurata
P < 0.001
0.003*
0.0001*
0.028*


