基本HTML版本

Computational Molecular Biology 2014, Vol. 4, No. 14, 1-9
http://cmb.biopublisher.ca
6
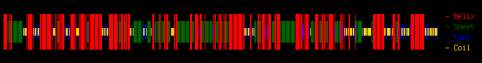
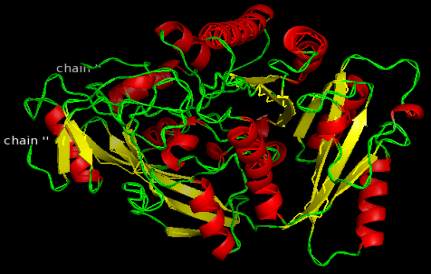
Figure 10 A2XVN3-CKX8(O.sativa)
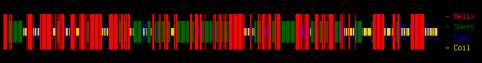
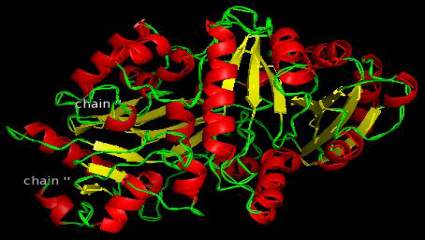
Figure 11 Q9T0N8-CKX1 (Zea mays)
Structural alignment
As the NMR crystallographic structures of these
enzymes are not available at PDB, so the tertiary
structures of all the enzymes of plants were designed
by using phyre2 server whichgenerate reliable protein
models when other widely used methods such as
PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 server (http://www.sbg.
bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index) generate
the model using the principles and techniques of
homology modeling. The target can be modelled with
reasonable accuracy on a very distantly related
sequence of template. The phyre2 server uses a
profile-profile alignment algorithm based on each
proteins position-specific scoring matrix. Phyre2
server include protein structure prediction, function
prediction, domain prediction, domain boundary
prediction, evolutionary classification of proteins,
guiding site-directed mutagenesis and solving protein
crystal structures by molecular replacement (Christie
et al., 2012, Bilal et al., 2013, Singh et al., 2009). The
homology models of enzymes are shown in Figure
12-Figure 21 and the detail information after
visualization is shown in Table 6.
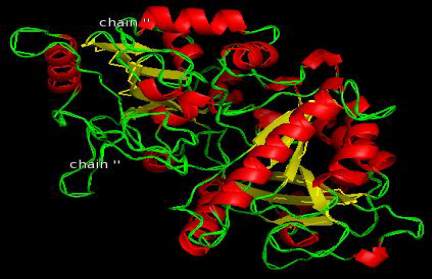
Figure 12 A2XVN3-CKX8(O.sativa)
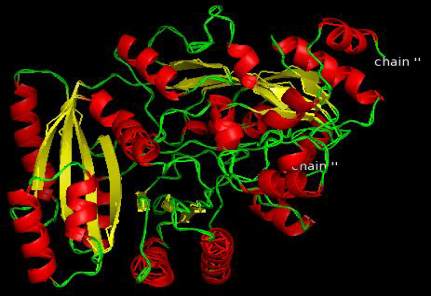
Figure 13 Q4ADV8-CKX2(O.sativa)
Figure 14 Q5JLP4-CKX4(O.sativa)
Figure 15 Q8LNV6-CKX3(O.sativa)

