基本HTML版本
Computational Molecular Biology
27
retrovirus may have been infecting AIDS patients, and
published their findings in the same issue of the
journal Science (Barre-Sinoussi et al., 1983; Gallo et
al., 1983). As the findings of these two research
groups LAV (Lymph Adeno-virus) and HTLV-III
(Human T-lymphotropic virus-III) were renamed HIV
(Aldrich, 2001).
1.2 Stages of HIV infection
HIV infection has four basic stages: incubation period,
acute infection, latency stage and AIDS.
Stage I: The initial incubation period upon infection is
asymptomatic (if a patient is a carrier for a disease or
infection but experiences no symptoms) or clinically
silent with a CD4
+
T cell count (also known as CD4
count) greater than 500/uL. It may include generalized
lymph node enlargement and usually lasts between
two and four weeks.
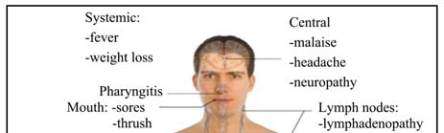
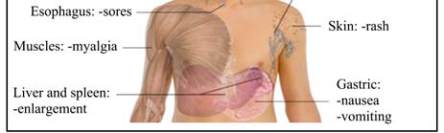
Stage II: This is a stage of acute infection (as shown in
Figure 1), in which mild symptoms like minor
mucocutaneous manifestations and recurrent upper
respiratory tract infections, fever, lymphadenopathy
(swollen lymph nodes), pharyngitis (sore throat), rash,
myalgia (muscle pain), malaise, and mouth and
oesophageal sores occurs. A CD4 count of less than
500/uL lasts an average of 28 days.
Figure 1 Main symptoms of acute HIV infection
Stage III: The latency stage, which shows advanced
symptoms may include unexplained chronic diarrhoea
for longer than a month, severe bacterial infections
including tuberculosis of the lung and CD4 count of a
person is found to be less than 350/uL and can last
anywhere from two weeks to twenty years and
beyond.
Stage IV: The final stage of HIV infection is AIDS,
this shows the symptoms of various opportunistic
infections.
Severe symptoms which includes
toxoplasmosis of the brain, candidiasis of the
oesophagus, trachea, bronchi or lungs and Kaposi's
sarcoma. A CD4 count of less than 200/uL (WHO case
2007) and viral load increases to millions (Weiss,
1993).
Today there is a plenty of patient data available in the
databases they need to be analysed and further
knowledge is needed for formulating the drugs
available for HIV-AIDS. Recent studies show that
association rule mining is used to discover frequent
patterns, correlations of genes/ proteins, protein
networks. But this study focus on the development of
association rules to diagnose disease on the basis of
symptoms, medical tests, associated infections etc. At
an earlier stage so anti retroviral therapy has been
started by medical practitioners and life of a patient
could be increased. These are possible due to data
mining approaches. Earlier some efforts have been
made by some scientists to develop such association
rules in medical databases (Abdullah et al., 2010).
2 Methodology
Data Mining refers to extracting or mining knowledge
from large amount of data. Data mining has been
around for several years for exploration of interesting
knowledge or information from a large amount of data.
Association rule mining is the discovery of association
rules showing attribute value conditions that occur
frequently together in a given set of data. These
algorithms search for interesting frequent patterns,
associations, correlations, or causal relationship
among sets of items or objects. Such relationships are
usually represented by association rules, rules that are
produced by association mining (Han and Kamber,
2011).
2.1 Association rule
The term was coined by Agrawal et al. (1993) and
amazingly it stills becomes an active area of research
in knowledge database discovery. Suppose the viruses
as the set of items causes disease, and then each virus
has a Boolean variable representing the presence or
absence of that disease. Each patient can then be
Computational
Molecular Biology

