Cotton Genomics and Genetics 2016, Vol.7, No.1, 1-7
4
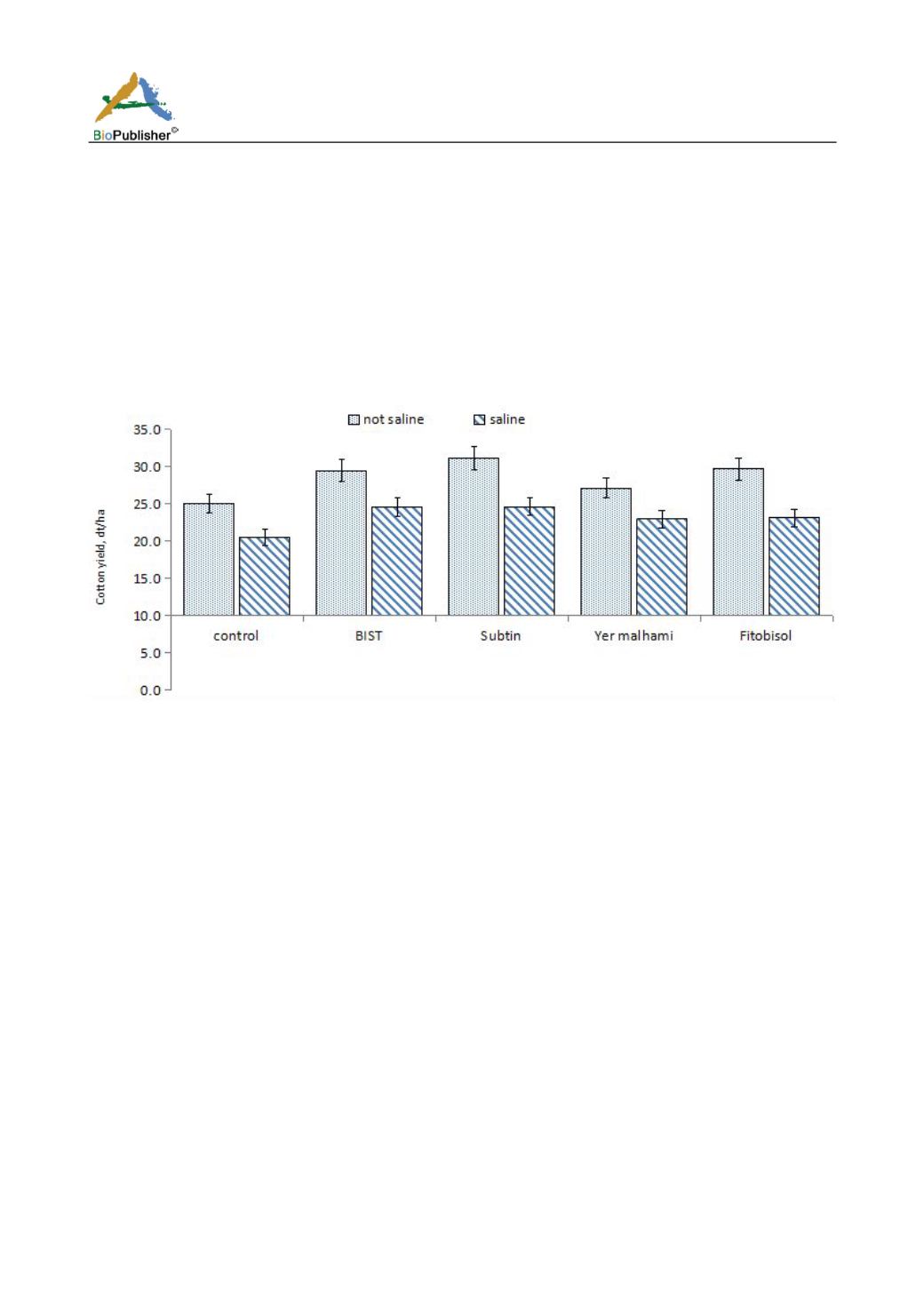
increase the cotton yield up to 31.2 and 29.7 dt ha
-1
while in control the yield was just 20.5 dt ha
-1
in non saline
soil condition. The greatest effects of inoculation were seen in salinated soil where the maximum yield was
observed after inoculation with Subtin (24.7 dt ha
-1
) followed by BIST (24.6 dt ha
-1
) and in control the yield was
20.5 dt ha
-1
. The other bacterial fertilizers also showed some increase in total cotton yield as compared to the
control. These results evaluated BIST and Subtin as a best growth promoting biofertilizers as they significantly
increased germination, plant biomass and cotton yield in both salinated and non-saline conditions (Figure 3).
These results indicate that bacterial fertilizers can be a good source to increase cotton yield in saline and not saline
arid regions of Uzbekistan.
Figure 3 Cotton yield in saline and not saline condition and effect of bacterial fertilizers
2 Discussion
This work demonstrated that bacterial fertilizers produced on the base of indigenous beneficial soil bacterias are
able to increase the plant growth and yield on both moderate saline and favorable soil conditions. All inoculated
treatments increased yield of cotton as compared to control plants. The use of these microbial inoculants may
increase the cotton yield with saving chemical fertilizers. We conclude that salinization of soils due to prolonged
irrigation and continous use of high amounts of fertilizers in cotton monoculture reduced cotton yield, and it is
important to inoculate of cotton seeds with bacterial fertilizers to overcome these challenges in cotton production
of Uzbekistan.
The aim of this research was to evaluate the application of bacterial fertilizers to the development and yield of
cotton under saline arid conditions. Further research is needed to assess the ability of bacterial fertilizers for
helping plant uptake nutrients both saline and non saline conditions.
3 Materials and Methods
3.1 Plant seeds
The seeds of cotton (
Gossypium hirsutum
L.) variety C-6524 were obtained from the Department of Plant Science,
Tashkent State Agrarian University, Uzbekistan and used in this study. Seeds were sorted to eliminate broken,
small and infected seeds. Seeds of cotton were surface-sterilized for 5 min with concentrated sulfuric acid
followed by 70% ethanol for 3 min and rinsed 5 times with sterile, distilled water.
3.2 Bacterial fertilizers
Bacterial fertilizers BIST (prepared on the base of
Pseudomonas putida
consists 1×10
7
CFU/mL), Er Malxami


