Basic HTML Version

Medicinal Plant Research 2014, Vol.4, No.3, 18
-
29
http://mpr.sophiapublisher.com
20
20.61%), nanophylls (19 spp., 11.52%) leptophylls (21
spp., 12.73%) and megaphylls (13 spp., 7.88%) (Table
2). In present work the plant species were classified
into different classes on the basis of different aspect
like growth habit, life span, light frequency and moister.
On the basis of growth habit 121 species were annual
while perennial have 44 species. Life span divided the
plant species into deciduous (138) and evergreen (27).
On the basis of light frequency and moisture the 163
species were found dominant in light and dry condition
while 2 plant species in water and shady condition.
Discussion
The research area is very interesting consist of both hill
and plain, changeable much in floristic composition.
The present work was design to explore the flora for
taxonomist and other researcher trying in this field.
Due to be present irrigation services the flora;
particularly cultivated flora has much difference from
hilly area. The chief agriculture crops are wheat, fodder
crops and barely. On hills different grasses,
Acacia
modesta, Achyranthus aspera, Calotropis procera,
Xanthium strumarium, Opuntia littoralis
and
Sorghum
halepense
etc are commonly found. With the passage
of time, increase in population and rising in need of
facilities in the culture declining the natural habitats.
Our result is similar with that of Khan et al. (2012).
Mostly the Xerophytes such as
Broussonitia papyrifera,
Ficus carica
,
Ficus palmata
,
Morus alba
,
Eucalyptus
camaldulensis
,
Eucalyptus lanceolatus
etc are found
on road sides. Such type of study was also taken by
Khan et al. (2011a; 2011b; 2012; 2013). In the research
area, commonly people depend on agricultural and
domestic animals. They also collect medicinal plants,
fodder, fuel wood and timber. The natural assets are
being over-used, indistinct and spoil.
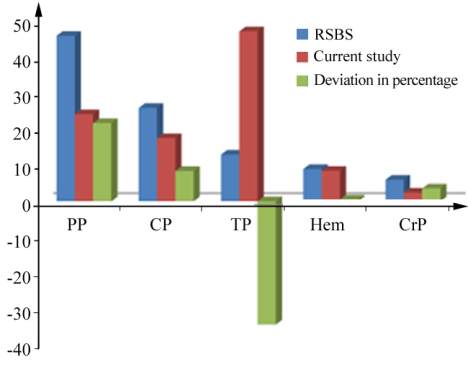
Comparisons of the percentage of the life form classes
of the research area with Raunkiaer standard biological
spectrum (RSBS), therophyte form the largest life form
class and their percentage is more than thrice (47.73%)
that of the RSBS (13%). The phanerophytes forms, the
second highest class with (24.24%). Their percentage
was 46.0 in the RSBS. Thus, the biological spectrum of
the research area marker “Therophytic” Phytoclimate
at the same time as this class proves the greatest
deviation from the standard spectrum. Hemicry-
ptophyte is equal (8.49 %) with that of the RSBS
(9.00 %). Cryptophytes was less 2.42% than in the
RSBS (6.00 %) (Figure 2). According to the Raunkiaer
(1934) that climate of a region is characterized by life
form. Plant species were identified and classified into
major life forms to build biospectrum. The biological
spectra is helpful to comparing geographically far and
wide separated plant life and used as an indicator of
prevailing environment. Biological spectrum may be
significantly changed due to preface of therophytes like
annual weeds, biotic pressure like agricultural practices
and grazing, deforestation and trampling etc. The
dominance of therophytic life form showed that the
area was under heavy biotic pressure. Khan et al.
(2011a; 2011b) and Khan et al. (2012) also agree with
the same statement.
Figure 2 Comparison of biological spectrum of the area with
Raunkiaer’s Standard Biological Spectrum (SBS)
The dominance of therophytes occurs due to
un-favorable environment conditions as definite by a
lot of research (Shimwell, 1971, Khan et al., 2011c,
2012). In this study, the domination of therophytes and
phanerophytes over other life forms give the idea to be
a response with to the topographic divergence, warm
sit out, human being and creature disturbance. The
current results in this regard also agree with them.
Khan et al., (2012) considered chamaephytes and
therophytes as the major life form in unfavorable

