Basic HTML Version


Molecular Pathogens 2012, Vol.3, No.1, 1
-
5
ht
t
p://mp.sophiapublisher.com
4
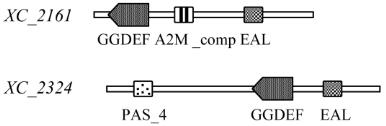
Figure 5 Domain architecture of GGDEF domain proteins
involved in biofilm formation in
Xcc
8004
1.2.4 Domain architecture of GGDEF domain
proteins involved in motility in
Xcc
8004
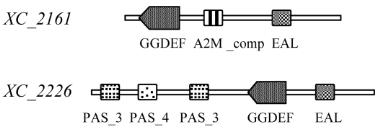
Ryan et al (2007) assayed the motorial ability of the
mutant GGEDE proteins, the results revealed that 2
GGDEF domain proteins encoded by
XC
_
2161
and
XC
_
2226
respectively were found to be related to
motility in
Xcc
8004. The 2 proteins were differed in
their common or local common domain architectures
from our domain architecture analysis (Figure 6). The
architecture of PAS_3
-
PAS_4
-
PAS_3 in
XC
_
2226
-
encoding protein was not found in the protein coded
by
XC
_
2161
. And the EAL domain follows the
GGDEF domain in the protein encoded by
XC
_
2226
,
which was also different from the domain arrange of
XC
_
2161
-
encoding protein.
Figure 6 Domain architecture of GGDEF domain proteins
involved in mobility in Xcc 8004
2 Discussion
The domain architecture analysis showed that the
interesting profile in the GGDEF domain proteins
functioning differently in
Xanthomonas campestris
,
such as, PAS_4
-
GGDEF, GGDEF-EAL and PAS_4
-
GGDEF-EAL were shared by the proteins which were
found to be involved in virulence; and PAS_4
-
PAS_4,
PAS_4
-
GGDEF and GGDEF-EAL were shared by
the proteins which involved in the production of
endoglucanase. The functions of the proteins with the
GGDEF domain, PAS domain or EAL domains in
large number of bacteria remains unknown, and the
proteins with these domains were reported playing
important roles in essential cell processes (Seshasayee
et al., 2010). So, the results provided some important
information to prediction the function of these
proteins containing GGDEF domain, PAS domain
including PAS_4, PAS and PAS_3 members (Hao et
al., 2011), or EAL domain. The results were benefit
for the plant disease research as they gave some clues
of structural characteristics to the proteins involved in
virulence, and also to hypothetical proteins (Nikolskaya
et al., 2007). Not similar to any protein known at
sequence level, the functions of the proteins with
GGDEF domain were hard to be predicted.
The knowledge for domain architectures of the proteins
functioning differently in
Xanthomonas campestris
should not be limited in our report because this
research only based on few functions of
Xcc
8004.
Many new characteristics may be drawn from domain
architecture of GGDEF domain proteins in other
Xcc
strains, for example, strain Xc17, containing
Xcc
1294,
the homologous gene with
XC
_
2946
, and
Xcc
2731,
homologous gene with
XC
_
1383
in
Xcc
8004. All of
them participated in the cell adhesion according to the
reports of Hsiao et al (2011a; 2011b). Strain XC1,
containing
ravR
/
Xcc1958
, homologous gene with
XC
_
2228
in
Xcc
8004. This stain involved in extra-
cellular polysaccharide and proteinase production (He
et al., 2009).
3 Materials and Methods
3.1 Data sources
The protein sequences of
Xcc
8004 were downloaded
from the database in NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.
gov/genome). The GenBank accession No. of
Xcc
8004 is NC_007086.
3.2 Identification of domain
By using the Pfam database (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/),
we searched the information of protein families and
domains which was constructed by the Hide Markov
Models. The SMART website (http://smart.embl-heidel
berg. de/), a simple modular architecture research tool,
providing the service for searching and annotation of
domain also can be used. We uploaded the protein
sequence documents, products of all genes, to the
website of Pfam to search batch domains to obtain the
annotation of all proteins. Using string
“
GGDEF domain”,
we could search the proteins containing GGDEF
domain, which could be analyzed via SMART, and
gained the information of proteins.

