Basic HTML Version


Molecular Plant Breeding Provisional Publishing
Molecular Plant Breeding 2012, Vol.3, No.5, 50
-
56
http://mpb.sophiapublisher.com
53
gene gun DNA delivery method. Putative transgenic
plants of both genotypes were selected on their
respective optimal basta dose.
1.3 Selection of transgenic plants of both genotypes
Twenty one (21) days old calli of genotype
S-2003-us-359 and 28 days old calli of S-2003-us-127
those were induce on CIM1 and CIM2 respectively
were bombarded with
bar
gene and shifted to RSM
having 10 and 5 mg/L basta. RSM with 10 mg/L basta
was used for the selection of transgenics of genotype
S-2003-us-359 and RSM with 5 mg/L basta was used
for the selection of transgenics of genotype
S-2003-su-127 (Figure 6).
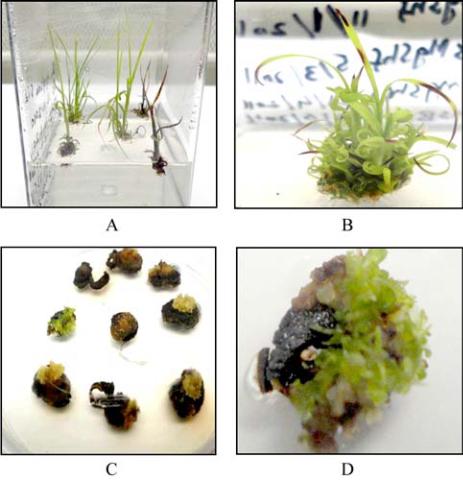
Figure 6 Selection of transgenics on selection regime having
basta as selective agent
Note: (A & B) transgenic plants selection of genotype
S-2003-us-359 on RSM having 10 mg/L basta; (C & D)
transgenic plants selection of genotype S-2003-us-127 on RSM
having 5 mg/L basta
1.4 Genomic analysis of putative transgenic plants
with PCR
Putative transgenic plants those bears the selection
pressures of basta were confirmed for the presence of
bar
gene in their genome with PCR analysis by using
gene specific primers. DNA of wild type plant as well
as putative transgenics those bear basta selection
pressure were extracted. PCR was performed by using
gene specific primers.
bar
gene sequence was absent
in wild type (non transformed plant) but presence of
bar gene sequence was observed in putative transgenics
(transformed plants) those were selected by giving the
selection pressure of basta (Figure 7).
Figure 7 PCR analysis of putative transgenics for bar
Note: M = I kb ladder, E= Empty lane, WT= Wild type plants,
P1, P2, P3 =Transgenic plants of genotype S-2003-us-359, P4,
P5 =Transgenic plants of genotype S-2003-us-127, -ve control
(water), E=Empty lane, + ve control (plasmid DNA)
2 Discussion
Selection of transformed cells containing stably
integrated gene is one of the major steps in production
of transgenic plants which can be achieved by
knowing the minimum concentration of selective
agent that can inhibit the growth of non-transformed
cells and allow transformed cells to survive. Due to
this, transformation process has become more efficient
that results in a very low occurrence of chimeras.
Sreeramanan et al., (2006) highlight the significance
of dose rate optimization of the selective agent and
determine that it is the most important step in the
selection of the transformed plants because it makes
the selection process very easy and efficient. Dose rate
optimization of the selective agent is highly tissue and
species specific described by Parveez et al (1996).
Due to high dependence against genotype in monocot,
it might be the variation in the endogenous resistance.
Therefore, optimization of the selective agent becomes
very crucial. Under these circumstances, this study was
organized for the efficient selection of transgenic
plants. It was observed that basta is an efficient
selective agent in the selection of sugarcane
transformed plants. It was also reported that prolonged
exposure to selection in medium containing Basta is
needed to reduce escapes.
Basta dose was optimized for transgenic selection and
five levels of basta (1 mg/L, 3 mg/L, 5 mg/L, 7 mg/L

