Basic HTML Version

Molecular Entomology 2013, Vol.4, No.2, 6-12
http://me.sophiapublisher.com
7
Table 1 Toxicity of preservative treated plywood against Powder post beetle
Damage
Treatment/Chemical
Concentration (%)
6MAE
12MAE
18MAE
24 MAE
30 MAE
2.5
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
3
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
CEB (10% w/v)
5
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
No exit hole
appear
Control
-
Exit
hole
appeared
Exit
hole
appeared
Severe
attack
Severe
attack
Severe
attack
from service its disposal can cause serious
environmental problems because it retains high levels
of toxic elements (Sye Hee Ahna, 2010). Humar et al.
(2004) predicted that the volume of the CCA-treated
waste wood would be 16 mm
3
in 2020.
Copper and Boron based wood preservatives have an
important drawback like leaching out from the treated
wood. Soluble metal salts could be made insoluble or
fixed inside wood by addition of chromium. Due to
the carcinogenic nature of chromium compounds most
of the European countries intend to ban the use of
chromium in wood preservatives. Some of them will
allow use of chromium preserved wood only for
special purposes that are classified as hazard class IV.
Use of chromium based wood preservatives will be
banned in future for children playground equipment
and garden furniture. Therefore, intense research is
going on in the world laboratories to develop
environmentally acceptable solution to fix Copper and
Boron in wood.
Chromium based preservatives are under constant
review due to environmental reasons and these
formulations face threat to be phased out in the future
(Tripathi et. al., 2005). On perusal of literature, it has
been found that the work on Copper Ethanolamine
Boron (CEB) based preservatives has not been done in
India and hence in the present study an attempt has
been made to evaluate the bioefficacy of CEB against
PPB and subterranean termite.
1 Result
Results of toxicity test for PPB covering exposure
periods of 6, 12, 18 and 30 months are presented in
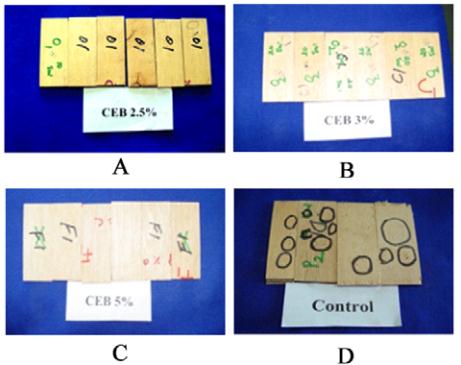
Table 1 (Figure 1). The results of borer tests indicated
that borer holes appeared within six months of
exposure in the untreated control samples. CEB
chemical at all tested concentrations proved to be
significantly superior in arresting the attack of power
post beetle. The samples treated with CEB at the
lowest concentration level of 2.5% resisted the attack
from
Lyctus africanus
. In CEB at all the tested
concentration level the samples were free of attack
from
Lyctus africanus
until the end of the study i.e.
thirty months. Hence, based on results of the toxicity
study the lethal dose to kill the powder post beetle in
the present investigation was found to be 2.5%.
Figure 1 Plywood samples after exposure study against Powder
post beetle
Note: A: CEB 2.5%; B: CEB 3%; C: CEB 5%; D: Control

