Basic HTML Version

Structural Analysis Mode Interactions SoxB Protein SoxYZ Complex
Allochromatium vinosum
3
Table 1 Protein-protein side chain-side chain hydrogen bonds
POS
CHAIN RES
ATOM POS
CHAIN RES
ATOM
41
Y
THR
OG1
49
X
GLU
OE1
81
Y
ARG
NH1
50
X
HIS
NE2
81
Y
ARG
NH1
50
X
HIS
NE2
81
Y
ARG
NH2
50
X
HIS
NE2
81
Y
ARG
NH2
50
X
HIS
NE2
81
Y
ARG
NH2
53
X
ASP
OD1
81
Y
ARG
NH2
53
X
ASP
OD1
81
Y
ARG
NH2
53
X
ASP
OD2
81
Y
ARG
NH2
53
X
ASP
OD2
18
Z
LYS
NZ
68
Y
GLU
OE1
18
Z
LYS
NZ
68
Y
GLU
OE2
62
Z
SER
OG
53
X
ASP
OD1
1.4 Interaction of C-terminal domain of SoxB with
SoxYZ complex
In order to find the interactions between the
C-terminal domain of SoxB with SoxYZ the three
dimensional structures of the proteins were docked by
the software tool cluspro 2.0. SoxYZ and SoxB
domain are found to interact strongly with each other.
There are extensive H-bonding interactions involving
both the main and the side chains of the two proteins.
There are also hydrophobic interactions between two
proteins. Apart from this there are protein-protein
ionic and aromatic-aromatic interactions. Table 1
represents the extensive protein-protein hydrogen
bonding interactions through their side chains between
SoxYZ protein complex and 5'-nucleotidase, C-terminal
domain of SoxB protein. The complex modelled
structure of SoxYZ and 5'-nucleotidase, C-terminal
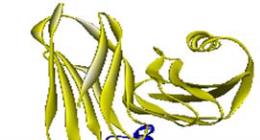
domain of SoxB protein is presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4 Interaction of SoxYZ complex (yellow) and
5'-nucleotidase, C-terminal domain of the SoxB (blue) are
shown in the complex
2 Discussion
In this study, an attempt has been made to elucidate
the structural basis of the involvements of SoxY, SoxZ
and 5'-nucleotidase, C-terminal domain of SoxB in
binding and their role in sulphur oxidation. For this
analysis the three-dimensional structures of the
proteins SoxY, SoxZ, and 5'-nucleotidase, C-terminal
domain of SoxB have been built and analyzed. Due to
large amino acid residues of SoxB only
5'-nucleotidase, C-terminal domain of SoxB has
modelled. Pfam has been used to predict domain
position in the SoxB protein and the result is also
verified by blast run. Domains are the conserved
portion of the protein structure responsible for
functionality. However there is no well documented
report regarding residue level interactions of SoxB
and SoxYZ complex protein. In a nutshell, the results
from our study may introduce a new understanding of
the three dimensional structures of the SoxYZ protein
complex and the C-terminal domain of SoxB.
Furthermore, our results may lead an elucidation of
the structural basis behind the molecular functions of
these proteins. This model provides a rational platform
to design experiments for the determination of the
contribution of the various amino acid residues in
SoxY, SoxZ and SoxB proteins to predict the
molecular basis of their interactions.
3 Materials and Method
3.1 Sequence analysis and homology modelling of
SoxY, SoxZ and C-terminal domain of SoxB protein
The amino acid sequences of SoxY, SoxZ and SoxB
proteins of
A.vino
were obtained from NCBI
Computational
Molecular Biology

