Basic HTML Version

International Journal of Marine Science 2014, Vol.4, No.35
http://ijms.biopublisher.ca
5
Table 2 Comparison between erosion and accretion profiles (W_R and E_B) and between erosion and accretion sites within the same
profile (E_R, W_B, W_S and E_S) according to the averages of
226
Ra,
232
Th and
40
K concentrations (Bq/kg) of the main erosion and
accretion sites within the profiles. west of Rosetta (W_R), East of Rosetta (E_R), West of El-Burullus (W_B), East of El-Burullus
(E_B), West of Ras El-Bar (W_S) and East of Ras El-Bar (E_S) during 2008
W_R
E_B
E_R
W_B
W_S
E_S
Erosion Accretion Erosion Accretion Erosion Accretion Erosion Accretion Erosion Accretion
226
Ra 31.17
>
18.13
14.75
<
23.68
28.00
>
17.67
37.92
>
23.67
23.75
>
18.83
232
Th 30.44
>
18.80
23.85
>
20.50
20.55
>
20.30
41.60
>
27.92
27.97
>
18.48
40
K 240.48
<
298.34
284.20
>
170.25 358.25
>
329.70
202.75
<
230.95
337.85
<
340.25
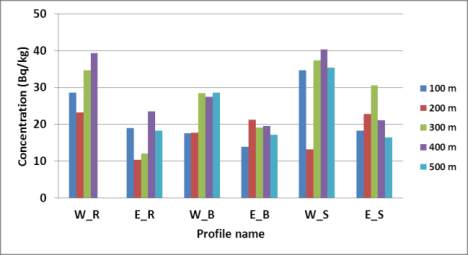
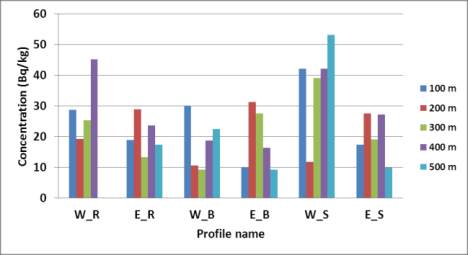
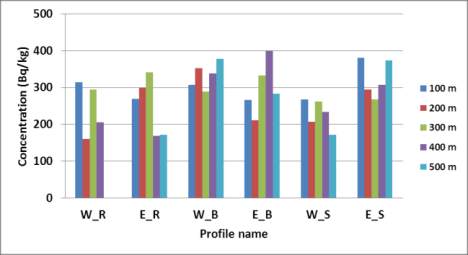
Figure 2 Average concentrations values (Bq/kg) of
226
Ra (A),
232
Th (B) and
40
K (C) at different distances along the Nile Delta
profiles. W_R = West Rosetta, E_R = East Rosetta, W_B =
West Burullus, E_B = East Burullus, W_S = West Ras El-Bar
and E_S = East Ras El-Bar
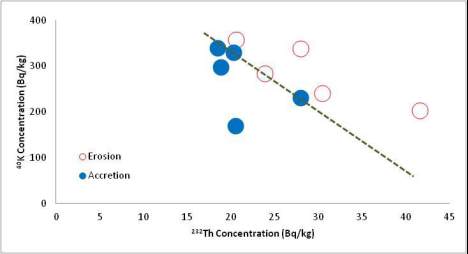
Figure 3 shows the discrimination between the erosion
and accretion sites according to their contents of
232
Th
and
40
K. The dashed line in Figure 3 is differentiating
them into two separate clusters. The erosion sites are
Figure 3 Clustering of the average concentrations of
232
Th
against
40
K in erosion and accretion sites at Nile Delta Profile
sediments during 2008.
characterized by relatively high
232
Th and relatively
low
40
K concentrations and the reverse distribution
occurred at accretion sites.
The average Ra
eq
activity in Nile Delta coastal area
was found to be 79.6±22.17 Bq/kg. The highest value
was calculated as 124.46 Bq/kg at 500 m distance
from west of Ras El-Bar profile, while the lowest
value was calculated as 45.99 Bq/kg at 200 m distance
at west of Ras El-Bar profile. The recommended
maximum levels of radium equivalents for building
materials to be used for homes are, 370 Bq/kg and for
industries is 370–740 Bq/kg (UNSCEAR, 1982). All
the materials examined are acceptable for use as
building materials as defined by the Organization for
Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
criterion.
The calculated outdoor gamma doses were listed in
Table 1 with average value 37.25±9.58 nGy/h. The
highest value was 55.64 nGy/h measured at 500 m
distance from west of Ras El-Bar profile sediment,
while the lowest dose value was 21.93 nGy/h
measured at 200 m distance from west of Ras El-Bar
A
B
C

