Basic HTML Version

International Journal of Marine Science 2013, Vol.3, No.23, 178-186
http://ijms.sophiapublisher.com
184
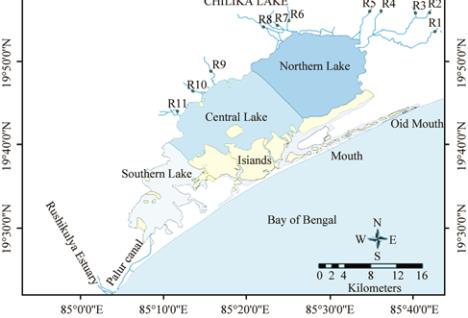
Figure 3 Map of Chilika Lake
rain water and influx from catchment through the
inlets. The salinity gradient of the lake is mostly
depended up on the precipitation, evaporation and
tidal frequency. The intermixing of marine water with
fresh water in the lagoon proper produces a very
unique kind of brackish water aquatic ecosystem that
provides an ideal habitat for colonisation of various
flora and faunal representatives. It is the largest
migratory bird congregation site and largest habitat for
Irrawaddy dolphin. Presently this lake supports for
225 species of birds, 227 species of fishes, 35 species
of crabs, 19 species of prawn, 14 species of marine
algae, 5 species of sea grass, 2 species of marine
mammal etc. Like other coastal lagoons Chilika Lake
is also getting stress from natural and anthropogenic
inputs such as eutrophication, infestation of fresh
water weeds, irregular changing of the position of
lagoon inlet, over fishing, oil and sound pollution,
aquaculture and Cage fishing. These are some of the
important and potential stressors to this lake (Table 3).
Proper management step should be taken to protect
this lake from edge of degradation.
Future Challenges: These ecosystems are very dynamic
Table 3 Problems of Chilika Lagoon
Natural origin
Anthropogenic origin
Siltation
Excess use of motor boat
Change in lagoon inlet
Noise pollution
Sea level rise
Oil pollution
Wind action
Plastic pollution
Tidal incursion
Chemical pollution from crop
land
Salinity reduction/salinity extreme
conditions
Organic pollution
Eutrophication
Nutrient enrichment
Siltation
Aquaculture and fisheries
Tourism
Coastal constrictions
Heavy metals, PCB
and productive due to the coexistence of different
ecosystems like fresh water influx marine water
intrusion and associated biodiversity. There are certain
problems which may create problem in recent future
are elucidating below.
(i) Sea Level Rise: as most of the coastal lagoon and
estuaries are located on the shoreline areas of the sea
or oceanic realm sea level rise due to melting of polar
ice can result loss of geographical area of these
transition water mass partially or completely.
(ii) Ocean Acidification: Continues anthropogenic
impact on sea and ocean and rise of greenhouse gasses
such as carbon dioxide can result global warming as a
consequence of which massive loss of phytoplankton
may be seen and this may be facilitate the ocean
acidification. As the ocean and coastal aquatic
ecosystems are integrated together drastic impact can
be seen on biodiversity.
(iii) Plastic Pollution: Increase trend of use plastic
materials and its debris in the coastal and marine
ecosystem already cause havoc in different parts of the
globe. As bio-non- degradable material, it persists in
the sediment or in the water for a longer period and
releases toxic chemicals to the surrounding. This may
bring a great challenge in future.
(iv) Sound Pollution: Due to excessive use of motor
boats sound pollution will be a major concern in the
recent future.
(v) Chemical Pollution: due to rampant use of chemical
fertilizers and pesticides, DDT etc. the nearby coastal

