Basic HTML Version

International Journal of Marine Science 2013, Vol.3, No.2, 4
-1
6
http://ijms.sophiapublisher.com
14
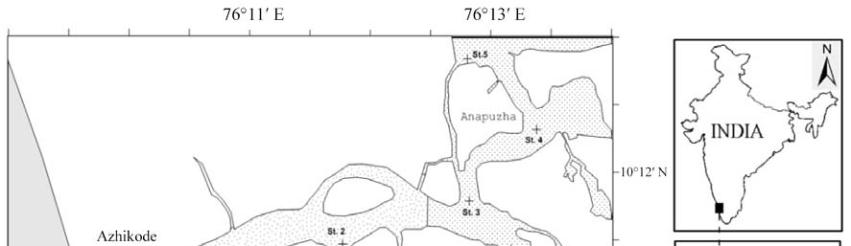
Figure 3 Location of the sampling sites in the Kodungallure-Azhikode Estuary.
4.2 Sampling methods
Estuary was classified into two zones based on general
morphology and environmental characteristics of
estuary, estuarine mouth zone (EMZ) and estuarine
upper zone (EUZ). Landing centre based direct data
collection method was adopted for the fish landing
estimation (FAO, 2002). Azhikode, Anapuzha and
Krishnankotta were the major fish landing centers of
the estuary.
The fish catch composition, gear wise catch (%) of the
fish diversity were studied in the KAE during July
2009 to June 2010 period. Catch per unit effort (CPUE)
is defined as one tow of the net which occurred once
per site or the number of fish collected per tow
.
CPUE
for fish assemblages were estimated using standard an
otter trawl (3.5 head rope, 30 mm mesh wings, 18 mm
mesh cod end) towed by small boat. CPUE was
expressed as No. 100 m-net hr
-1
and used as index of
relative abundance (FAO, 2002). The total catch was
sort out into finfish, shrimp, prawn, crab, molluscs and
other species by visual assessment. After sorting and
counting, representative samples were preserved in
10% formalin for taxonomic studies in the Laboratory.
The species wise identification of fishery was done
based on standard works (Day, 1889; Talwar and
Jhingran, 1991; Jayaram, 1999; Munro, 2000) and also
Fish Base (Fishbase, 2012).
Water quality parameters from different zones were
also collected on an array of environmental variables
that can be potentially influence the fish communities.
Water transparency (Secchi disk transparency; SD) was
measured by Secchi disk in the field. Dissolved oxygen
(DO) was estimated according to Winkler’s method
(Grasshoff et al., 1983). pH by Systronics pH meter
(No. 335; accuracy ± 0.01). For the estimation of Chl-
a
,
acetone extraction method was employed (Parsons et
al., 1984). Primary productivity was estimated by in
situ incubation method using the light and dark bottle
oxygen method (Strickland and Parsons, 1972).
Temperature of water samples were measured with a
centigrade thermometer, conductivity by Systronics
digital potentiometer (No. 318), turbidity by Systronics
water analyser (No. 317) and salinity by Systronics
water analyser (Model No. 317; accuracy ± 0.01)
calibrated with standard seawater (APHA, 2005).
Carbon dioxide, alkalinity, hardness and biological
oxygen demand (BOD) was determined by standard
procedures (APHA, 2005).

