International Journal of Aquaculture, 2016, Vol.6, No.3, 1
-
9
3
media- Mumbai) for the enumeration of heterotrophic bacteria. The plates were then incubated at 30°C for 24- 48
hours. Colonies developed on the plate were counted and expressed as colony forming units (cfu) / gm of fish gut.
Well separated and morphologically different colonies were picked up using a sterile inoculation needle and
transferred to sterile nutrient agar slants. The isolates were purified by quadrant streaking and were stored in
nutrient agar slants for further study.
Characterisation of microbiota of the gut was done using standard methods (Ringo et al., 1995). The isolated
strains were identified up to generic level using the taxonomic key by Buchanan and Gibbons (1984). For generic
level classification of the isolates they were subjected to various tests such as Gram stain, spore stain, motility,
Kovac’s oxidase test, catalase activity, and oxidation/ fermentation test.
2.2 Antibiotic susceptibility testing
The antibiotic sensitivity of the bacterial isolates were analysed using the disc diffusion method (Bauer et al.,
1966). Antibiotic impregnated discs (Himedia, India) of 8-mm diameter were used for the test. Antibiotic discs of
carbenicillin (Cb – 100 μg), cephalothin (Cep- 30 μg), cefpodoxime (Cpd- 10 μg), chloramphenicol (C – 30 μg),
ciprofloxacin (Cip - 5 μg), gentamicin (G -10 μg), nalidixic acid (Na- 30 μg), streptomycin (S - 10 μg),
sulfafurazole (Sf- 300 μg), tetracycline (T - 30 μg) and trimethoprim (Tr- 5 μg)were then placed on the sterile
Mueller Hinton agar plates swabbed with enriched bacterial culture (equivalent to 0.5 McFarland standard) and
incubated at 37°C for 16-18 hours. The antibiotics belonged to eight different classes according to their chemical
structure: aminoglycocides (streptomycin, gentamicin), quinolones (nalidixic acid), fluorquinolones
(ciprofloxacin), tetracyclines (tetracycline), penicillin (carbenicillin), cephalosporins (cephalothin, cefpodoxime),
sulphonamides (sulfafurazole, trimethoprim), phenicol (chloramphenicol).
After incubation, the diameter of the zone of inhibition was measured and the results were interpreted based on
recommendations of Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI, 2007).
E.coli
isolate (ATCC 25922) is used as
referebce strain. Isolates that are resistant to three or more antibiotics were grouped as multiple antibiotic resistant
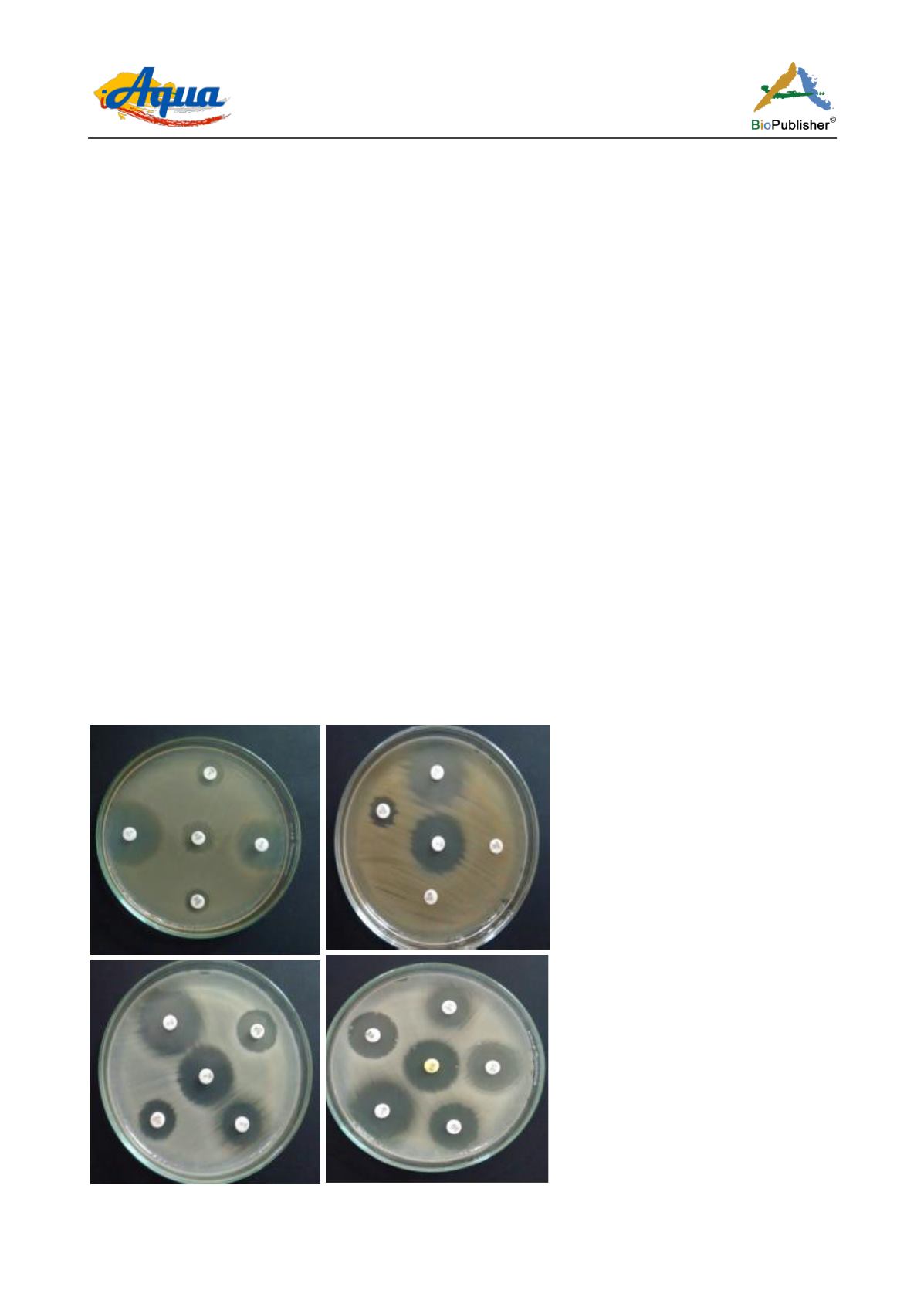
isolates. Images of the antibiotic sensitivity testing are presented as Figure 2.
Figure 2 Plates showing antibiotic resistance of isolates from the gut of
Aplochileus lineatus
and
Etroplus maculatus


