Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics 2018, Vol.6, No.4, 25-32
26
development, the biological activities of the four promoters are different, tissue-specific and related to
developmental stages.
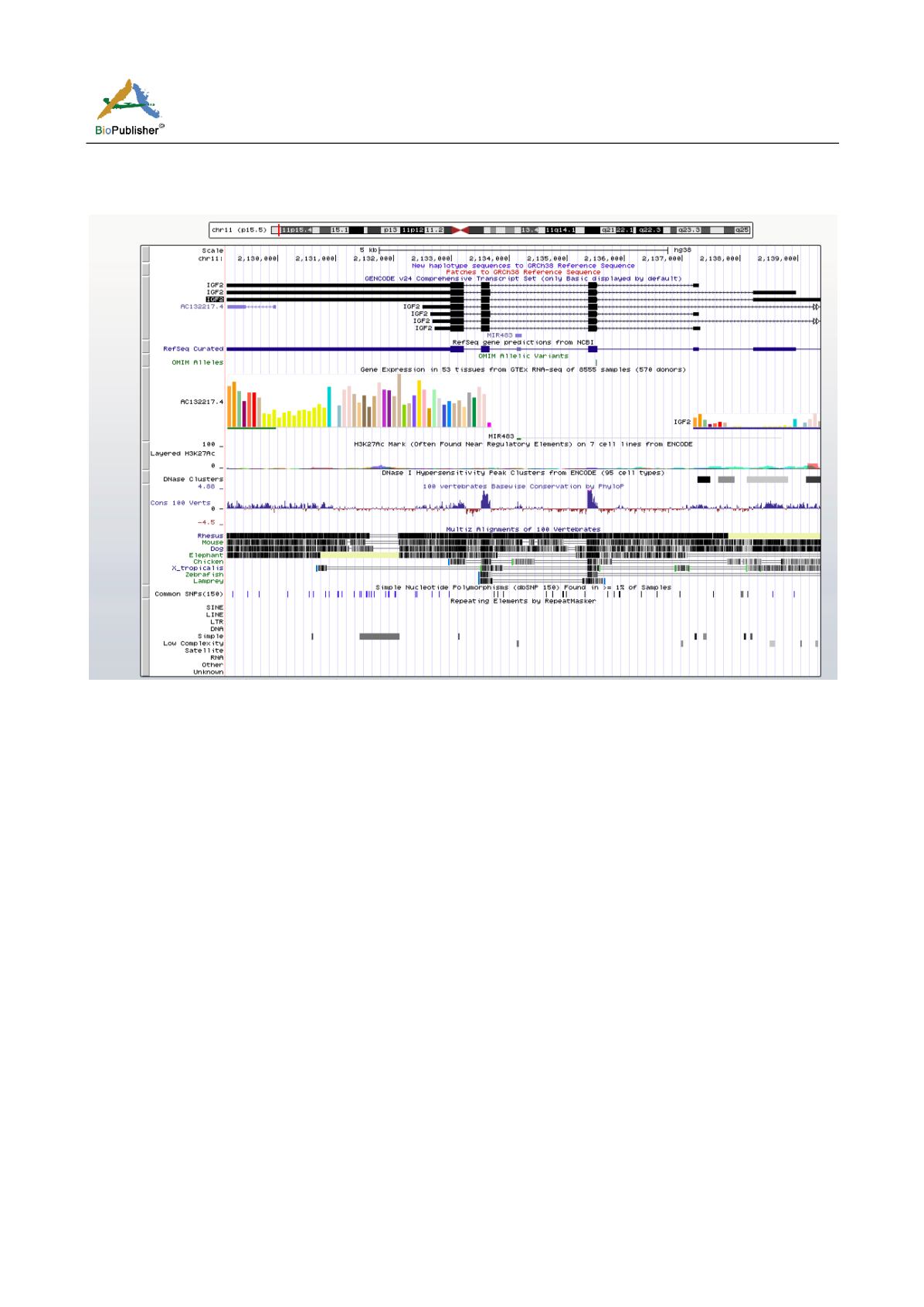
Figure 1 IGF2 gene structure diagram from UCSC database
1.2 Mechanisms of IGF2
IGF2 cannot exist alone in blood after secretion. It must be bound to target cells by IGFBPs and bind to
insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGFR) on the surface of target cells. Only through PIK3/AKt and Ras/MAPK
2 signaling pathways (Figure 2) can it play its biological role (Massoner et al., 2010; Unger et al., 2017). There are
two types of insulin-like growth factor receptors, type I and type II. Type I receptor is a heterosexual
transmembrane receptor. It consists of two alpha subunits of extracellular matrix and two beta subunits of
intracellular matrix connected by disulfide bond. Type I receptors bind to ligands, triggering tyrosine-specific
phosphorylation of receptors and subsequently producing various physiological reactions. Type II receptor is a
single chain protein located on almost all cell surfaces, which is related to lysosomal enzymes and classification of
cell phagocytosis.
1.3 IGF2 gene imprinting
Gene imprinting does not conform to Mendel’s law of inheritance. Loss of gene imprinting (LOI) is a common
phenomenon in tumors. The activation of maternal alleles silenced by IGF2 under normal conditions is a typical
example in cancer. IGF2 encodes an important autocrine growth factor (Mishima et al., 2015). Mouse IGF2 gene
is the first endogenous imprinted gene identified. It is expressed only in paternal alleles and regulated by
enhancers, DNA differential methylation domains (DMD) and promoters (Zhao et al., 2016). Usually, only the
paternal IGF2 gene is expressed and the maternal IGF2 gene is turned off, but the abnormal expression of the
maternal IGF2 gene can cause the abnormal binding of insulator CTCF to DMD, which is caused by the
methylation of damaged CTCF or DMD. IGF2 imprinting loss (IGF2 LOI) as a marker has been widely studied in
various human tumors. It has been reported that abnormal imprinting of IGF2 is closely related to childhood
tumors such as Wilms’ tumors and some adult tumors such as renal clear cell sarcoma and ovarian cancer (Tserga
et al., 2017). LOI leads to overexpression of IGF2 gene, which activates IGF1R and AKT1, which is a powerful
driving force for cell proliferation (Belharazem et al., 2016). Venkatraman et al. (2013) demonstrated that the


