Basic HTML Version


Legume Genomics and Genetics 2014, Vol.5, No.7, 1-7
http://lgg.biopublisher.ca
6
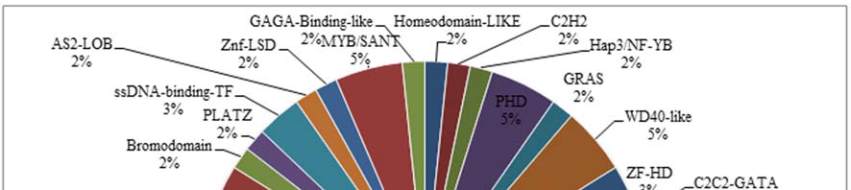
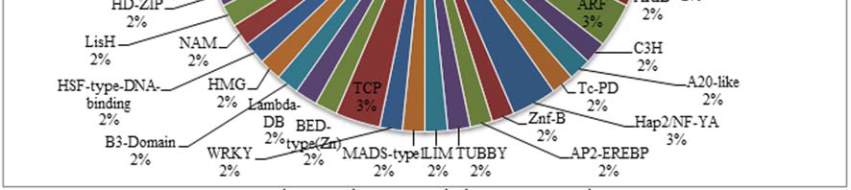
Figure 5 Plant Transcription Factor Result
454 sequencing. In this study, we performed de novo
functional annotation of the
Trigonella foenum-graecum
L. transcriptome without considering any reference
species with significant non-redundant set of 7256
transcripts. The detailed analyses of the data set has
provided several important features of
Trigonella
foenum-graecum
L. transcriptome such as GC content,
conserved genes across legumes and other plant
species, assignment of functional categories by GO
terms and identification of SSRs by MISA tool.
Trigonella foenum-graecum
L. contains many useful
components like; Polysaccharide galactomannan,
saponins (diosgenin, yamogenin, gitogenin, tigogenin,
neotigogens), mucilage, volatile oils, alkaloids (choline
and trigonelline). It is noted that this study of
Trigonella foenum-graecum L.
will be useful for
further functional genomics studies as it includes
useful information of each transcript.
Acknowledgement
We are heartily thankful to Prof. (Dr.) P.V. Virparia, Director,
GDCST, Sardar Patel University, Vallabh Vidyanagar, for
providing us facilities for the research work.
References
J. L. Collins, J. P. Biggs, C. Voelckel and S. Joly, 2008, An approach to
transcriptome analysis of non-model organisms using short-read
sequences, Genome Informatics 21:3-14
http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/9781848163324_0001
Jianan Zhang, Shan Liang, Jialei Duan, Jin Wang, Silong Chen, Zengshu
Cheng, Qiang Zhang, Xuanqiang Liang and Yurong Li, 2012, De novo
assembly and Characterisation of the Transcriptome during seed
development, and generation of genic-SSR markers in Peanut (Arachis
hypogaea L.), BMC Genomics 2012 13:90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-90
Libault, M., Joshi, T., Benedito, V.A., Xu, D., Udvardi, M.K., and Stacey, G.,
2009, Legume Transcription Factor Genes: What makes legumes so
special?. Plant Physiology 151: 991-1001
http://dx.doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.144105
Mortazavi, A., Williams, B.A., McCue, K., Schaeffer, L., and Wold, B., 2008.
Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat
Methods. 5(7): 621-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1226
Ness, R.W., Siol, M., and Barrett S.C.H., 2011, De novo sequence assembly
and characterization of the floral transcriptome in cross and
self-fertilizing plants, BMC Genomics 12: 298
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-298
Patel RK, Jain M, 2012, NGS QC Toolkit: A Toolkit for Quality Control of
Next Generation Sequencing Data, PLoS ONE 7(2): e30619.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030619
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030619
Rohini Garg, Ravi K. Patel, Akhilesh K. Tyagi, and Mukesh Jain., 2011, De
Novo Assembly of Chickpea Transcriptome Using Short Reads for
Gene Discovery and Marker Identification, DNA RESEARCH 18,
53–63; doi:10.1093/dnares/dsq028
http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsq028
Shi, C.Y., Yang, H., and Wei, C.L., 2011, Deep sequencing of the Camellia
sinensis transcriptome revealed candidate genes for major metabolic
pathways of tea-specific compounds, BMC Genomics 12 : 131
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-131
Vaidya K., Ghosh A., Kumar V, Chaudhary S, Srivastava N, Katudia K,
Tiwari T and Chikara K., 2012, De novo transcriptome sequencing in
Trigonella foenum-graecum to identify genes involved in the
biosynthesis of diosgenin. The Plant Genome:doi: 10.3835/

