Basic HTML Version


Molecular Plant Breeding 2011, Vol.2 No.2
http://mpb.sophiapublisher.com
11
eventually the plant died dur to toxic ammonia
accumulation (Zhao, 1999). while glutamine (Gln)
inhibits action mode of acetyltransferase Therefore,
glutamine should be removed in screening medium.
Screening shoud be initiated in the phase of most of
the callus with green spot appearing.
3 Materials and Methods
3.1 Plant Materials and culture medium
Experimental materials, Taipei 309 and Nipponbare,
were planted in greenhouse of transgenic plant
experimental station in the Guizhou University.
Plant medium were partly modified according to the
literature (Lin et al., 2008; Xiang et al., 2004; Yu et al.,
2008). Added 36 g/L glucose into the re-suspension,
sterilization methods: high pressure and temperature
(121
℃
, 15 minutes) (Table 1).
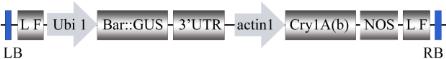
3.2 Agrobacterium strain and plasmid
Monocot expression vector pCAMBIA0390 harboring
the T-DNA region containing screening report fusion
gene Bar::GUS drived by ubiquitin promoter Ubi1, Bt
genes drived by rice actin promoter Actin1 and the
terminator sequence nos. L and F were recognition sites
loxp
and
frt
of Cre and Flp recombinase, respectively,
the sites can be recognised by FLP and the foreign
gene canbe deleted on site (Zhao et al., 2008,; Luo et
al., 2005). The structure of T-DNA region shown in
figure 6.
Table 1 The composition of culture medium used in this study
The name of medium The composition of medium
Callus induction
NB (N
6
macro+B
5
micro+B
5
vitamine)+CH; 300 mg/L+Pro; 500 mg/L+Gln; 500 mg/L+2,4
-
D; 2 mg/L
+sucrose; 30 g/L+Agar; 8 g/L, pH: 5.8
co-culture
NB+CH; 300 mg/L+Pro; 500 mg/L+Gln; 500 mg/L+2,4
-
D; 2 mg/L+AS; 100 umol/L+sucrose; 65 g/L+Agar;
8 g/L, pH: 5.2
Sterilization
NB+CH; 300 mg/L+Pro; 500 mg/L+Gln; 500 mg/L+2,4
-
D; 2 mg/L+Timentin; 300 mg/L+sucrose; 30
g/L+Agar; 8 g/L, pH: 5.8
Selection
NB+6
-
BA; 2 mg/L+KT; 0.5 mg/L+NAA; 0.5 mg/L+Timentin; 300 mg/L+PPT; 4 mg/L+sucrose; 30
g/L+Agar; 8 g/L, pH: 5.8
Differentiation
NB+CH; 300 mg/L+Pro; 500 mg/L+Gln; 500 mg/L+6
-
BA; 2 mg/L+KT; 0.5 mg/L+NAA; 0.5
mg/L+Timentin; 300 mg/L+sucrose; 30 g/L+Agar; 8g/L, pH: 5.8
Rooting
1/2MS+ NAA; 0.5 mg/L+sucrose; 30 g/L+Cef; 150 mg/L+Agar; 8 g/L, pH: 5.8
Resuspension liquid
NB+CH; 300 mg/L+Pro; 500 mg/L+Gln; 500 mg/L+2,4
-
D; 2 mg/L+AS; 100 umol/L+sucrose; 68.5
g/L+glucose; 36 g/L+Agar; 8 g/L, pH: 5.2
YEP
Peptone; 5 g/L+Yeast extract; 10 g/L+Nacl; 5 g/L+Km ;50 mg/L+Rif; 100 mg/L, pH: 7.2
Figure 6 The T-DNA Region of plasmid pCAMBIA0390
3.3 Explants and acquirement and Callus induction
In the experiment, we employed the mature embryo of
Taipei 309 and Nipponbare as callus induction explant.
Removed the seed-coat of the mature seeds, and select
the seeds with normal color to be sterilized by using
75% alcohol 1min, and following by 0.1% HgCl
2
10
min, washing 5 to 6 times by distilled water.
Sterilized explants soaked 8-12 hours in sterile distilled
water, then excise the endosperm. the embryoes was
planted on callus induction medium. Distilled water
and immersed explants volume ratio is 4:1 (50 explants
of rice each treatment, a total of 250 treatments, to
remove contaminated callus, 200 rice explants were
used for callus induction rate statistics analysis, callus
induction rate (%)=no. of embryos with callus/no. of
inoculated immature embryos×100%).
3.4 Light culture conditions
After buds grown in 28
℃
non-light culture for 3-4
days, excise buds completely with a scalpel and
inoculate mature embryos on induction medium by
using the following procedures: (1)28
℃
, under 21
days light culture, with 2000 lux, 13 h/d. (2)28
℃
, 21
days non-light culture (50 explants of rice for each

